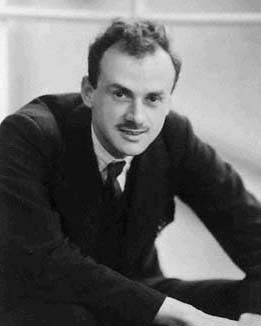|
Ben Mottelson
Ben Roy Mottelson (9 July 1926 – 13 May 2022) was an American-Danish nuclear physicist. He won the 1975 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the non-spherical geometry of atomic nuclei. Early life Mottelson was born in Chicago, Illinois on 9 July 1926, the son of Georgia (Blum) and Goodman Mottelson, an engineer. After graduating from Lyons Township High School in La Grange, Illinois, he joined the United States Navy and was sent to attend officers training at Purdue University, where he received a Bachelor's degree in 1947. He then earned a PhD in nuclear physics from Harvard University in 1950. His thesis adviser was Julian Schwinger, the theoretical physicist who later won the Nobel Prize in 1965 for his work on quantum electrodynamics. Career He moved to Institute for Theoretical Physics (later the Niels Bohr Institute) at the University of Copenhagen on the Sheldon Traveling Fellowship from Harvard, and remained in Denmark. In 1953 he was appointed staff member in CE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = State , subdivision_type2 = Counties , subdivision_name1 = Illinois , subdivision_name2 = Cook and DuPage , established_title = Settled , established_date = , established_title2 = Incorporated (city) , established_date2 = , founder = Jean Baptiste Point du Sable , government_type = Mayor–council , governing_body = Chicago City Council , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Lori Lightfoot ( D) , leader_title1 = City Clerk , leader_name1 = Anna Valencia ( D) , unit_pref = Imperial , area_footnotes = , area_tot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Electrodynamics
In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction. In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it "the jewel of physics" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen. History The first formulation of a quantum theory describing radiation and matter interaction is attributed to British scientist Paul Dirac, who ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Pines
David Pines (June 8, 1924 May 3, 2018) was the founding director of the Institute for Complex Adaptive Matter (ICAM) and the International Institute for Complex Adaptive Matter (I2CAM) (respectively, United States-wide and international institutions dedicated to research in and the understanding of emergent phenomena), distinguished professor of physics, University of California, Davis, research professor of physics and professor emeritus of physics and electrical and computer engineering in the Center for Advanced Study, University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign (UIUC), and a staff member in the office of the Materials, Physics, and Applications Division at the Los Alamos National Laboratory. His seminal contributions to the theory of many-body systems and to theoretical astrophysics were recognized by two Guggenheim Fellowships, the Feenberg Medal, the Edward A. Frieman Prize for Excellence in Graduate Student Research, Dirac and Drucker prizes, and by his election to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review
''Physical Review'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1893 by Edward Nichols. It publishes original research as well as scientific and literature reviews on all aspects of physics. It is published by the American Physical Society (APS). The journal is in its third series, and is split in several sub-journals each covering a particular field of physics. It has a sister journal, ''Physical Review Letters'', which publishes shorter articles of broader interest. History ''Physical Review'' commenced publication in July 1893, organized by Cornell University professor Edward Nichols and helped by the new president of Cornell, J. Gould Schurman. The journal was managed and edited at Cornell in upstate New York from 1893 to 1913 by Nichols, Ernest Merritt, and Frederick Bedell. The 33 volumes published during this time constitute ''Physical Review Series I''. The American Physical Society (APS), founded in 1899, took over its publication in 1913 and star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-empirical Mass Formula
In nuclear physics, the semi-empirical mass formula (SEMF) (sometimes also called the Weizsäcker formula, Bethe–Weizsäcker formula, or Bethe–Weizsäcker mass formula to distinguish it from the Bethe–Weizsäcker process) is used to approximate the mass and various other properties of an atomic nucleus from its number of protons and neutrons. As the name suggests, it is based partly on theory and partly on empirical measurements. The formula represents the liquid-drop model proposed by George Gamow, which can account for most of the terms in the formula and gives rough estimates for the values of the coefficients. It was first formulated in 1935 by German physicist Carl Friedrich von Weizsäcker, and although refinements have been made to the coefficients over the years, the structure of the formula remains the same today. The formula gives a good approximation for atomic masses and thereby other effects. However, it fails to explain the existence of lines of greater binding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |