|
Beeroth (biblical City)
Beeroth ( he, בְּאֵרוֹת; Be'erot, lit. "wells"; in LXX grc, Βηρωθ) was a Biblical city seven miles northwest of Jerusalem. The city was an ancient Hivite settlement, and is mentioned in Joshua 9:17, 18:25, 2 Samuel 4:2-3, Ezra 2:25 and Nehemiah 7:29. Another town named Beeroth is mentioned in Deuteronomy 10:6. Identification Because there are no known ruins for Beeroth, the location of the city is disputed. The most noted source materials are the texts of the Bible, the Onomastikon of Eusebius, the annotations of this same text by Jerome, and the Madaba Map The distance Eusebius gives puts Beeroth somewhere between modern Biddu and Nebi Samwil. The city was part of an Hivite confederacy under the apparent rule of Gibeon, "a royal city" that sued for peace after the Hebrews destroyed Jericho and Ai as described in Joshua 9. Later much of the area taken in this initial campaign (including Beeroth) was given to Benjamin as inheritance in Joshua 18. Beeroth may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Murray (publishing House)
John Murray is a British publisher, known for the authors it has published in its long history including, Jane Austen, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, Lord Byron, Charles Lyell, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Herman Melville, Edward Whymper, Thomas Malthus, David Ricardo, and Charles Darwin. Since 2004, it has been owned by conglomerate Lagardère under the Hachette UK brand. Business publisher Nicholas Brealey became an imprint of John Murray in 2015. History The business was founded in London in 1768 by John Murray (1737–1793), an Edinburgh-born Royal Marines officer, who built up a list of authors including Isaac D'Israeli and published the ''English Review''. John Murray the elder was one of the founding sponsors of the London evening newspaper ''The Star'' in 1788. He was succeeded by his son John Murray II, who made the publishing house important and influential. He was a friend of many leading writers of the day and launched the '' Quarterly Review'' in 1809. He was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
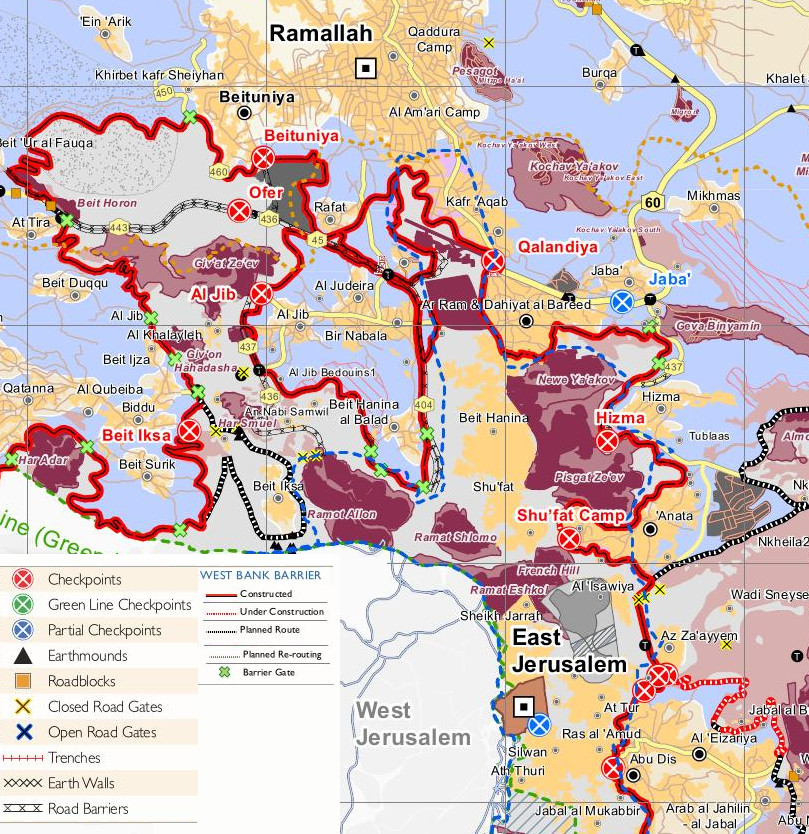
Nebi Samwil
An-Nabi Samwil, also called al-Nabi Samuil ( ar, النبي صموئيل ''an-Nabi Samu'il'', translit: "the prophet Samuel"), is a Palestinian village of nearly 220 inhabitants in the Quds Governorate of the State of Palestine, located in the West Bank ( Area C), four kilometers north of Jerusalem. The village is built up around the Mosque of Nabi Samwil, containing the Tomb of Samuel; the village's Palestinian population has since been removed by the Israeli authorities from the village houses to a new location slightly down the hill. A tradition dating back to the Byzantine period places here the tomb of Prophet Samuel. In the 6th century, a monastery was built at the site in honor of Samuel, and during the early Arab period the place was known as ''Dir Samwil'' (the Samuel Monastery). In the 12th century, during the Crusader period, a fortress was built on the area. In the 14th century, during the Mameluk period, a mosque was built over the ruins of the Crusader fortr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities In The Book Of Joshua
The Book of Joshua lists almost 400 ancient Levantine city names (including alternative names and derivatives in the form of words describing citizens of a town) which refer to over 300 distinct locations in Israel, the West Bank, Jordan, Lebanon and Syria. Each of those cities, with minor exceptions (e.g. Hamath, Gubla) is placed in one of the 12 regions, according to the tribes of Israel and in most cases additional details like neighbouring towns or geographical landmarks are provided. It has been serving as one of the primary sources for identifying and locating a number of Middle Bronze to Iron Age Levantine cities mentioned in ancient Egyptian and Canaanite documents, most notably in the Amarna correspondence. The list of cities and suggested locations See also * List of biblical places * List of biblical names * List of minor biblical places * List of modern names for biblical place names * Amarna letters–localities and their rulers References {{reflist Heb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biddu, Jerusalem
Biddu ( ar, بدّو) is a Palestinian town in the Jerusalem Governorate, located 6 kilometers northwest of Jerusalem in the West Bank. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, the town had a population of 6,368 in 2006. Biddu is at an altitude of 806m to 834m. Giv'on HaHadashah lies 2 km east of Biddu. Location Biddu is located (horizontally) north-west of Jerusalem. It is bordered by Beit Iksa to the east, Beit Ijza to the north, Al Qubeiba to the west, and Beit Surik to the south. History Bagatti suggested that several buildings in the town are from the 12th century. South-west of the centre is the ruined wali of Sheikh Abu Talal, which might have been a Crusader church. Ottoman era In the Ottoman tax records of the 1500s, Biddu was located in the ''nahiya'' of Jerusalem. In 1738 Richard Pococke noted the village, as he passed between Biddu and Beit Surik. In 1838 Edward Robinson noted the village during his travels in the area. It was describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beit Iksa
Beit Iksa ( ar, بيت إكسا;) is a Palestinian village in the Jerusalem Governorate, located northwest of Jerusalem in the West Bank. The village is surrounded on all sides by the Israeli West Bank barrier, and outside Palestinians are denied access through the one Israeli checkpoint leading to it. In 2014 Israeli military authorities announced they would confiscate a further 3,167 acres of Beit Iksa lands, leaving the township, according to the village head, Saada al-Khatib, as a 2,500-dunum area. Beit Iksa contains two primary schools run by the Palestinian National Authority. Students attending secondary school travel to Jerusalem or nearby towns for education. Location Beit Iksa is a Palestinian village located (horizontally) north-west of Jerusalem. It is bordered by Beit Hanina al Balad and Shu'fat to the east, An Nabi Samwil to the north, Beit Surik and Lifta to the west. History Beit Iksa lies on one of the historical routes that joined the Mediterranean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Robinson (scholar)
Edward Robinson (April 10, 1794 – January 27, 1863) was an American biblical scholar known for his magnum opus, '' Biblical Researches in Palestine'', the first major work in Biblical Geography and Biblical Archaeology, which earned him the epithets "Father of Biblical Geography" and "Founder of Modern Palestinology." He studied in the United States and Germany, a center of biblical scholarship and exploration of the Bible as history. He translated scriptural works from classical languages, as well as German translations. His ''Greek and English Lexicon of the New Testament'' (1836; last revision, 1850) became a standard authority in the United States, and was reprinted several times in Great Britain. Biography Robinson was born in Southington, Connecticut, and raised on a farm. His father was a minister in the Congregational Church of the town for four decades. The younger Robinson taught at schools in East Haven and Farmington in 1810–11 to earn money for college. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonian Captivity
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile is the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were captives in Babylon, the capital city of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, following their defeat in the Jewish–Babylonian War and the destruction of Solomon's Temple in Jerusalem. The event is described in the Hebrew Bible, and its historicity is supported by archaeological and extra-biblical evidence. After the Battle of Carchemish in 605 BCE, the Babylonian king Nebuchadnezzar II besieged Jerusalem, which resulted in tribute being paid by the Judean king Jehoiakim. In the fourth year of Nebuchadnezzar II's reign, Jehoiakim refused to pay further tribute, which led to another siege of the city in Nebuchadnezzar II's seventh year (598/597 BCE) that culminated in the death of Jehoiakim and the exile to Babylonia of his successor Jeconiah, his court, and many others; Jeconiah's successor Zedekiah and others were exiled when N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
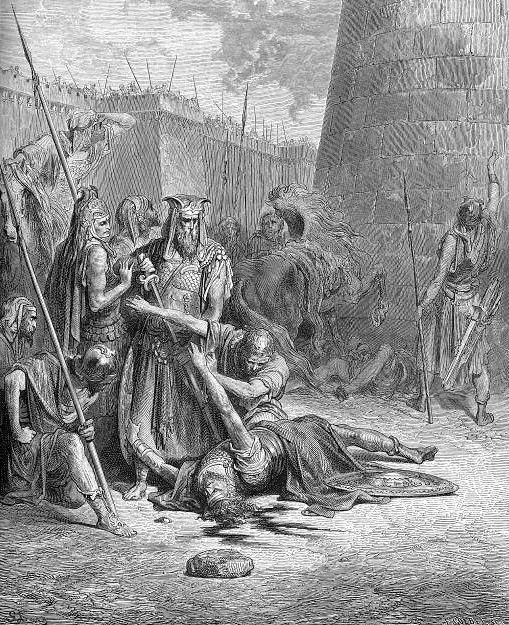
Abimelech (Judges)
Abimelech (; ''’'') was the king of Shechem and a son of biblical judge Gideon. His name can best be interpreted as "my father is king", claiming the inherited right to rule. He is introduced in Judges 8:31 as the son of Gideon and his Shechemite concubine, and the biblical account of his reign is described in chapter nine of the Book of Judges. According to the Bible, he was an unprincipled and ambitious ruler who often engaged in war against his own subjects. Ascension to nobility The killing of seventy brothers According to the Book of Judges, Abimelech went to Shechem to meet with his uncles and grandfather of his mother's side, and claimed to them that he should be the sole ruler over them and Shechem and not his brothers. He asked them whether they'd prefer to be ruled by seventy rulers or just by the individual, and he affirmed them as equal brothers. Because of Abimelech's affirmation to them, the men inclined to follow him, and gave him seventy silver shekels fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joatham
Jotham or Yotam (; (retrieved 2012-02-25), Wikipedia:IPA for English, IPA-ified from «jō´thum» , "Yahweh is perfect" or "Yahweh is complete"; el, Ιωαθαμ; la, Joatham) was the youngest of Gideon's seventy sons. He escaped when the rest were put to death by the order of his half-brother Abimelech (Judges), Abimelech (Judges 9:5). When "the citizens of Shechem and the whole house of Millo" were gathered together "by the plain of the pillar" (i.e., the stone set up by Joshua, 24:26; compare Book of Genesis, Genesis 35:4) "that was in Shechem, to make Abimelech king", from one of the heights of Mount Gerizim he protested against their doing so in the earliest parable, that of the bramble-king. This parab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gideon
Gideon (; ) also named Jerubbaal and Jerubbesheth, was a military leader, judge and prophet whose calling and victory over the Midianites are recounted in of the Book of Judges in the Hebrew Bible. Gideon was the son of Joash, from the Abiezrite clan in the tribe of Manasseh and lived in Ephra (Ophrah). As a leader of the Israelites, he won a decisive victory over a Midianite army despite a vast numerical disadvantage, leading a troop of 300 "valiant" men. Archaeologists in southern Israel have found a 3,100-year-old fragment of a jug with five letters written in ink that appear to represent the name Jerubbaal, or Yeruba'al. Names The nineteenth-century Strong's Concordance derives the name "Jerubbaal" from "Baal will contend", in accordance with the folk etymology, given in . According to biblical scholar Lester Grabbe (2007), " udges6.32 gives a nonsensical etymology of his name; it means something like 'Let Baal be great. Likewise, where Strong gave the meaning " hewe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua 9
Joshua 9 is the ninth chapter of the Book of Joshua in the Hebrew Bible or in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. According to Jewish tradition the book was attributed to the Joshua, with additions by the high priests Eleazar and Phinehas,Gilad, ElonWho Really Wrote the Biblical Books of Kings and the Prophets? ''Haaretz'', June 25, 2015. Summary: The paean to King Josiah and exalted descriptions of the ancient Israelite empires beg the thought that he and his scribes lie behind the Deuteronomistic History. but modern scholars view it as part of the Deuteronomistic History, which spans the books of Deuteronomy to 2 Kings, attributed to nationalistic and devotedly Yahwistic writers during the time of the reformer Judean king Josiah in 7th century BC. This chapter focuses on the deception by the people of Gibeon to avoid annihilation by having a treaty with the people of Israel under the leadership of Joshua, a part of a section comprising Joshua 5:13–12:24 about the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




%2C_cisterns_(marked_Cis)_and_Caves.png)