|
Battle Of Utica
The Battle of Utica took place early in 240 BC between a Carthaginian army commanded by Hanno and a force of rebellious mutineers possibly led by Spendius. It was the first major engagement of the Mercenary War between Carthage and the combined forces of mutinous ex-Carthaginian troops and rebellious African cities which broke out in the wake of the First Punic War. Both sides were routed during the course of the battle, which ended with the rebels occupying the field but was strategically inconclusive. The rebel army, some 10,000 strong, was blockading the city of Utica when the Carthaginian army of 8,000–10,000 men and 100 elephants stormed their camp and routed them. Satisfied with their victory, the Carthaginians failed to pursue and dispersed to loot, forage and celebrate. The rebels regrouped, returned, attacked the Carthaginians who were occupying their old camp and routed them in turn. The Carthaginians were also not effectively pursued and regrouped to continu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides the Carthaginians were defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war. The First Punic War had ended in a Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
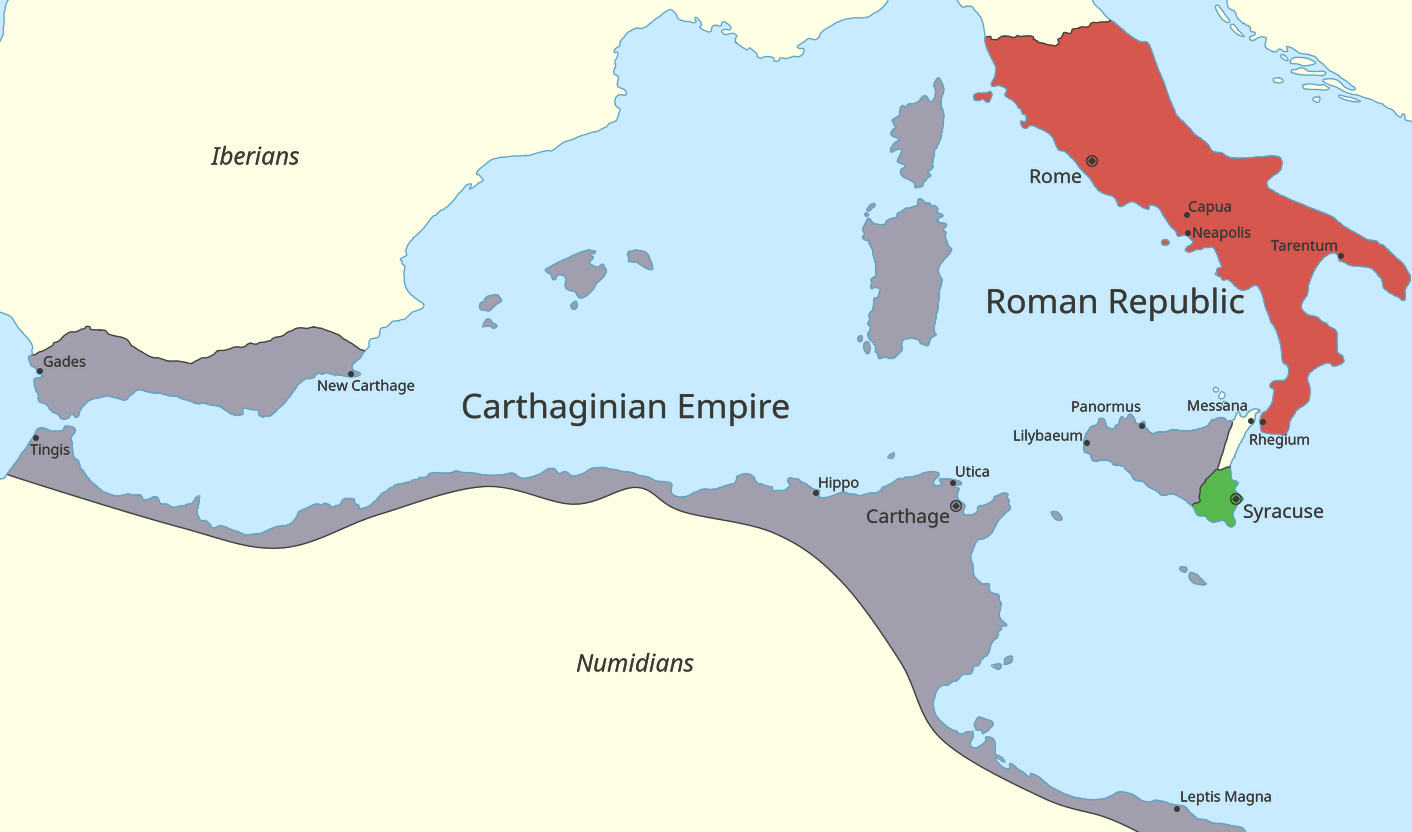
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious powers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spendius (Mercenary War)
Spendius (died late 238BC) was a former Roman slave who led a rebel army against Carthage, in what is known as the Mercenary War. He escaped or was rescued from slavery in Campania and was recruited into the Carthaginian Army during the First Punic War at some point prior to 241 BC. Spendius's date of birth is unknown, as are most details of his activities prior to his coming to prominence as a mutineer in 241 BC. After the First Punic War, Carthage attempted to pay its soldiers less than the full amount due to them before demobilising them. Spendius faced death by torture if he were returned to Roman authority and took a dim view of the increasingly warm relationship between Carthage and Rome. He came to the fore as a member of the army most vocal in resisting Carthaginian efforts to settle the dispute. When the disagreement broke down into a full-scale mutiny in late 241 BC he was elected co-general with the African Mathos by his fellow mutineers. Mathos spread the new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
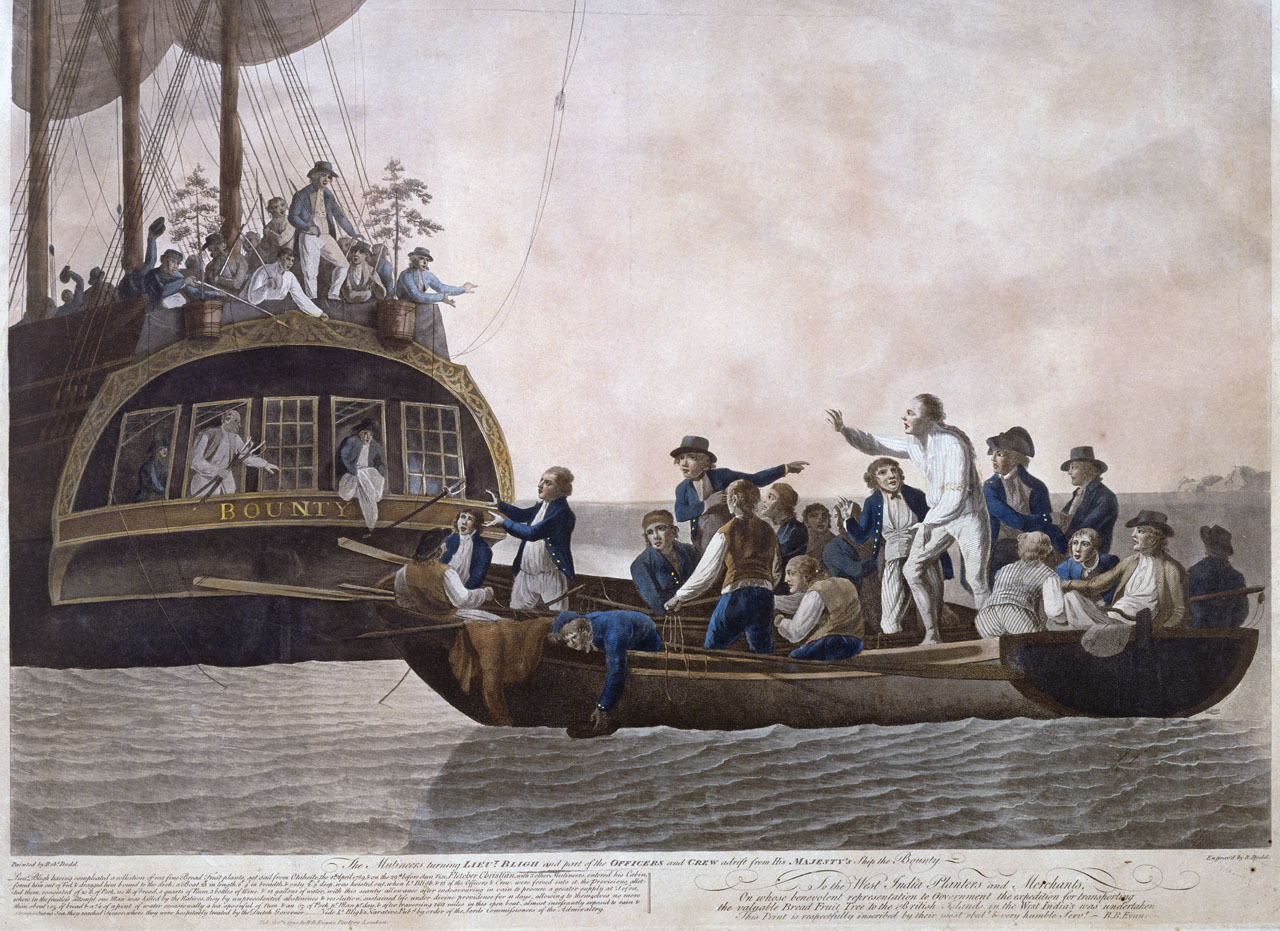
Mutiny
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military, of a crew or of a crew of pirates) to oppose, change, or overthrow an organization to which they were previously loyal. The term is commonly used for a rebellion among members of the military against an internal force, but it can also sometimes mean any type of rebellion against any force. Mutiny does not necessarily need to refer to a military force and can describe a political, economic, or power structure in which there is a change of power. During the Age of Discovery, mutiny particularly meant open rebellion against a ship's captain. This occurred, for example, during Ferdinand Magellan's journeys around the world, resulting in the killing of one mutineer, the execution of another, and the marooning of others; on Henry Hudson's ''Discovery'', resulting in Hudson and others being set adrift in a boat; and the notorious mutiny on the ''Bounty''. Penalty Those convicted of mutiny often faced capital punis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Kef
El Kef ( ar, الكاف '), also known as ''Le Kef'', is a city in northwestern Tunisia. It serves as the capital of the Kef Governorate. El Kef is situated to the west of Tunis and some east of the border between Algeria and Tunisia. It has a population of (2004 census). The old town is built on the cliff face of the table-top Jebel Dyr mountain. El Kef was the provisional capital of Tunisia during World War II. It was the command centre of the Front de Libération Nationale during the Algerian War of Independence against the French in the 1950s. The Sidi Bou Makhlouf Mausoleum entombs the patron saint of the city. Geography The highest-elevated city of Tunisia, at , its metropolitan area reaches of which lie within the interior of the old walled Medina quarter. The municipality of El Kef is shared between two national delegates, East Kef and West Kef, which correspond to the two municipal boroughs. History Etymology First known by the name of Sicca during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classical world. The city developed from a Canaanite Phoenician colony into the capital of a Punic empire which dominated large parts of the Southwest Mediterranean during the first millennium BC. The legendary Queen Alyssa or Dido, originally from Tyre, is regarded as the founder of the city, though her historicity has been questioned. According to accounts by Timaeus of Tauromenium, she purchased from a local tribe the amount of land that could be covered by an oxhide. As Carthage prospered at home, the polity sent colonists abroad as well as magistrates to rule the colonies. The ancient city was destroyed in the nearly-three year siege of Carthage by the Roman Republic during the Third Punic War in 146 BC and then re-developed as Roman Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Lutatius
The Treaty of Lutatius was the agreement between Carthage and Rome of 241 BC (amended in 237 BC), that ended the First Punic War after 23 years of conflict. Most of the fighting during the war took place on, or in the waters around, the island of Sicily and in 241 BC a Carthaginian fleet was defeated by a Roman fleet commanded by Gaius Lutatius Catulus while attempting to lift the blockade of its last, beleaguered, strongholds there. Accepting defeat, the Carthaginian Senate ordered their army commander on Sicily, Hamilcar Barca, to negotiate a peace treaty with the Romans, on whatever terms he could negotiate. Hamilcar refused, claiming the surrender was unnecessary, and the negotiation of the peace terms was left to Gisco, the commander of Lilybaeum, as the next most senior Carthaginian on the island. A draft treaty was rapidly agreed, but when it was referred to Rome for ratification it was rejected. Rome then sent a ten-man commission to settle the matter. This in turn agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gisco (died 239 BC)
Gisco was a Carthaginian general who served during the closing years of the First Punic War (264–241 BC) and took a leading part in the events which sparked the Mercenary War. He was a citizen of the city state of Carthage, which was located in what is now Tunisia. His date of birth and age at death are both unknown, as are his activities prior to his rise to prominence towards the end of the First Punic War. When the Carthaginians conceded defeat in the war in 241 BC, Gisco was commander of the major base of Lilybaeum (modern Marsala) on Sicily, subordinate to Hamilcar Barca, the overall Carthaginian commander on the island. On being ordered to negotiate a peace treaty, Hamilcar retired to Carthage in a rage, leaving Gisco, as the next most senior commander, in charge of negotiations with the Romans. These resulted in the Treaty of Lutatius, which ended the war. By this time the troops whom he had sent from Sicily to Africa to be repatriated were in a mutinous state over a pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamilcar Barca
Hamilcar Barca or Barcas ( xpu, 𐤇𐤌𐤋𐤒𐤓𐤕𐤟𐤁𐤓𐤒, ''Ḥomilqart Baraq''; –228BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman, leader of the Barcid family, and father of Hannibal, Hasdrubal and Mago. He was also father-in-law to Hasdrubal the Fair. Hamilcar commanded the Carthaginian land forces in Sicily from 247BC to 241BC, during the latter stages of the First Punic War. He kept his army intact and led a successful guerrilla war against the Romans in Sicily. Hamilcar retired to Carthage after the peace treaty in 241BC, following the defeat of Carthage. When the Mercenary War burst out in 239BC, Hamilcar was recalled to command and was instrumental in concluding that conflict successfully. Hamilcar commanded the Carthaginian expedition to Spain in 237BC, and for eight years expanded the territory of Carthage in Spain before dying in battle in 228 BC. He may have been responsible for creating the strategy which his son Hannibal implemented in the Second Pun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conquered or otherwise threatened to conquer. In case of alliances, lesser parties may pay tribute to more powerful parties as a sign of allegiance and often in order to finance projects that would benefit both parties. To be called "tribute" a recognition by the payer of political submission to the payee is normally required; the large sums, essentially protection money, paid by the later Roman and Byzantine Empires to barbarian peoples to prevent them attacking imperial territory, would not usually be termed "tribute" as the Empire accepted no inferior political position. Payments ''by'' a superior political entity to an inferior one, made for various purposes, are described by terms including " subsidy". The ancient Persian Achaemenid Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algeria
) , image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Algiers , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , religion = , official_languages = , languages_type = Other languages , languages = Algerian Arabic (Darja) French , ethnic_groups = , demonym = Algerian , government_type = Unitary semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Abdelmadjid Tebboune , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Aymen Benabderrahmane , leader_title3 = Council President , leader_name3 = Salah Goudjil , leader_title4 = Assembly President , leader_name4 = Ibrahim Boughali , legislature = Parliament , upper_house = Council of the Nation , lower_house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tébessa
Tébessa or Tebessa ( ar, تبسة ''Tibissa'', ''Tbessa'' or ''Tibesti''), the classical Theveste, is the capital city of Tébessa Province region of northeastern Algeria. It hosts several historical landmarks, the most important one being the wall that surrounds the city and its gates. The city is also known for its traditional Algerian carpets. Tébessa was home to over 190,000 people in 2007. Name Tebessa, written ' in French, was known to the ancient Greeks as () or (, 'Hundred Gates'). This was Latinized as ''Theveste''. History In antiquity, Theveste formed part of the Roman empire. After the establishment of the Roman Empire, the 3rd Augustan Legion was based in Theveste before being transferred to Lambaesis. Theveste later became a Roman colony, probably under Trajan in the early 2nd century. At the time of Trajan it was a flourishing city with around 30,000 inhabitants. The ruins surviving in present-day Tebessa are very rich in ancient monuments, among them b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)





.png)

