|
Battle Of Morotai
The Battle of Morotai, part of the Pacific War, began on 15 September 1944, and continued until the end of the war in August 1945. The fighting started when United States and Australian forces landed on the southwest corner of Morotai, a small island in the Netherlands East Indies (NEI), which the Allies needed as a base to support the liberation of the Philippines later that year. The invading forces greatly outnumbered the island's Japanese defenders and secured their objectives in two weeks. Japanese reinforcements landed on the island between September and November, but lacked the supplies needed to effectively attack the Allied defensive perimeter. Intermittent fighting continued until the end of the war, with the Japanese troops suffering heavy loss of life from disease and starvation. Morotai's development into an Allied base began shortly after the landing, and two major airfields were ready for use in October. These and other base facilities played an important role in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western New Guinea Campaign
The Western New Guinea campaign was a series of actions in the New Guinea campaign of World War II. Dutch East Indies KNIL, United States and Australian forces assaulted Japanese bases and positions in the northwest coastal areas of Netherlands New Guinea and adjoining parts of the Australian Territory of New Guinea. The campaign began with Operations Reckless and Persecution, which were amphibious landings by the U.S. I Corps at Hollandia and Aitape on 22 April 1944. Fighting in western New Guinea continued until the end of the war. Major battles and sub-campaigns *Landing at Aitape *Battle of Hollandia * Battle of Wakde * Battle of Lone Tree Hill * Battle of Morotai * Battle of Biak * Battle of Noemfoor * Battle of Driniumor River * Battle of Sansapor * Aitape-Wewak campaign See also *Operation Semut *Operation Agas * Naval Base Borneo *US Naval Advance Bases *List of Royal Australian Navy bases The following is a list of current and former commissioned bases used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Western Pacific, New Guinea And The Philippine Islands
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South West Pacific Area (command)
South West Pacific Area (SWPA) was the name given to the Allied supreme military command in the South West Pacific Theatre of World War II. It was one of four major Allied commands in the Pacific War. SWPA included the Philippines, Borneo, the Dutch East Indies (excluding Sumatra), East Timor, Australia, the Territories of Papua and New Guinea, and the western part of the Solomon Islands. It primarily consisted of United States and Australian forces, although Dutch, Filipino, British and other Allied forces also served in the SWPA. General Douglas MacArthur was appointed as the Supreme Commander, Southwest Pacific Area, on its creation on 18 April 1942. He created five subordinate commands: Allied Land Forces, Allied Air Forces, Allied Naval Forces, United States Army Forces in Australia (USAFIA), and the United States Army Forces in the Philippines. The last command disappeared when Corregidor surrendered on 6 May 1942, while USAFIA became the United States Army Services of Sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was Chief of Staff of the United States Army during the 1930s, and he played a prominent role in the Pacific theater during World War II. MacArthur was nominated for the Medal of Honor three times, and received it for his service in the Philippines campaign. This made him along with his father Arthur MacArthur Jr. the first father and son to be awarded the medal. He was one of only five men to rise to the rank of General of the Army in the U.S. Army, and the only one conferred the rank of field marshal in the Philippine Army. Raised in a military family in the American Old West, MacArthur was valedictorian at the West Texas Military Academy where he finished high school, and First Captain at the United States Military Academy at West Point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic security systems and gain access to the contents of encrypted messages, even if the cryptographic key is unknown. In addition to mathematical analysis of cryptographic algorithms, cryptanalysis includes the study of side-channel attacks that do not target weaknesses in the cryptographic algorithms themselves, but instead exploit weaknesses in their implementation. Even though the goal has been the same, the methods and techniques of cryptanalysis have changed drastically through the history of cryptography, adapting to increasing cryptographic complexity, ranging from the pen-and-paper methods of the past, through machines like the British Bombes and Colossus computers at Bletchley Park in World War II, to the mathematically advanced comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely operated vehicles and Autonomous underwater vehicle, robots, as well as medium-sized or smaller vessels, such as the midget submarine and the wet sub. Submarines are referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships'' irrespective of their size. Although experimental submarines had been built earlier, submarine design took off during the 19th century, and they were adopted by several navies. They were first widely used during World War I (1914–1918), and are now used in many navy, navies, large and small. Military uses include attacking enemy surface ships (merchant and military) or other submarines, and for aircraft carrier protection, Blockade runner, blockade running, Ballistic missile submarine, nuclear deterrence, reconnaissance, conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Take Ichi Convoy
The was a Japanese convoy of World War II. The convoy left Shanghai on 17 April 1944, carrying two infantry divisions to reinforce Japan's defensive positions in the Philippines and western New Guinea. United States Navy (USN) submarines attacked the convoy on 26 April and 6 May, sinking four transports and killing more than 4,000 soldiers. These losses caused the convoy to be diverted to Halmahera, where the surviving soldiers and their equipment were unloaded. The ''Take Ichi'' convoy's losses had important strategic results. The failure to bring the two divisions to their destination without loss contributed to the Japanese Imperial General Headquarters' decision to move Japan's defensive perimeter back by . The divisions' combat power was also blunted by their losses, and while they both saw action against United States Army forces, they contributed little to Japan's attempt to defend its empire. Background In September 1943, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) and Imperial Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
32nd Division (Imperial Japanese Army)
The Imperial Japanese Army's was an infantry division during World War II. Its call sign was the . The division was raised 7 February 1939 in Tokyo, simultaneously with 33rd, 34th, 35th, 36th and 37th divisions. Action The ''32nd Division'' was subordinated to the 12th Army and transferred to China in May 1939 to participate in the Second Sino-Japanese War, initially posted to Shanxi. Due to the Japanese defeat in the Battle of Suixian–Zaoyang, the initially assigned positions became unreachable and the 32nd Division arrived in southeast Shantung in June 1939 and saw action in the 1939–40 Winter Offensive, initially protecting the Tai'an - Tengzhou line. The division was able to start a counter-attack on 2 December 1939 as part of the ''Shandong Operation''. After the offensive, the 32nd Division was garrisoned at Jinan. In April 1944, the 32nd Division was assigned to the 14th Army and departed for Mindanao. The 32nd Division suffered heavy losses from United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor of Japan as supreme commander of the army and the Imperial Japanese Navy. Later an Inspectorate General of Aviation became the third agency with oversight of the army. During wartime or national emergencies, the nominal command functions of the emperor would be centralized in an Imperial General Headquarters (IGHQ), an ad hoc body consisting of the chief and vice chief of the Army General Staff, the Minister of the Army, the chief and vice chief of the Naval General Staff, the Inspector General of Aviation, and the Inspector General of Military Training. History Origins (1868–1871) In the mid-19th century, Japan had no unified national army and the country was made up of feudal domains (''han'') with the Tokugawa shogunate (''bakufu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands East Indies Campaign
The Dutch East Indies campaign of 1941–1942 was the conquest of the Dutch East Indies (present-day Indonesia) by forces from the Empire of Japan in the early days of the Pacific campaign of World War II. Forces from the Allies attempted unsuccessfully to defend the islands. The East Indies were targeted by the Japanese for their rich oil resources which would become a vital asset during the war. The campaign and subsequent three and a half year Japanese occupation was also a major factor in the end of Dutch colonial rule in the region. Background The East Indies was one of Japan's primary targets if and when it went to war because the colony possessed abundant valuable resources, the most important of which were its rubber plantations and oil fields; the colony was the fourth-largest exporter of oil in the world, behind the U.S., Iran, and Romania. The oil made the islands enormously important to the Japanese, so they sought to secure the supply for themselves. They sent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
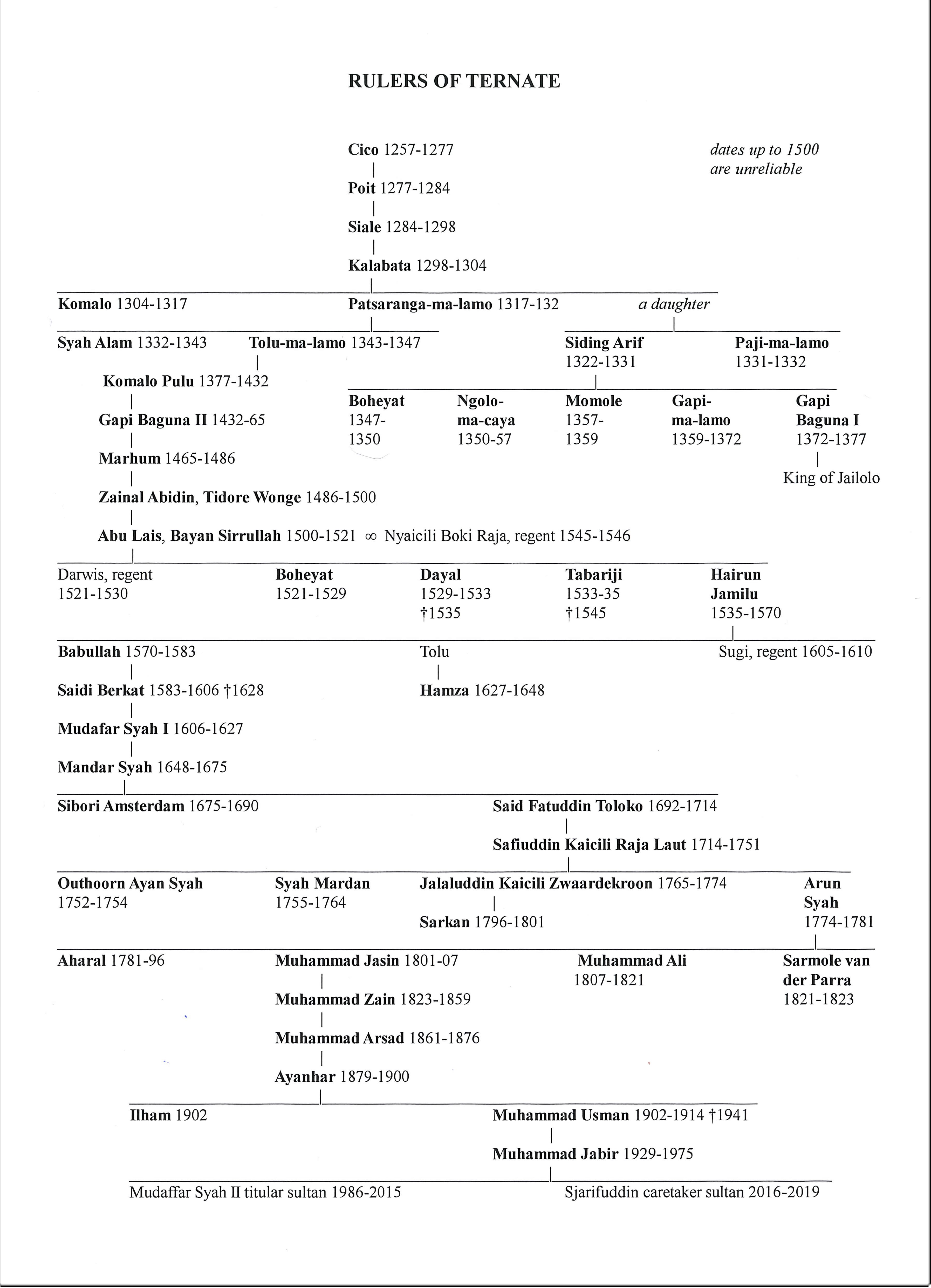
Sultanate Of Ternate
The Sultanate of Ternate (Jawi alphabet: كسلطانن ترنتاي), previously also known as the Kingdom of Gapi is one of the oldest Muslim kingdoms in Indonesia besides Tidore, Jailolo, and Bacan. The Ternate kingdom was established by Momole Cico, the first leader of Ternate, with the title Baab Mashur Malamo, traditionally in 1257. It reached its Golden Age during the reign of Sultan Baabullah (1570–1583) and encompassed most of the eastern part of Indonesia and a part of southern Philippines. Ternate was a major producer of cloves and a regional power from the 15th to 17th centuries. The dynasty founded by Baab Mashur Malamo continues to the present, as does the Sultanate itself, although it no longer holds any political power. History Pre-colonial period The sultanate was originally named the Kingdom of Gapi, but later changed the name to be based on that of its capital, Ternate. Originally there were four villages in Ternate and led by clan leaders called Mom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowland
Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland. Definitions Upland and lowland are portions of plain that are conditionally categorized by their elevation above the sea level. Lowlands are usually no higher than , while uplands are somewhere around to . On unusual occasions, certain lowlands such as the Caspian Depression lie below sea level. Upland habitats are cold, clear and rocky whose rivers are fast-flowing in mountainous areas; lowland habitats are warm with slow-flowing rivers found in relatively flat lowland areas, with water that is frequently colored by sediment and organic matter. These classifications overlap with the geological definitions of "upland" and "lowland". In geology an "upland" is generally considered to be land that is at a higher elevation than the alluvial plain or stream terrace, which are considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)