|
Battle Of Boonesboro
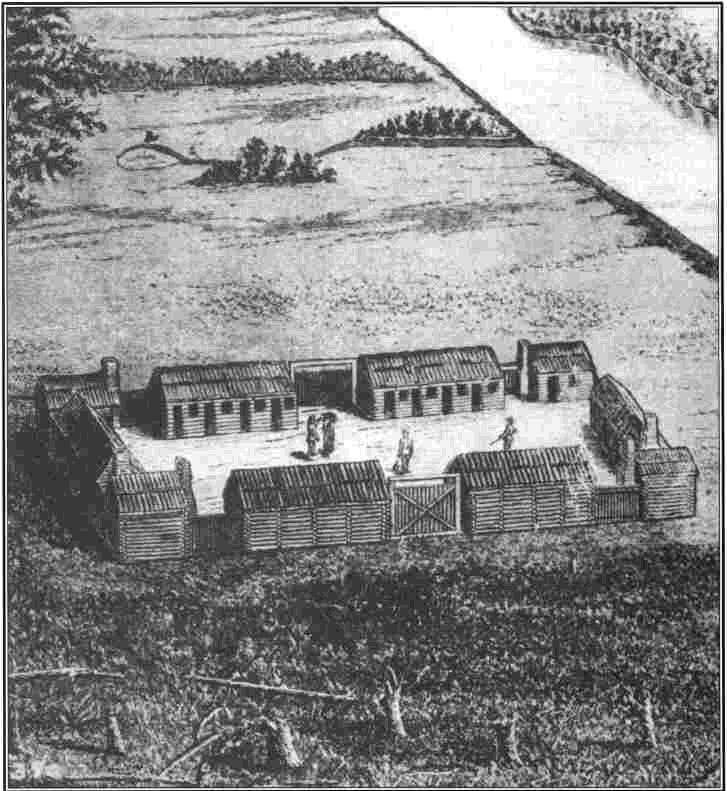
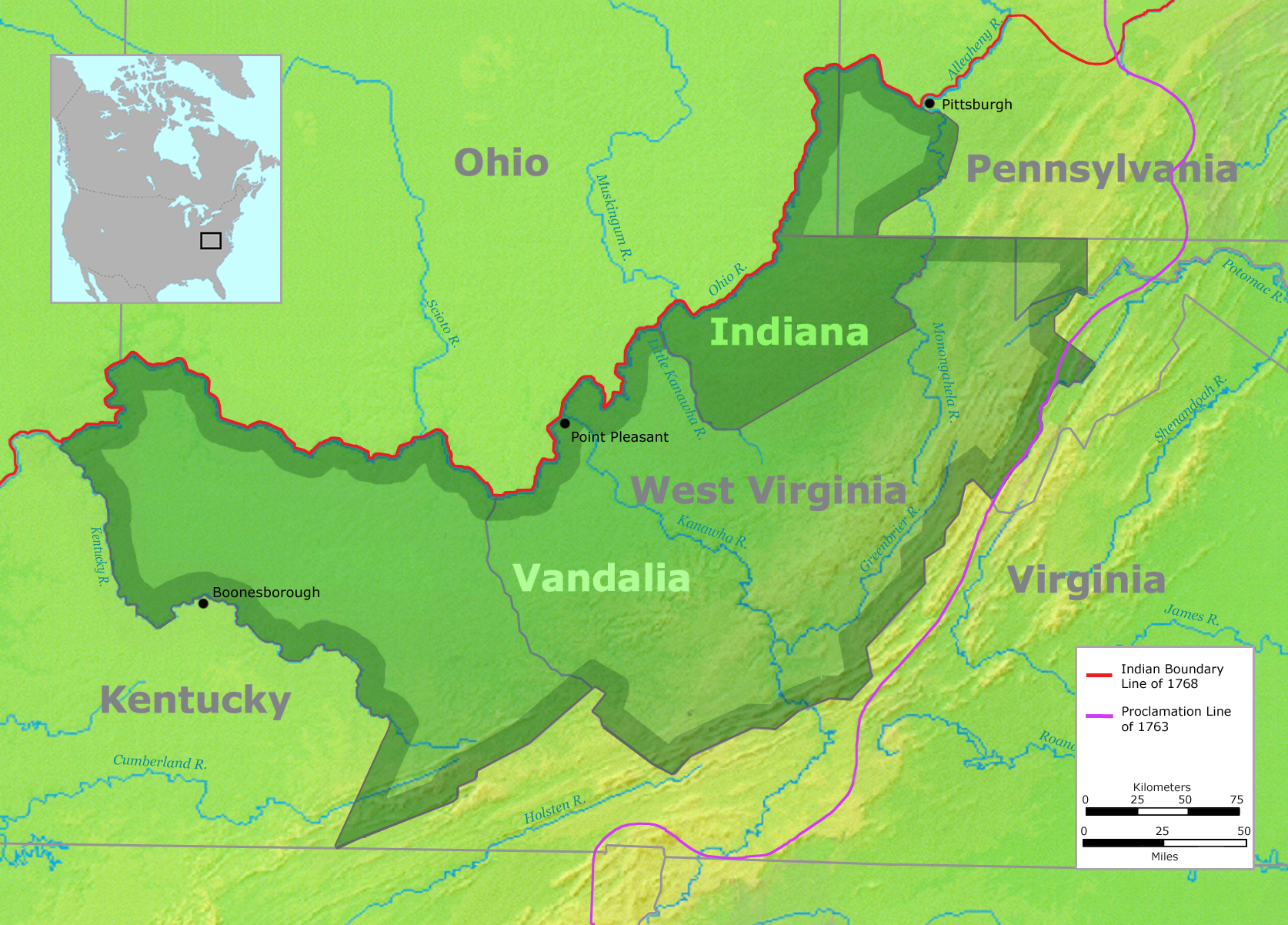
} The siege of Boonesborough was a military engagement which took place in September 1778 during the American Revolutionary War. On September 7, Shawnee chief Blackfish, who was allied to the British, led an attack on the Kentucky settlement of Boonesborough. Months before the battle, Blackfish had captured and adopted Daniel Boone, the founder of Boonesborough. Boone escaped the Shawnees in time to lead the defense of the settlement. Blackfish's siege was unsuccessful and was lifted after eleven days. Boone was then court-martialed by fellow officers who suspected him of harboring Loyalist sympathies. He was acquitted, but soon left the settlement. Background Settlement of Kentucky In 1774, the Colony of Virginia defeated a coalition of Native Americans in the Ohio Country, primarily Shawnees, in Dunmore's War. In the treaty that ended the war, the Ohio River was established as the boundary between Shawnee lands north of the river and western Virginia (present West Virginia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. Established by royal charter in the 17th and 18th centuries, the American colonies were largely autonomous in domestic affairs and commercially prosperous, trading with Britain and its Caribbean colonies, as well as other European powers via their Caribbean entrepôts. After British victory over the French in the Seven Years' War in 1763, tensions between the motherland and he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunmore's War
Lord Dunmore's War—or Dunmore's War—was a 1774 conflict between the Colony of Virginia and the Shawnee and Mingo American Indian nations. The Governor of Virginia during the conflict was John Murray, 4th Earl of Dunmore—Lord Dunmore. He asked the Virginia House of Burgesses to declare a state of war with the Indian nations and call out the militia. The conflict resulted from escalating violence between white settlers, who, in accordance with previous treaties, were exploring and moving into land south of the Ohio River (modern West Virginia, southwestern Pennsylvania, and Kentucky), and Native Americans, who had rights to hunt there. As a result of incursions and successive attacks by settlers upon Indian lands, provoking Indian war bands to retaliate, war was declared "to pacify the hostile Indian war bands". The war ended soon after Virginia's victory in the Battle of Point Pleasant on October 10, 1774. As a result of this victory, the Colony of Virginia took away t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalahgawtha
Chalahgawtha (or, more commonly in English, Chillicothe) was the name of one of the five divisions (or bands) of the Shawnee, a Native American people, during the 18th century. It was also the name of the principal village of the division. The other four divisions were the Mekoche, Kispoko, Pekowi, and Hathawekela. (All five division names have been spelled in a great variety of ways.) Together these divisions formed the loose confederacy that was the Shawnee tribe. Chillicothe division By tradition, each Shawnee division had certain roles it performed on behalf of the entire tribe. These customs were fading by the time they were recorded in writing by European Americans. The Chillicothe division often provided political leadership for the tribe. A well-known Chillicothe leader was Chief Blackfish. Chillicothe villages The village where the chief of the Chillicothe division lived was also known as "Chillicothe". When this principal village was relocated, often as a result of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Licking River (Kentucky)
The Licking River is a partly navigable, U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 13, 2011 tributary of the Ohio River in northeastern Kentucky. The river and its tributaries drain much of the region of northeastern Kentucky between the watersheds of the Kentucky River to the west and the Big Sandy River to the east. The North Fork Licking River, in Pendleton County, Kentucky, is one of its tributaries. The South Fork Licking River, in counties including Harrison County, Kentucky, is another. Origin of name The Native Americans of the area called the river ''Nepernine''. When the explorer Thomas Walker first saw it in 1750, he called it Frederick's River. An earlier name given by hunters and frontiersmen, Great Salt Lick Creek, makes reference to the many saline springs near the river that attracted animals to its salt licks. The origin of the present name is unclear, though likely related to the previou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boonesborough
Boonesborough or Boonesboro may refer to a place in the United States: * Boonesboro, Iowa, now part of Boone, Iowa *Boonesborough, Kentucky *Boonesboro, Missouri Boonesboro is a community in Howard County, Missouri, United States. It is located on Route 87 midway between Boonville and Glasgow in the historical Boone's Lick country.''Missouri Atlas & Gazetteer,'' 1998, Delorme p.30 The community was lai ... * Boonesborough, Missouri * Boonesborough, West Virginia {{geodis de:Boonesborough ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalping
Scalping is the act of cutting or tearing a part of the human scalp, with hair attached, from the head, and generally occurred in warfare with the scalp being a trophy. Scalp-taking is considered part of the broader cultural practice of the taking and display of human body parts as trophies, and may have developed as an alternative to the taking of human heads, for scalps were easier to take, transport, and preserve for subsequent display. Scalping independently developed in various cultures in both the Old and New Worlds. Europe Several human remains from the stone-age Ertebølle culture in Denmark show evidence of scalping. A man found in a grave in the Alvastra pile-dwelling in Sweden had been scalped approximately 5,000 years ago. Georg Frederici noted that “Herodotus provided the only clear and satisfactory portrayal of a scalping people in the old world” in his description of the Scythians, a nomadic people then located to the north and west of the Black Sea. Herodot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Detroit
Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit or Fort Detroit (1701–1796) was a fort established on the north bank of the Detroit River by the French officer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac and the Italian Alphonse de Tonty in 1701. In the 18th century, French colonial settlements developed on both sides of the river, based on the fur trade, missions, and farms. The site of the former fort, north of the Rouge River, is now within the city of Detroit in the U.S. state of Michigan, an area bounded by Larned Street, Griswold Street, Washington Blvd. and the Civic Center (now occupied by office towers). The fort was taken over by the British after the French surrendered Montreal in 1760 during the French and Indian War (part of the Seven Years' War). The British held it until the American Revolutionary War, and it was taken over by the United States afterward. The British built Fort Lernoult to the north along the river in 1779. This was later renamed Fort Shelby and was abandoned by the US mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Hamilton (governor)
Henry Hamilton (c. 1734 – 29 September 1796) was an Anglo-Irish military officer and later government official of the British Empire. He served in North America as Lieutenant Governor of the Province of Quebec and later as Deputy Governor after the American Revolutionary War. He later served as Governor of Bermuda and lastly, as Governor of Dominica, where he died in office. In 1779, Hamilton was captured during the Revolutionary War by rebel forces at Fort Sackville in present-day Indiana, while serving as the Lieutenant Governor and Superintendent of Indian Affairs, at the British outpost of Fort Detroit. He was transported to Virginia, where he was held by Governor Thomas Jefferson's rebel government until October 1780. He was sent to New York and gained freedom in a prisoner exchange in 1781, being allowed to depart for London, England. Early life Henry was probably born in Dublin, Ireland, a younger son of Henry Hamilton, an Irish Member of Parliament, and his wife. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilderness Trail
The Wilderness Road was one of two principal routes used by colonial and early national era settlers to reach Kentucky from the East. Although this road goes through the Cumberland Gap into southern Kentucky and northern Tennessee, the other (more northern route) is sometimes called the "Cumberland Road" because it started in Fort Cumberland in Maryland. Despite Kentucky Senator Henry Clay's advocacy of this route, early in the 19th century, the northern route was selected for the National Road, connecting near Washington, Pennsylvania into the Ohio Valley of northern Kentucky and Ohio. In 1775, Daniel Boone blazed a trail for the Transylvania Company from Fort Chiswell in Virginia through the Cumberland Gap. It was later lengthened, following Indian trails, to reach the Falls of the Ohio at Louisville. The Wilderness Road was steep, rough and narrow, and could be traversed only on foot or horseback. By contrast, wagons could travel along the National Road route (originally the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transylvania (colony)
The Transylvania Colony, also referred to as the Transylvania Purchase, was a short-lived, extra-legal colony founded in early 1775 by North Carolina land speculator Richard Henderson, who formed and controlled the Transylvania Company. Henderson and his investors had reached an agreement to purchase a vast tract of Cherokee lands west of the southern and central Appalachian Mountains through the acceptance of the Treaty of Sycamore Shoals with most leading Cherokee chieftains then controlling these lands. In exchange for the land the tribes received goods worth, according to the estimates of some scholars, about 10,000 British pounds ($1.5 million U.S. in 2016). To further complicate matters, this early American frontier land was also claimed by both the Virginia Colony (particularly following Lord Dunmore's War) and Province of North Carolina. The Transylvania Colony was located in what is now the central and western parts of Kentucky, and a chunk of north central Tennessee. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia, and northeastern Alabama. The Cherokee language is part of the Iroquoian language group. In the 19th century, James Mooney, an early American ethnographer, recorded one oral tradition that told of the tribe having migrated south in ancient times from the Great Lakes region, where other Iroquoian peoples have been based. However, anthropologist Thomas R. Whyte, writing in 2007, dated the split among the peoples as occurring earlier. He believes that the origin of the proto-Iroquoian language was likely the Appalachian region, and the split betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of North Carolina
Province of North Carolina was a province of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain that existed in North America from 1712(p. 80) to 1776. It was one of the five Southern Colonies, Southern colonies and one of the Thirteen Colonies, thirteen American colonies. The Monarchy of the United Kingdom, monarch of Great Britain was represented by the List of governors of North Carolina (1712–1776), Governor of North Carolina, until the United States Declaration of Independence, colonies declared independence on Independence Day (United States), July 4, 1776. Etymology "Carolina" is taken from the Latin word for "Charles" (Carolus (name), Carolus), honoring King Charles II of England, Charles II, and was first named in the 1663 Royal Charter granting to Edward Hyde, 1st Earl of Clarendon, Edward, Earl of Clarendon; George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle, George, Duke of Albemarle; William Craven, 1st Earl of Craven (1608–1697), William, Lord Craven; John Berkeley, 1st Baron Ber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |