|
Battle Of Wadi (1916)
The Battle of Wadi, occurring on 13 January 1916, was an unsuccessful attempt by British forces fighting in Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq) during World War I to relieve beleaguered forces under Sir Charles Townshend then under siege by the Ottoman Sixth Army at Kut-al-Amara. Pushed by regional British Commander-in-Chief Sir John Nixon, General Fenton Aylmer launched an attack against Ottoman defensive positions on the banks of the Wadi River. The Wadi was a steep valley of a stream that ran from the north into the River Tigris, some upstream towards Kut-al-Amara from Sheikh Sa'ad. The attack is generally considered as a failure, as although Aylmer managed to capture the Wadi, it cost him 1,600 men. The British failure led to Townshend's surrender, along with 10,000 of his men, in the largest single surrender of British troops up to that time. However, the British recaptured Kut in February 1917, on their way to the capture of Baghdad sixteen days later on 11 March 1917. Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamian Campaign
The Mesopotamian campaign was a campaign in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I fought between the Allies represented by the British Empire, troops from Britain, Australia and the vast majority from British India, against the Central Powers, mostly the Ottoman Empire. Background The Ottoman Empire had conquered the region in the early 16th century, but never gained complete control. Regional pockets of Ottoman control through local proxy rulers maintained the Ottomans' reach throughout Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). With the turn of the 19th century came reforms. Work began on a Baghdad Railway in 1888; by 1915 it had only four gaps, and travel time from Istanbul to Baghdad had fallen to 21 days. The Anglo-Persian Oil Company (APOC) had obtained exclusive rights to petroleum deposits throughout the Persian Empire, except in the provinces of Azerbaijan, Ghilan, Mazendaran, Asdrabad, and Khorasan.The Encyclopedia Americana, 1920, v.28, p.403 In 1914, months before the war b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadi River
Wadi ( ar, وَادِي, wādī), alternatively ''wād'' ( ar, وَاد), North African Arabic Oued, is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some instances, it may refer to a wet (ephemeral) riverbed that contains water only when heavy rain occurs. Etymology The term ' is very widely found in Arabic toponyms. Some Spanish toponyms are derived from Andalusian Arabic where ' was used to mean a permanent river, for example: Guadalcanal from ''wādī al-qanāl'' ( ar, وَادِي الْقَنَال, "river of refreshment stalls"), Guadalajara from ''wādī al-ḥijārah'' ( ar, وَادِي الْحِجَارَة, "river of stones"), or Guadalquivir, from ''al-wādī al-kabīr'' ( ar, اَلْوَادِي الْكَبِير, "the great river"). General morphology and processes Wadis are located on gently sloping, nearly flat parts of deserts; commonly they begin on the distal portions of alluvial fans and extend to inland sabkhas or dry lakes. In basin and ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris Corps
The III Corps is a formation of the Indian Army that was formed during World War I in Mesopotamia during its respective campaign. Prior to the reorganization of the British and Indian forces in Mesopotamia, it was designated as the Tigris Corps. A new III Corps was formed by the Indian Army during World War II for service in Southeast Asia. The corps fought in the Battle of Singapore where it surrendered in February 1942. It is located in the state of Nagaland of India in the city of Dimapur, at Rangapahar Military Station. History First World War Initially formed in December 1915, it took part in the Mesopotamian campaign under the command of Frederick Stanley Maude. In November 1916, it was split in two to form the I Corps and III Corps (also known as III (Tigris) Corps). Among its component divisions during World War I were the Cavalry Division, 3rd (Lahore) Division, 6th (Poona) Division, 7th (Meerut) Division, 12th Indian Division, 13th (Western) Division, 14th Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th (Meerut) Division
The 7th (Meerut) Division was an infantry division of the British Indian Army that saw active service during World War I. Pre-1857 The Meerut Division first appeared in the Indian Army List in 1829, under the command of Sir Jasper Nicolls, KCB.''East India Register and Directory'' 1829. At this period Divisions were primarily administrative organisations controlling the brigades and stations in their area, rather than field formations, but they did provide field forces when required. There were generally one Indian cavalry and two Indian infantry regiments stationed at Meerut itself, in addition to British troops: in 1829 these were the 4th Bengal Light Cavalry, 29th and 32nd Bengal Native Infantry. Indian Rebellion of 1857 In May 1857, on the eve of the 'Indian Rebellion of 1857' (or 'First War of Independence'), the troops at Meerut comprised the 6th Dragoon Guards (Carabiniers) and a battalion of the 60th (King's Royal Rifle Corps), the 3rd Bengal Light Cavalry, and 11t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
28th Indian Brigade
The 28th Indian Brigade was an infantry brigade of the British Indian Army that saw active service with the Indian Army during the First World War. Formed in October 1914, it defended the Suez Canal in early 1915, ended the Ottoman threat to Aden in July 1915, took part in the Mesopotamian Campaign in 1916 and 1917, before finishing the war in the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. It remained in Palestine until it was broken up in 1920. History ;Egypt and Aden The 28th Indian Brigade was formed in October 1914 as part of Indian Expeditionary Force F (along with the 29th and 30th Indian Brigades) and sent to Egypt. After arriving in Egypt, it joined the 10th Indian Division when it was formed on 24 December. It served on the Suez Canal Defences, notably taking part in the Actions on the Suez Canal on 3–4 February 1915. In July 1915, the brigade was detached to Aden with 1/B Battery, HAC and 1/1st Berkshire Battery, RHA. They fought a sharp action at Sheikh Othman on 20 Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the Persian Gulf. Geography The Tigris is 1,750 km (1,090 mi) long, rising in the Taurus Mountains of eastern Turkey about 25 km (16 mi) southeast of the city of Elazığ and about 30 km (20 mi) from the headwaters of the Euphrates. The river then flows for 400 km (250 mi) through Southeastern Turkey before becoming part of the Syria-Turkey border. This stretch of 44 km (27 mi) is the only part of the river that is located in Syria. Some of its affluences are Garzan, Anbarçayi, Batman, and the Great and the Little Zab. Close to its confluence with the Euphrates, the Tigris splits into several channels. First, the artificial Shatt al-Hayy branches off, to join the Euphrates near Nasiriy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Al-Gharbi
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, عَلِيّ بْن أَبِي طَالِب; 600 – 661 common era, CE) was the last of four Rashidun, Rightly Guided Caliphs to rule Islam (r. 656 – 661) immediately after the death of Muhammad, and he was the first Shia Imam. The issue of his succession caused a major rift between Muslims and divided them into Shia Islam, Shia and Sunni Islam, Sunni groups. Ali was assassinated in the Grand Mosque of Kufa in 661 by the forces of Mu'awiya I, Mu'awiya, who went on to found the Umayyad Caliphate. The Imam Ali Shrine and the city of Najaf were built around Ali's tomb and it is visited yearly by millions of devotees. Ali was a cousin and son-in-law of Muhammad, raised by him from the age of 5, and accepted his claim of divine revelation by age 11, being among the Chronological list of early Muslims, first to do so. Ali played a pivotal role in the early years of Islam while Muhammad was in Mecca and under severe persecution. After Muhammad's Hij ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Tigris Corps
The III Corps is a formation of the Indian Army that was formed during World War I in Mesopotamia during its respective campaign. Prior to the reorganization of the British and Indian forces in Mesopotamia, it was designated as the Tigris Corps. A new III Corps was formed by the Indian Army during World War II for service in Southeast Asia. The corps fought in the Battle of Singapore where it surrendered in February 1942. It is located in the state of Nagaland of India in the city of Dimapur, at Rangapahar Military Station. History First World War Initially formed in December 1915, it took part in the Mesopotamian campaign under the command of Frederick Stanley Maude. In November 1916, it was split in two to form the I Corps and III Corps (also known as III (Tigris) Corps). Among its component divisions during World War I were the Cavalry Division, 3rd (Lahore) Division, 6th (Poona) Division, 7th (Meerut) Division, 12th Indian Division, 13th (Western) Division, 14th Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamian Campaign
The Mesopotamian campaign was a campaign in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I fought between the Allies represented by the British Empire, troops from Britain, Australia and the vast majority from British India, against the Central Powers, mostly the Ottoman Empire. Background The Ottoman Empire had conquered the region in the early 16th century, but never gained complete control. Regional pockets of Ottoman control through local proxy rulers maintained the Ottomans' reach throughout Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). With the turn of the 19th century came reforms. Work began on a Baghdad Railway in 1888; by 1915 it had only four gaps, and travel time from Istanbul to Baghdad had fallen to 21 days. The Anglo-Persian Oil Company (APOC) had obtained exclusive rights to petroleum deposits throughout the Persian Empire, except in the provinces of Azerbaijan, Ghilan, Mazendaran, Asdrabad, and Khorasan.The Encyclopedia Americana, 1920, v.28, p.403 In 1914, months before the war b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. In 762 CE, Baghdad was chosen as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, and became its most notable major development project. Within a short time, the city evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning". Baghdad was the largest city in the world for much of the Abbasid era during the Islamic Golden Age, peaking at a population of more than a million. The city was largely destroyed at the hands of the Mongol Empire in 1258, resulting in a decline that would linger through many ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
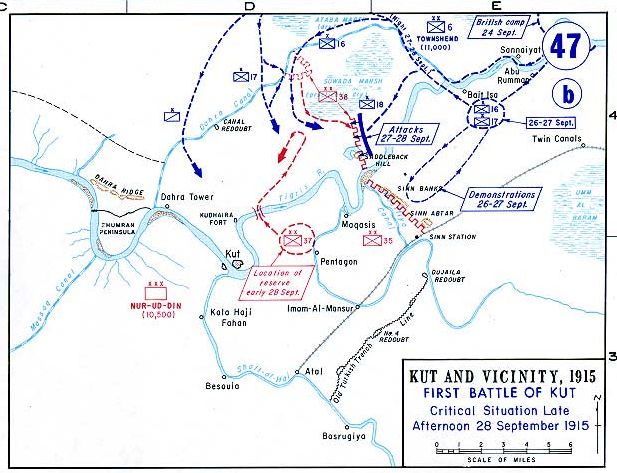
Siege Of Kut
The siege of Kut Al Amara (7 December 1915 – 29 April 1916), also known as the first battle of Kut, was the besieging of an 8,000 strong British Army garrison in the town of Kut, south of Baghdad, by the Ottoman Army. In 1915, its population was around 6,500. Following the surrender of the garrison on 29 April 1916, the survivors of the siege were marched to imprisonment at Aleppo, during which many died. Historian Christopher Catherwood has called the siege "the worst defeat of the Allies in World War I". Ten months later, the British Indian Army, consisting almost entirely of newly recruited troops from Western India, conquered Kut, Baghdad and other regions in between in the Fall of Baghdad. Prelude The 6th (Poona) Division of the Indian Army, under Major-General Charles Townshend, had fallen back to the town of Kut after retreating from Ctesiphon. The British Empire forces arrived at Kut around 3 December 1915. They had suffered significant losses, numbering only 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |