|
Bat Influenza
Bat influenza is a type of influenza A viruses found in bats. Bats were not considered to host Influenza A viruses until 2012-2013, when two phylogenetically distinct lineages, designated Influenza A virus subtype H17N10 and H18N11, were identified in Central and South American bats. Discovery The species of bats currently known to carry bat influenza are common in Central and South America. The first bat flu virus, IAV H17N10, was first discovered in 2009 in little yellow-shouldered bats (''Sturnira lilium'') in Guatemala. In 2012 a novel influenza virus (H18N11) was discovered in bats in South America. This strain was found to be divergent from the better-understood Influenza A viruses most commonly found in fowls and humans. The complete sequence of IAV H17N10 was extracted from ''Sturnira lilium'' in 2012. In 2013, the sequence of IAV H18N11 was extracted from flat-faced fruit-eating bats (''Artibeus planirostris'') from Peru. In contrast to human and avian influenza A viru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza A Virus
''Influenza A virus'' (''IAV'') causes influenza in birds and some mammals, and is the only species of the genus ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' of the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. Strain (biology)#Microbiology or virology, Strains of all subtypes of influenza A virus have been isolated from wild birds, although disease is uncommon. Some primary isolate, isolates of influenza A virus cause severe disease both in domestic poultry and, rarely, in humans. Occasionally, viruses are transmitted from wild aquatic birds to domestic poultry, and this may cause an outbreak or give rise to human influenza pandemics. Influenza A viruses are Sense (molecular biology), negative-sense, single-stranded, segmented RNA viruses. The several subtypes are labeled according to an H number (for the type of Hemagglutinin (influenza), hemagglutinin) and an N number (for the type of viral neuraminidase, neuraminidase). There are 18 different known H antigens (H1 to H18) and 11 different known N antigens (N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sialic Acid
Sialic acids are a class of alpha-keto acid sugars with a nine-carbon backbone. The term "sialic acid" (from the Greek for saliva, - ''síalon'') was first introduced by Swedish biochemist Gunnar Blix in 1952. The most common member of this group is ''N''-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac or NANA) found in animals and some prokaryotes. Sialic acids are found widely distributed in animal tissues and related forms are found to a lesser extent in other organisms like in some micro-algae, bacteria and archaea. Sialic acids are commonly part of glycoproteins, glycolipids or gangliosides, where they decorate the end of sugar chains at the surface of cells or soluble proteins. However, sialic acids have been also observed in ''Drosophila'' embryos and other insects. Generally, plants seem not to contain or display sialic acids. In humans the brain has the highest sialic acid content, where these acids play an important role in neural transmission and ganglioside structure in synaptogene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Viral Diseases
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza A Virus
''Influenza A virus'' (''IAV'') causes influenza in birds and some mammals, and is the only species of the genus ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' of the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. Strain (biology)#Microbiology or virology, Strains of all subtypes of influenza A virus have been isolated from wild birds, although disease is uncommon. Some primary isolate, isolates of influenza A virus cause severe disease both in domestic poultry and, rarely, in humans. Occasionally, viruses are transmitted from wild aquatic birds to domestic poultry, and this may cause an outbreak or give rise to human influenza pandemics. Influenza A viruses are Sense (molecular biology), negative-sense, single-stranded, segmented RNA viruses. The several subtypes are labeled according to an H number (for the type of Hemagglutinin (influenza), hemagglutinin) and an N number (for the type of viral neuraminidase, neuraminidase). There are 18 different known H antigens (H1 to H18) and 11 different known N antigens (N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reassortment
Reassortment is the mixing of the genetic material of a species into new combinations in different individuals. Several different processes contribute to reassortment, including assortment of chromosomes, and chromosomal crossover. It is particularly used when two similar viruses that are infecting the same cell exchange genetic material. In particular, reassortment occurs among influenza viruses, whose genomes consist of eight distinct segments of RNA. These segments act like mini-chromosomes, and each time a flu virus is assembled, it requires one copy of each segment. If a single host (a human, a chicken, or other animal) is infected by two different strains of the influenza virus, then it is possible that new assembled viral particles will be created from segments whose origin is mixed, some coming from one strain and some coming from another. The new reassortant strain will share properties of both of its parental lineages. Reassortment is responsible for some of the major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Cell
There are many different types of cells in the human body. Cells derived primarily from endoderm Exocrine secretory epithelial cells * Brunner's gland cell in duodenum (enzymes and alkaline mucus) *Insulated goblet cell of respiratory and digestive tracts (mucus secretion) *Stomach **Foveolar cell (mucus secretion) **Chief cell ( pepsinogen secretion) **Parietal cell (hydrochloric acid secretion) * Pancreatic acinar cell (bicarbonate and digestive enzyme secretion) *Paneth cell of small intestine (lysozyme secretion) *Type II pneumocyte of lung ( surfactant secretion) *Club cell of lung Barrier cells *Type I pneumocyte (lung) * Gall bladder epithelial cell * Centroacinar cell (pancreas) *Intercalated duct cell (pancreas) *Intestinal brush border cell (with microvilli) Hormone-secreting cells *Enteroendocrine cell **K cell (secretes gastric inhibitory peptide) **L cell (secretes glucagon-like peptide-1, peptide YY3-36, oxyntomodulin, and glucagon-like peptide-2) ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
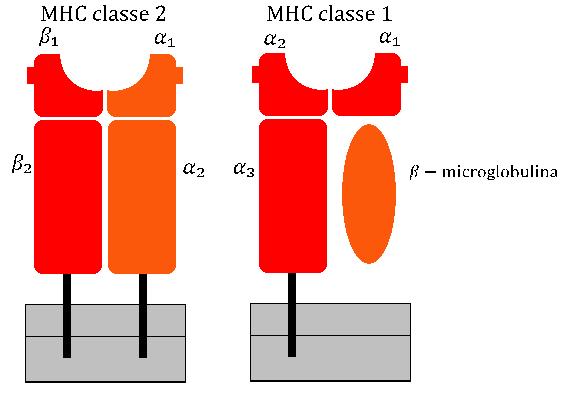
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. This locus got its name because it was discovered via the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules: binding an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bringing the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own phenotype or of other biologic entities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza A Virus Subtype H17N10
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms begin from one to four days after exposure to the virus (typically two days) and last for about 2–8 days. Diarrhea and vomiting can occur, particularly in children. Influenza may progress to pneumonia Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ..., which can be caused by the virus or by a subsequent bacterial infection. Other complications of infection include acute respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, encephalitis, and worsening of pre-existing health problems such as asthma and cardiovascular disease. There are four types of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat-faced Fruit-eating Bat
The flat-faced fruit-eating bat (''Artibeus planirostris'') is a South American species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is sometimes considered a subspecies of the Jamaican fruit bat, but can be distinguished by its larger size, the presence of faint stripes on the face, and of a third molar tooth on each side of the upper jaw. Genetic analysis has also shown that the two species may not be closely related. Description Flat-faced fruit-eating bats are moderately sized bats, with adults measuring in total length and weighing . The fur is brownish-grey over most of the body, becoming grey on the underparts, although there are faint whitish stripes on the face. As their name suggests, the bats have a broad skull with a short snout. The ears are triangular, with rounded tips, although short compared with those of many other bats, and with a small tragus. The snout bears a prominent triangular nose-leaf. The wings are dark brown or blackish, with white tips. A well-developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)