|
Basilemys
''Basilemys'' () is a large, terrestrial trionychoid turtle from the Upper Cretaceous. In Greek, the word "Basil" means royal or kingly and the word "Emys" means turtle. Therefore, ''Basilemys'' means King Turtle. ''Basilemys'' has been found in rocks dating to the Campanian and Maastrichtian subdivisions of the Late Cretaceous and is considered to be the largest terrestrial turtle of its time. ''Basilemys'' has solely been found in North America. The family Nanhsiungchelyidae, which is the family ''Basilemys'' belongs to, made its first appearance in the Lower Cretaceous, in what we now call Asia. Because of ''Basilemys,'' we know that this family appeared in North America in the Upper Cretaceous. It is possible that ''Basilemys'' and other nanhsiungchelyids are immigrants from Asia. They might have arrived in North America by passing through what we now call the Bering Strait somewhere during the Cretaceous. In an analysis made by Sukhanov et al. on a new Nansiunghelyid turtle fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanhsiungchelyidae
Nanhsiungchelyidae ( or ) is an extinct family of land turtles known from Cretaceous deposits in Asia and North America. Nanhsiungchelyids were more terrestrial than many of their contemporaries, and may have gone extinct at the end of the Cretaceous as a result. Classification The name Nanhsiungchelyidae was coined by Yeh in 1966, in the same paper in which the type genus ''Nanhsiungchelys'' was described. The name is derived from the name of the type species, with the suffix of a family, -idae, added to it. Taxonomy According to phylogenetic analyses, Nanhsiungchelyidae is the sister group to Adocidae The Adocidae are an extinct family of aquatic and omnivorous turtle Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups ..., and thus both are included within the clade Adocusia. Nanhsiungchelyidae is split into two major clades, one including most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
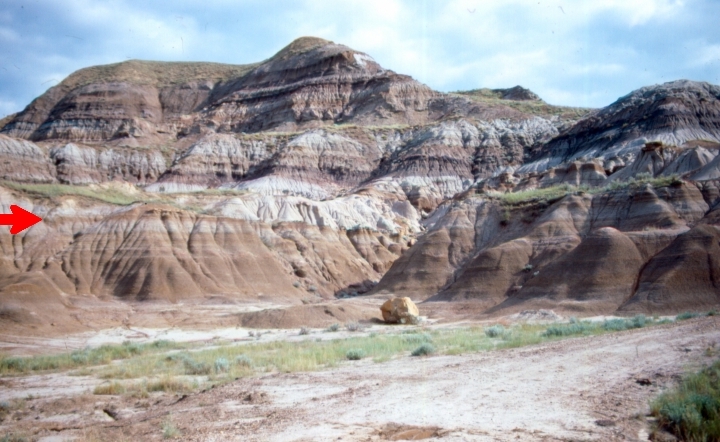
Horseshoe Canyon Formation
The Horseshoe Canyon Formation is a stratigraphic unit of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in southwestern Alberta. It takes its name from Horseshoe Canyon, an area of badlands near Drumheller. The Horseshoe Canyon Formation is part of the Edmonton Group and is up to thick. It is of Late Cretaceous age, Campanian to early Maastrichtian stage (Edmontonian Land-Mammal Age), and is composed of mudstone, sandstone, carbonaceous shales, and coal seams. A variety of depositional environments are represented in the succession, including floodplains, estuarine channels, and coal swamps, which have yielded a diversity of fossil material. Tidally-influenced estuarine point bar deposits are easily recognizable as Inclined Heterolithic Stratification (IHS). Brackish-water trace fossil assemblages occur within these bar deposits and demonstrate periodic incursion of marine waters into the estuaries. The Horseshoe Canyon Formation crops out extensively in the area around Drumheller, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur Park Formation
The Dinosaur Park Formation is the uppermost member of the Belly River Group (also known as the Judith River Group), a major geologic unit in southern Alberta. It was deposited during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, between about 76.5 and 74.4 million years ago. It was deposited in alluvial and coastal plain environments, and it is bounded by the nonmarine Oldman Formation below it and the marine Bearpaw Formation above it.Eberth, D.A. 2005. The geology. In: Currie, P.J., and Koppelhus, E.B. (eds), Dinosaur Provincial Park: A Spectacular Ancient Ecosystem Revealed. Indiana University Press: Bloomington and Indianapolis, p.54-82. . The Dinosaur Park Formation contains dense concentrations of dinosaur skeletons, both articulated and disarticulated, which are often found with preserved remains of soft tissues. Remains of other animals such as fish, turtles, and crocodilians, as well as plant remains, are also abundant. The formation has been named after Dinosaur Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian spans the time from 83.6 (± 0.2) to 72.1 (± 0.2) million years ago. It is preceded by the Santonian and it is followed by the Maastrichtian. The Campanian was an age when a worldwide sea level rise covered many coastal areas. The morphology of some of these areas has been preserved: it is an unconformity beneath a cover of marine sedimentary rocks. Etymology The Campanian was introduced in scientific literature by Henri Coquand in 1857. It is named after the French village of Champagne in the department of Charente-Maritime. The original type locality was a series of outcrop near the village of Aubeterre-sur-Dronne in the same region. Definition The base of the Campanian Stage is defined as a place in the stratigraphic column wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trionychia
Trionychia is a superfamily of turtles which encompasses the species that are commonly referred to as softshelled turtles as well as some others. The group contains two families, Carettochelyidae, which has only one living species, the pig-nosed turtle (''Carettochelys insculpta'') native to New Guinea and Northern Australia, and Trionychidae, the softshelled turtles, containing numerous species native to Asia, North America and Africa. These families likely diverged during the late Jurassic. The oldest known stem-trionychian is '' Sinaspideretes'' from the Late Jurassic of China. Systematics Except for those not assigned to a family, only living genera are listed here. *Family Carettochelyidae ** Subfamily Carettochelyinae *** Genus '' Carettochelys'' *Pan-Trionychidae ** Family PlastomenidaeOne or more basal lineages formerly believed to be a distinct family (fossil) ** Family Trionychidae ***Subfamily Cyclanorbinae **** Genus '' Cyclanorbis'' **** Genus '' Cycloderma' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adocus
''Adocus'' is an extinct genus of aquatic turtles belonging to the family Adocidae. ''Adocus'' was once considered to belong to the family Dermatemyidae. Description Species of the genus ''Adocus'' had flattened and smoothly contoured shells with horny sculptured plates. The shells could reach a length of about 80 cm. These large freshwater turtles had an omnivorous diet. They lived from the Late Cretaceous to the Paleocene in North America, but in Asia, they were also present during the Oligocene. Distribution These turtles have been found in Cretaceous to Paleogene of Canada, United States, Mongolia, China, Japan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Species * '' Adocus agilis'' * '' Adocus aksary'' * '' Adocus beatus'', type species In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanhsiungchelys
''Nanhsiungchelys'' ( or) is a trionychoid turtle from the Upper Cretaceous of Nanhsiung, China. Its genus is derived from the location where it was found, Nanhsiung and the greek word "χελωνα" (chelona), which means turtle. Therefore, ''Nanhsiungchelys'' means "turtle from Nanxiong". ''Nanhsiungchelys'' has been found in rocks dating to the Maastrichtian of Asia Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ... and North America. References Nanhsiungchelyidae Late Cretaceous turtles of Asia Fossil taxa described in 1966 {{paleo-turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hickatee
The hickatee (''Dermatemys mawii'') or in Spanish ''tortuga blanca'' ('white turtle'), also called the Central American river turtle, is the only living species in the family Dermatemydidae. The species is found in the Atlantic drainages of Central America, specifically Belize, Guatemala, southern Mexico and probably Honduras. It is a relatively large-bodied species, with records of straight carapace length and weights of ; although most individuals are smaller. This is a herbivorous and almost completely aquatic turtle that does not even surface to bask. Bizarrely for reptiles, the eggs can remain viable even after being underwater for weeks -in the recent past, some scientists mistakenly claimed it nests underwater, likely due to visiting Central America during a frequent flood, when nests are often submerged. In the culture of the Ancient Mayan civilisation this species and turtles in general had numerous uses such as being used in warfare, as musical instruments and as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aguja Formation
The Aguja Formation is a geological formation in North America, exposed in Texas, United States and Chihuahua and Coahuila in Mexico, whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel et al., 2004, "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous, North America).", pp.574-588 Fossil palms have also been unearthed here. Age The ages of the Aguja Formation and its primary fossil-bearing unit, the Upper Shale, are not well understood. Due to the presence of the ammonite ''Baculites mclearni'', which only occurs from 80.67 - 80.21 Ma, in the underlying Rattlesnake Mountain Sandstone and the Terlingua Creek Sandstone, it is likely that the Upper Shale was younger than 80.2 Ma. A radiometric date of 76.9 Ma was recovered in the Upper Shale, making it likely the formation wasn't younger than 76.9 Ma. The contact with the overlying Javelina Formation has been estimated at about 70 Ma agoWoodward, H. N. (2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |