|
Baoding Military Academy
Baoding Military Academy or Paoting Military Academy () was a military academy based in Baoding, during the late Qing dynasty and early Republic of China, in the first two decades of the 20th century. For a time, it was the most important military academy in China, and its cadets played prominent roles in the political and military history of the Republic of China. The Baoding Military Academy closed in 1923, but served as a model for the Whampoa Military Academy, which was founded in Guangzhou in 1924. It, along with the Yunnan Military Academy and the Whampoa Military Academy, was one of the “three major strategist cradles in modern China”. During the Second Sino-Japanese War, half of 300 divisions in China's armed forces were commanded by Whampoa graduates and one-third were Baoding cadets. Predecessors In 1885 Li Hongzhang founded the Tianjin Military Academy 天津武備學堂 for Chinese army officers, with German advisers, as part of his military reforms. The move was su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Site
A historic site or heritage site is an official location where pieces of political, military, cultural, or social history have been preserved due to their cultural heritage value. Historic sites are usually protected by law, and many have been recognized with the official national historic site status. A historic site may be any building, landscape, site or structure that is of local, regional, or national significance. Usually this also means the site must be at least 50 years or older. The National Park Service, U.S. National Park Service defines a historic site as the "location of a significant event, a prehistoric or historic occupation or activity, or a building or structure, whether standing, ruined, or vanished, where the location itself possesses historic, cultural, or archeological value regardless of the value of any existing structure". Historic sites can also mark Public-order crime, public crimes, such as Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum in Phnom Penh, Cambodia or Robben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
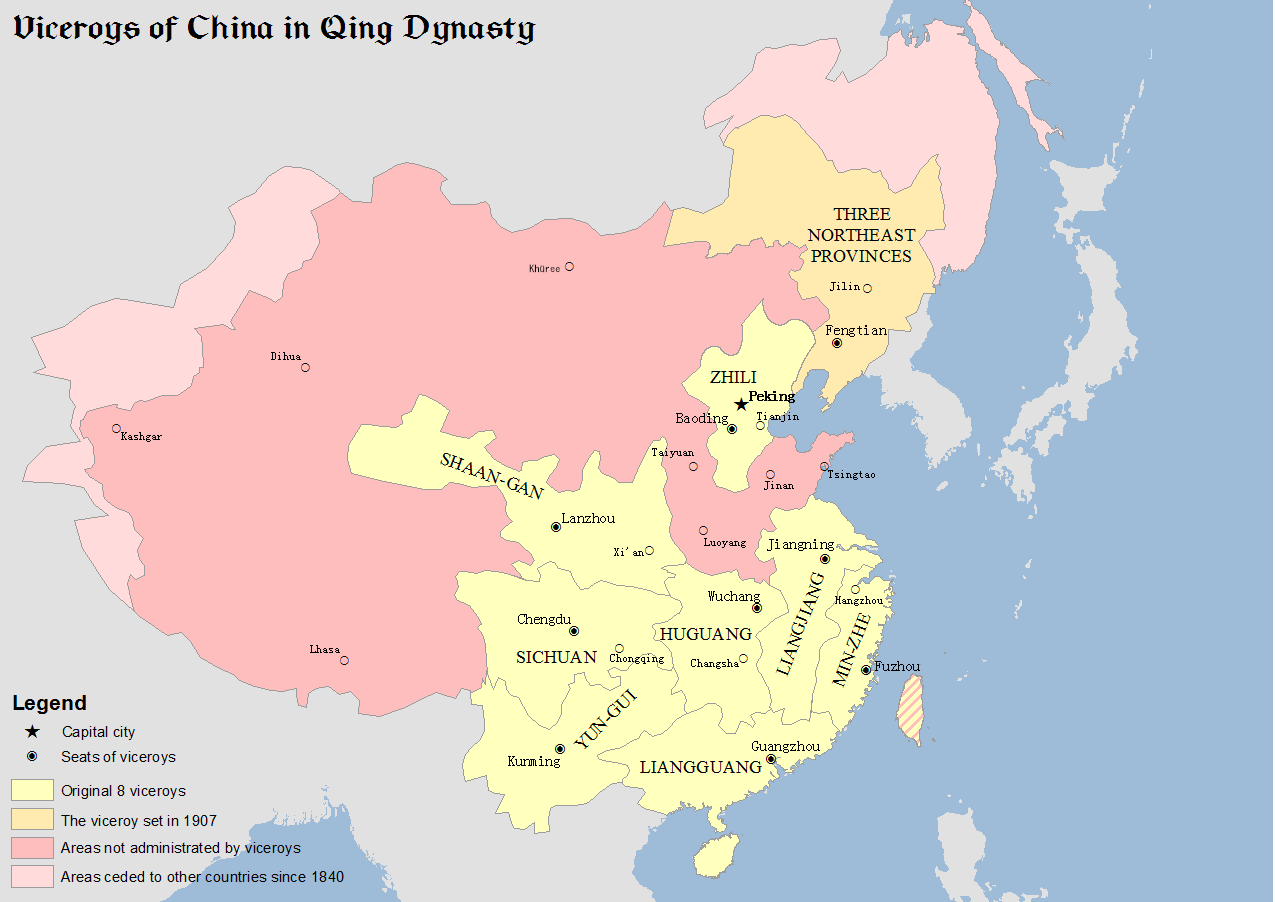
Viceroy Of Zhili Province
The Viceroy of Zhili, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of Zhili and Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Affairs and Food Production, Manager of Waterways, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys in China, Viceroys during the Qing dynasty. The Viceroy of Zhili was an important post because the province of Zhili, which literally means "directly ruled", was the area surrounding the imperial capital, Beijing. The administrative centre was in Tianjin even though the provincial capital was in Baoding. The Viceroy's duties as well as responsibilities have never been defined entirely. Generally speaking, the Viceroy oversaw the military and civil affairs of Zhili, Shandong and Henan provinces. The Viceroy of Zhili was also highly influential in imperial court politics. History The office was first created on 30 September 1649 during the reign of the Shunzhi Emperor, but was later abolished on 1 June 1658. On 23 November 1661, during the reign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xia Wei
Orville Hickock Schell III (born May 20, 1940) is an American writer, academic, and activist. He is known for his works on China, and is the Arthur Ross Director of the Center on U.S.-China Relations at the Asia Society in New York. He previously served as dean of the University of California, Berkeley Graduate School of Journalism. Background and education Schell's father Orville Hickok Schell, Jr., was a prominent lawyer who headed the New York City Bar Association and also the New York City Ballet. The senior Schell also chaired the human rights group Americas Watch from its founding in 1981 until his death in 1987, co-founded Helsinki Watch, forerunner to Human Rights Watch, and became the namesake of the Orville H. Schell, Jr. Center for International Human Rights at Yale Law School. Orville Schell III is the older brother of writer Jonathan Schell. Schell attended Pomfret School in Pomfret, Connecticut, after which he attended Harvard University, leaving in 1960 after h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Zhizhong
Zhang Zhizhong or Chang Chih-chung (27 October 1890 – 6 April 1969) was a Chinese military commander and politician, general in the National Revolutionary Army of the Republic of China and later a pro-Communist politician in the People's Republic of China. Originally a supporter and close associate of Chiang Kai-shek, Zhang belonged to the left wing of the Kuomintang, advocating policies such as collaboration with the Communists against Japan and nationalization of foreign-owned businesses. In 1949 he defected from the Nationalists, becoming a follower of Mao Zedong, and went on to hold high office in the new Communist government, serving as Vice Chairman of the National Defense Council (1954–1969) and Vice Chairman of the National People's Congress (1965–1969).ZHANG ZHIZHONG (1890–1969), in ''Historical Dictionary of Modern China (1800–1949)'', by James Z. Gao, 2009, p.p. 437-438, The Scarecrow Press Life He was born in Chaohu, Anhui, and attended the Baoding Milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huang Shaohong
Huang Shaohong (1895 – August 31, 1966) was a warlord in Guangxi province and governed Guangxi as part of the New Guangxi Clique through the latter part of the Warlord era, and a leader in later years of the Republic of China. Biography Huang was born in 1895 in Rong County, Guangxi, China. After the 1911 revolution he attended Guangxi Military Cadre Training School in Guilin along with Bai Chongxi and Li Zongren. Later he rose to command the Model Battalion, a modern professional military formation equipped with machine guns. In the confused power struggles following the Ao-Gui Wars, local military figures began to carve out territory in Guangxi and dominate it. In the southwest were the opium trails from both Yunnan and Guizhou that ran through Baise and then down the river to Nanning, from whence opium usually went out through Wuzhou, where the trade was financed. During the Ao-Gui wars Huang, then the commander of the Model Battalion, attempted to stay neutr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cai Tingkai
Cai Tingkai (; 1892–1968) was a Chinese general. Cai was in overall command of the 19th Route Army of the Republic of China's National Revolutionary Army and other Chinese forces responsible for holding off the Imperial Japanese Army during the Shanghai War of 1932 on 28 January 1932. In November 1933 Cai and fellow 19th Route Army officer Li Jishen rebelled against the ruling Kuomintang regime and, with Jiang Guangnai, established the Fujian People's Government on 22 November 1933. However, the rebellion—known as the Fujian Incident—did not receive Communist support and, on 21 January 1934, it was defeated by the Kuomintang and Cai was forced to leave China for several years. Later, in the Second Sino-Japanese War (World War II), Cai returned to command the 26th Army Group in the Battle of South Guangxi. He also traveled to the United States to gain support from Chinese-Americans for the war effort. During the final stages of the Chinese Civil War Cai supported the Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bai Chongxi
Bai Chongxi (18 March 1893 – 2 December 1966; , , Xiao'erjing: ) was a Chinese general in the National Revolutionary Army of the Republic of China (ROC) and a prominent Chinese Nationalist leader. He was of Hui ethnicity and of the Muslim faith. From the mid-1920s to 1949, Bai and his close ally Li Zongren ruled Guangxi province as regional warlords with their own troops and considerable political autonomy. His relationship with Chiang Kai-shek was at various times antagonistic and cooperative. He and Li Zongren supported the anti-Chiang warlord alliance in the Central Plains War in 1930, then supported Chiang in the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Chinese Civil War. Bai was the first defense minister of the Republic of China from 1946 to 1948. After losing to the Communists in 1949, he fled to Taiwan, where he died in 1966. Warlord era Bai was born in Guilin, Guangxi and given the courtesy name Jiansheng (). He was a descendant of a Persian merchant of the name Baider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Qun
Zhang Qun or Chang Ch'ün (; May 9, 1889 – December 14, 1990) also known as Zhang Yuejun (張岳軍), was premier of the Republic of China and a prominent member of the Kuomintang. He served as secretary general to the President of the Republic from 1954 to 1972 and senior advisor to Presidents Chiang Kai-shek, Yen Chia-kan, Chiang Ching-kuo, and Lee Teng-hui. Under the influence of his wife, Ma Yu-ying, he became a Christian in the 1930s. Education and early career Born in the Huayang County (now part of Shuangliu County), Sichuan province, Chang was admitted in 1906 to the Baoding Military Academy, just southwest of Beijing. The next year, he was selected to go to Japan to study at the Tokyo Shimbu Gakko, a preparatory military school, where he specialized in artillery. Together with his classmate, Chiang Kai-shek, he joined the T'ung-meng-hui the same year. After completing their preparatory studies, they both served in the Takada regiment of the Imperial Japanese Army’s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 to his death in 1975 – until 1949 in mainland China and from then on in Taiwan. After his rule was confined to Taiwan following his defeat by Mao Zedong in the Chinese Civil War, he continued to head the ROC government until his death. Born in Chekiang (Zhejiang) Province, Chiang was a member of the Kuomintang (KMT), and a lieutenant of Sun Yat-sen in the revolution to overthrow the Beiyang government and reunify China. With help from the Soviets and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), Chiang organized the military for Sun's Canton Nationalist Government and headed the Whampoa Military Academy. Commander-in-chief of the National Revolutionary Army (from which he came to be known as a Generalissimo), he led the Northern Expedition from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinhai Revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China. The revolution was the culmination of a decade of agitation, revolts, and uprisings. Its success marked the collapse of the Chinese monarchy, the end of 2,132 years of imperial rule in China and 276 years of the Qing dynasty, and the beginning of China's early republican era.Li, Xiaobing. 007(2007). ''A History of the Modern Chinese Army''. University Press of Kentucky. , . pp. 13, 26–27. The Qing dynasty had struggled for a long time to reform the government and resist foreign aggression, but the program of reforms after 1900 was opposed by conservatives in the Qing court as too radical and by reformers as too slow. Several factions, including underground anti-Qing groups, revolutionaries in exile, reformers who wanted to save the monarchy by modernizing it, and activists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boxer Protocol
The Boxer Protocol was signed on September 7, 1901, between the Qing Empire of China and the Eight-Nation Alliance that had provided military forces (including Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, United Kingdom, Italy, Japan, Russia, and the United States as well as Belgium, Spain, and the Netherlands), after China's defeat in the intervention to put down the Boxer Rebellion. It is regarded as one of the unequal treaties. Negotiations during the Boxer Rebellion The Qing dynasty was by no means defeated when the Allies took control of Beijing. The Allies had to temper the demands they sent in a message to Xi'an to get the Empress Dowager Cixi to agree with them; for instance, China did not have to give up any land. Many of the Dowager Empress' advisers in the Imperial Court insisted that the war continue against the foreigners, arguing that China could defeat them since it was the disloyal and traitorous people within China who allowed Beijing and Tianjin to be captured by the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total population of 13,866,009 inhabitants during the 2020 Chinese census. Its built-up (''or metro'') area, made up of 12 central districts (all but Baodi, Jizhou, Jinghai and Ninghe), was home to 11,165,706 inhabitants and is also the world's 29th-largest agglomeration (between Chengdu and Rio de Janeiro) and 11th- most populous city proper. It is governed as one of the four municipalities under the direct administration of Chinese central government and is thus under direct administration of the State Council. Tianjin borders Hebei Province and Beijing Municipality, bounded to the east by the Bohai Gulf portion of the Yellow Sea. Part of the Bohai Economic Rim, it is the largest coastal city in Northern China and part of the Jing-Jin-Ji megap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_2016.jpg)