|
Bannu Resolution
The Bannu Resolution ( ps, د بنو فیصله), or the Pashtunistan Resolution ( ps, د پښتونستان قرارداد), was a formal political statement adopted by Pashtun tribesmen who had wanted an independent Pashtun state on 21 June 1947 in Bannu in the North-West Frontier Province of British India (in present-day Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan). The resolution demanded the British to offer the option of independence for Pashtunistan, comprising all Pashtun territories in British India, rather than choosing unfairly between the independent dominions of India and Pakistan. The British, however, refused the request and the North-West Frontier Province was joined with Pakistan on July 1947 NWFP referendum. However, Bacha Khan, his elder brother and then Chief Minister Dr Khan Sahib, and the Khudai Khidmatgars, as well as Many Pashtun tribes of North-West Frontier Province boycotted the referendum in response, citing that it did not have the options of the NWFP becoming i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bannu
Bannu ( ps, بنو, translit=banū ; ur, , translit=bannū̃, ) is a city located on the Kurram River in southern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It is the capital of Bannu Division. Bannu's residents are primarily members of the Banuchi tribe and speak Banuchi (Baniswola) dialect of Pashto which is similar to the distinct Waziristani dialect. Total 5 Tehsil in Bannu. The major industries of Bannu are cloth weaving, sugar mills and the manufacturing of cotton fabrics, machinery and equipment. It is famous for its weekly ''Jumma'' fair. The district forms a basin drained by the Kurram and Gambila (or Tochi) rivers. Etymology According to the philologist Michael Witzel, the city was originally known in Avestan as ''Varəna'', from which its modern name derives. The ancient Sanskrit grammarian, Pāṇini, recorded its name as ''Varṇu''. During the 6th century BCE, the basin around Bannu was known as '' Sattagydia'' ( Old Persian: 𐎰𐎫𐎦𐎢𐏁 ''Thataguš'', count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
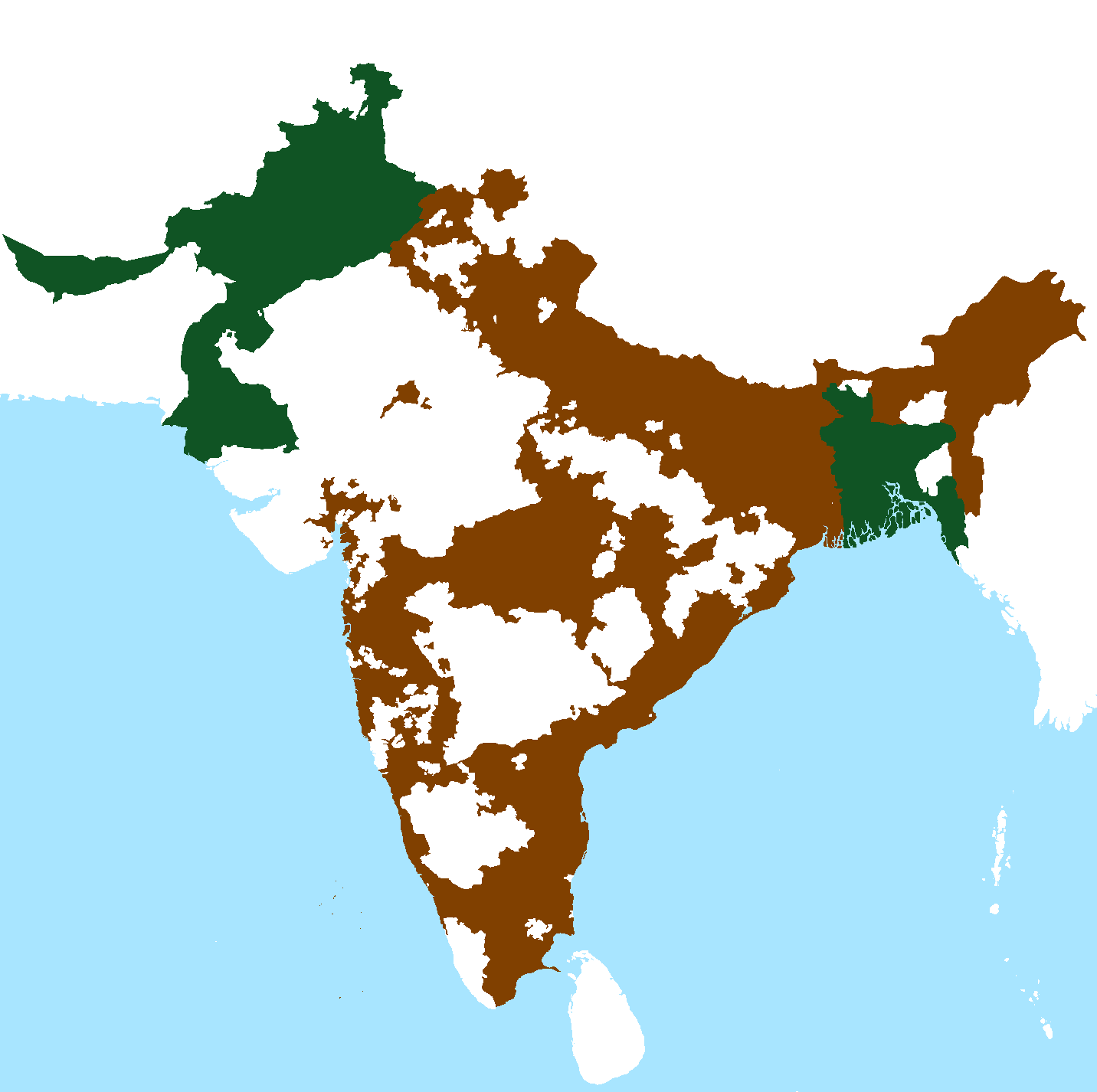
Partition Of British India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. The Dominion of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan—which at the time comprised two regions lying on either side of India—is now the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The partition was outlined in the Indian Independence Act 1947. The change of political borders notably included the division of two provinces of British India, Bengal and Punjab. The majority Muslim districts in these provinces were awarded to Pakistan and the majority non-Muslim to India. The other assets that were divided included the British Indian Army, the Royal Indian Navy, the Royal Indian Air Force, the Indian Civil Service, the railways, and the central treasury. Self-governing independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durand Line
The Durand Line ( ps, د ډیورنډ کرښه; ur, ), forms the Pakistan–Afghanistan border, a international land border between Pakistan and Afghanistan in South Asia. The western end runs to the border with Iran and the eastern end to the border with China. The Durand Line was established in 1893 as the international border between India and the Emirate of Afghanistan by Mortimer Durand, a British diplomat of the Indian Civil Service, and Abdur Rahman Khan, the Afghan Emir, to fix the limit of their respective spheres of influence and improve diplomatic relations and trade. The British considered Afghanistan to be an independent state at the time, although they controlled its foreign affairs and diplomatic relations. The single-page Agreement, dated 12 November 1893, contains seven short articles, including a commitment not to exercise interference beyond the Durand Line. A joint British-Afghan demarcation survey took place starting from 1894, covering some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pashtun Nationalism
Pashtun nationalism ( ps, پښتون ملتپالنه) generally refers to the idea that Pashtuns must always be united to preserve their culture and defend their homeland against any oppressor. It propagates the view that Muslims are not a nation and that ethnic loyalty must come before religious loyalty.Zalmay Khalilzad, ''"The Security of Southwest Asia"'', University of Michigan, 2006, Those who strongly advocate Pashtun nationalism favor the idea of a " Greater Afghanistan", which includes Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Balochistan, and be ruled directly under Pashtun principles. Therefore, the concept of Pashtun nationalism overlaps with Afghan nationalism as Afghanistan is rich in resources and ruled under Pashtun principles. History One of the earliest Pashtun nationalists was the 16th-century revolutionary leader Bayazid Pir Roshan from Waziristan. Another early Pashtun nationalist was the 17th-century "warrior-poet" Khushal Khan Khattak, who was imprisoned by the Mughal emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khudai Khidmatgar
Khudai Khidmatgar ( ps, خداۍ خدمتګار; literally "servants of God") was a predominantly Pashtun nonviolent resistance movement known for its activism against the British Raj in colonial India; it was based in the country's North-West Frontier Province (now in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan). Also called ''Surkh Posh'' or "Red Shirts" or "red-dressed", this was originally a social reform organisation focusing on education and the elimination of blood feuds; it was known as the ''Anjuman-e-Islah-e Afghania'' (society for the reformation of Afghans/Pashtoons). The movement was led by Abdul Ghaffar Khan, known locally as Bacha Khan, Badshah Khan, or Sarhadi Gandhi."Red Shirt Movement".(2008) ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved 14 September 2008, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: ww.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/494519/Red-Shirt-Movement/ref> It gradually became more political as its members were being targeted by the British Raj. By 1929 its leadership was exiled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a new policy or specific law, or the referendum may be only advisory. In some countries, it is synonymous with or commonly known by other names including plebiscite, votation, popular consultation, ballot question, ballot measure, or proposition. Some definitions of 'plebiscite' suggest it is a type of vote to change the constitution or government of a country. The word, 'referendum' is often a catchall, used for both legislative referrals and initiatives. Etymology 'Referendum' is the gerundive form of the Latin verb , literally "to carry back" (from the verb , "to bear, bring, carry" plus the inseparable prefix , here meaning "back"Marchant & Charles, Cassell's Latin Dictionary, 1928, p. 469.). As a gerundive is an adjective,A gerundi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Independence Act 1947
The Indian Independence Act 1947 947 CHAPTER 30 10 and 11 Geo 6is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that partitioned British India into the two new independent dominions of India and Pakistan. The Act received Royal Assent on 18 July 1947 and thus modern-day India and Pakistan, comprising west (modern day Pakistan) and east (modern day Bangladesh) regions, came into being on 15 August. The legislature representatives of the Indian National Congress, the Muslim League, and the Sikh community came to an agreement with Lord Mountbatten on what has come to be known as the ''3 June Plan'' or ''Mountbatten Plan''. This plan was the last plan for independence. Prelude Attlee's announcement Clement Attlee, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, announced on 20 February 1947 that: #The British Government would grant full self-government to British India by 30 June 1948 at the latest, #The future of the Princely States would be decided after the date of final transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of The United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy and thereby ultimate power over all other political bodies in the UK and the overseas territories. Parliament is bicameral but has three parts, consisting of the sovereign ( King-in-Parliament), the House of Lords, and the House of Commons (the primary chamber). In theory, power is officially vested in the King-in-Parliament. However, the Crown normally acts on the advice of the prime minister, and the powers of the House of Lords are limited to only delaying legislation; thus power is ''de facto'' vested in the House of Commons. The House of Commons is an elected chamber with elections to 650 single-member constituencies held at least every five years under the first-past-the-post system. By constitutional convention, all govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford University Press
Stanford University Press (SUP) is the publishing house of Stanford University. It is one of the oldest academic presses in the United States and the first university press to be established on the West Coast. It was among the presses officially admitted to the Association of American University Presses (now the Association of University Presses) at the organization's founding, in 1937, and is one of twenty-two current member presses from that original group. The press publishes 130 books per year across the humanities, social sciences, and business, and has more than 3,500 titles in print. History David Starr Jordan, the first president of Stanford University, posited four propositions to Leland and Jane Stanford when accepting the post, the last of which stipulated, “That provision be made for the publication of the results of any important research on the part of professors, or advanced students. Such papers may be issued from time to time as ‘Memoirs of the Leland Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth" , former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821) , budget = $10.3 billion (2021) , endowment = $17 billion (2021)As of October 25, 2021. , president = Santa Ono , provost = Laurie McCauley , established = , type = Public research university , academic_affiliations = , students = 48,090 (2021) , undergrad = 31,329 (2021) , postgrad = 16,578 (2021) , administrative_staff = 18,986 (2014) , faculty = 6,771 (2014) , city = Ann Arbor , state = Michigan , country = United States , coor = , campus = Midsize City, Total: , including arboretum , colors = Maize & Blue , nickname = Wolverines , spor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loya Jirga
A jirga ( ps, جرګه, ''jərga'') is an assembly of leaders that makes decisions by consensus according to Pashtunwali, the Pashtun social code. It is conducted in order to settle disputes among the Pashtuns, but also by members of other ethnic groups who are influenced by them in present-day Afghanistan and Pakistan. Historically, a ''loya jirga'' or a "great council" has been convened in order to elect a new head of state, approve a new constitution or resolve critical issues. ''Loya jirgas'' have reportedly been organized since the rise to power of the Hotak dynasty in the early 18th century. In July 1747, Afghan chiefs assembled in Kandahar to elect a new king, choosing the 25-year-old Ahmad Shah Durrani, who is credited with founding the modern state of Afghanistan. From 11 to 14 March 2022, the inaugural meeting of the Pashtun National Jirga was held in Bannu, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa to discuss the critical issues faced by the Pashtuns in Pakistan and Afghanistan. Etymology T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |