|
Banjarmasin War
The Banjarmasin War (in old spelling ''Bandjermasin War'', Dutch: ''Bandjermasinse Oorlog'', or formally ''Expeditie naar de Zuider- en Oosterafdeling van Borneo'') (1859–1863) was a war of succession in the Sultanate of Banjarmasin, as well as a colonial war for the restoration of Dutch authority in the eastern and southern section of Borneo. Background 17th century Since 1606 the East United India Company maintained contacts with the island of Borneo. In 1635 the first contract was signed with the Sultanate of Banjarmasin for the provision of pepper - at the time, a luxury product in Europe and a major reason for the Dutch interest in this region. In following decades there were several skirmishes and armed clashes, especially related to such pepper contracts being unfulfilled. One of the most serious was the 1638 killing of 64 Dutch and 21 of their Japanese partners, at Kota Waring in Bandjermasin. Early 19th century In 1809 Herman Willem Daendels, then governor o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banjarmasin
) , translit_lang1 = Other , translit_lang1_type1 = Jawi , translit_lang1_info1 = بنجر ماسين , settlement_type = City , motto = ''Kayuh Baimbai'' ( Banjarese: 'Rowing Together') , image_skyline = , image_caption = Clockwise from top: Banjarmasin seen from above, Soetji Nurani Chinese Temple, Banjarmasin watchtower, and Banjarmasin floating market. , image_flag = Flag of Banjarmasin City.png , image_shield = Lambang Kota Banjarmasin.gif , image_map = , mapsize = , map_caption = Interactive map outlining Banjarmasin , pushpin_map = Indonesia , pushpin_label_position = right , pushpin_map_caption = Location within Indonesia , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Indonesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Motley
James Motley (2 May 1822 – 1 May 1859) was a Yorkshireman closely associated with South Wales and Borneo. Life Born in Leeds, the son of Thomas Motley (1781–1863) and Caroline Osburn (1795–1869), sister of noted Egyptologist William Osburn. James was educated at St Peter's School, York and St John's College, Cambridge. He spent at least some of his youth in South Wales where his father, a woolstapler, had investments in iron, coal, and tin works, being an early partner in the Maesteg Ironworks, Yskyn Colliery at Briton Ferry, Margam tinworks, and the Dafen tinworks at Llanelli. He published a volume of poetry ''Tales of Cymry'' in 1848. He worked as an engineer and manager (at Tewgoed (or 'Terrgoed') Colliery at Cwmavon); then underground surveyor to William Chambers of Llanelli; and finally, at Abercrave colliery, iron works, iron mines, and limestone quarries while maintaining an active interest in natural history, especially botany (he left a herbarium at the Royal Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martapura, South Kalimantan
Martapura is the capital of the Banjar Regency in South Kalimantan province, Indonesia. It is located close to the city of Banjarbaru (with which it forms a continuous built-up area) and it consists of three Districts of Indonesia, districts within the Regency - Martapura (district), Martapura, West Martapura and East Martapura, with a combined population at the 2010 Census of 147,654 people. Originally this town was named "Kayutangi", which was the last capital of the former Sultanate of Banjar. The famous Banjar people, Banjarese ulema Sheikh Muhammad Arsyad al-Banjari, author of Sabilal Muhtadin, comes from this town. This town is famous as ''kota santri'' or the "city of ''santri'' (Muslim students)" in Kalimantan, because of the ''pesantren'' (Islamic boarding school) of Pondok Pesantren Darussalam Martapura. Martapura is often called "Veranda of Mecca" because there are many santris wearing white clothes in this town who walk up and down to study Islam, similar to Mecca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
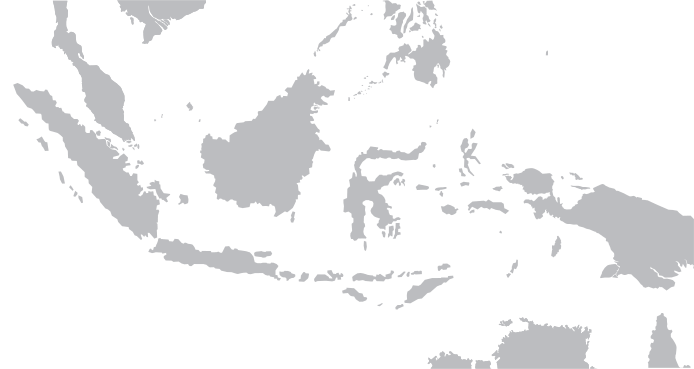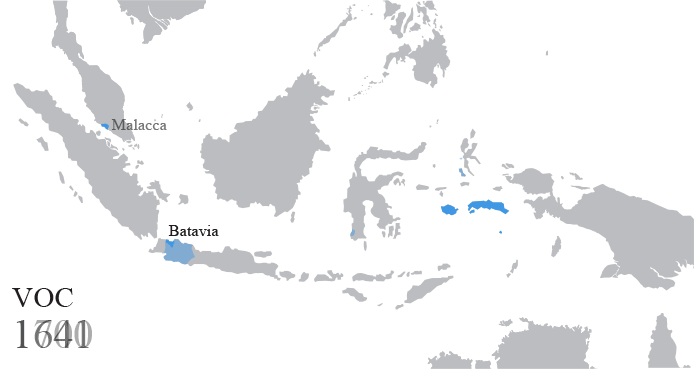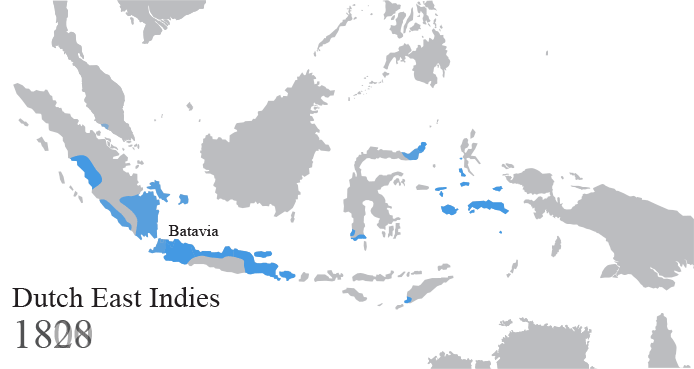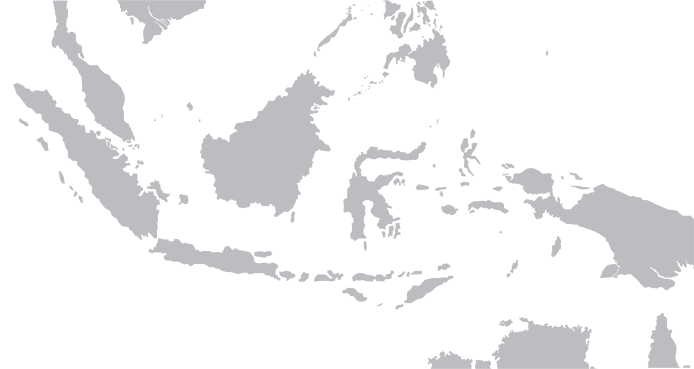
Batavia (Dutch East Indies)
Batavia was the capital of the Dutch East Indies. The area corresponds to present-day Jakarta, Indonesia. Batavia can refer to the city proper or its suburbs and hinterland, the Ommelanden, which included the much-larger area of the Residency of Batavia in the present-day Indonesian provinces of Jakarta, Banten and West Java. The founding of Batavia by the Dutch in 1619, on the site of the ruins of Jayakarta, led to the establishment of a Dutch colony; Batavia became the center of the Dutch East India Company's trading network in Asia. Monopolies on local produce were augmented by non-indigenous cash crops. To safeguard their commercial interests, the company and the colonial administration absorbed surrounding territory. Batavia is on the north coast of Java, in a sheltered bay, on a land of marshland and hills crisscrossed with canals. The city had two centers: Oud Batavia (the oldest part of the city) and the relatively-newer city, on higher ground to the south. It was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maluka
Maluka (or Maluko) was a small independent state located around the Sungei Maluka, southeast of Bandjermassin on the island of Borneo .''De man die vrouwen verzamelde; Een koloniale geschiedenis van de Kokos-eilanden'' by Joop van den Berg (‘s-Gravenhage 1998) It was established in a land concession acquired by an English adventurer Alexander Hare from the Sultan of Banjarmassin in 1812 and lasted 4 years until 1816. History After the successful British invasion of the previously Dutch territory of Java in 1811 (part of the wider Napoleonic Wars of the time), Lieutenant-Governor Stamford Raffles of the British East India Company sent the private merchant Alexander Hare to the region and appointed him Resident of Banjarmasin and Commissioner of the Island of Borneo (1811–16). Hare then acquired 1,400 square miles of land from the Sultan of Banjarmasin stretching along the coast from the mouth of the Barito River to Tanjong Selatan and inland to the north up to the Sungei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Hare
Alexander Hare (1775–1834) was an English merchant, infamous for his polygamous lifestyle. He is also known for his attempts at founding settlements near Banjarmasin on the island of Borneo and the Cocos-Keeling Islands. Malacca The son of a London watchmaker of the same name and his wife Janet, Alexander joined a trading company in Portugal around 1800, moved to Calcutta, and settled as a merchant in Malacca in 1807. Among the places he traded to was Banjarmasin, on the southern coast of Borneo. Banjarmasin had a Dutch trading post, but it was abandoned in 1809 due to British naval hostilities. The Sultan, seeking a replacement for the Dutch, and having developed a good relationship with Hare, asked him to establish a British trading post. But Hare was cautious and waited until his own interests converged with the rising star of Stamford Raffles of the British East India Company (EIC) before acting. Hare had first met Stamford Raffles when the later stopped in Malacca in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of French domination over most of continental Europe. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and the French Revolutionary Wars consisting of the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). The Napoleonic Wars are often described as five conflicts, each termed after the coalition that fought Napoleon: the Third Coalition (1803–1806), the Fourth (1806–1807), the Fifth (1809), the Sixth (1813–1814), and the Seventh (1815) plus the Peninsular War (1807–1814) and the French invasion of Russia (1812). Napoleon, upon ascending to First Consul of France in 1799, had inherited a republic in chaos; he subsequently created a state with stable financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British People
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs modern British citizenship and nationality, which can be acquired, for instance, by descent from British nationals. When used in a historical context, "British" or "Britons" can refer to the Ancient Britons, the indigenous inhabitants of Great Britain and Brittany, whose surviving members are the modern Welsh people, Cornish people, and Bretons. It also refers to citizens of the former British Empire, who settled in the country prior to 1973, and hold neither UK citizenship nor nationality. Though early assertions of being British date from the Late Middle Ages, the Union of the Crowns in 1603 and the creation of the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707 triggered a sense of British national identity.. The notion of Britishness and a shared Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |