|
Banguingui
Banguingui, also known as Sama Banguingui or Samal Banguingui (alternative spellings include Bangingi’, Bangingi, Banguingui, Balanguingui, and Balangingi) is a distinct ethnolinguistic group native to Balanguingui Island but also dispersed throughout the Greater Sulu Archipelago and southern and western coastal regions of the Zamboanga Peninsula in Mindanao, Philippines. They are one of the ethnic groups usually collectively known as the Sama-Bajau peoples. People The Banguingui are not officially recognized by law either in the Philippines or in the neighboring Malaysian state of Sabah. The Banguingui language has both written and oral traditions. Its written language is in Jawi script and is fast becoming a dying tradition. Oral traditions are handed down by the ''kamattoahan'' (elders) to the ''kaanakan'' or ''anak baha-u'' (new generations). The Banguingui built ''kuta'' (forts) throughout the Sulu Archipelago. Like their other Sama cousins, they sailed various ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanong
''Lanong'' were large outrigger warships used by the Iranun and the Banguingui people of the Philippines. They could reach up to in length and had two biped shear masts which doubled as boarding ladders. They also had one to three banks of oars rowed by galley slaves. They were specialized for naval battles. They were prominently used for piracy and slave raids from the mid-18th century to the early 19th century in most of Southeast Asia. The name ''lanong'' is derived from ''Lanun'',''Lanun'' also became the word for "pirate" in the Malay language an exonym of the Iranun people. Like the ''karakoa'', large ''lanong'' were also known by the Spanish as ''joanga'' or '' juanga'' (Spanish for " junk"), a name which was also applied to other large ships in Southeast Asia. Description ''Lanong'' can reach up to long and wide amidships. They were crewed by up to 150 to 200 men, led by a ''panglima'' (commander). Unlike the similar ''karakoa'', the ''lanong'' were heavily armed spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulu Province
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu ( Tausūg: ''Wilāya sin Lupa' Sūg''; tl, Lalawigan ng Sulu), is a province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM). Its capital is Jolo on the island of the same name. Maimbung, the royal capital of the Sultanate of Sulu, is also located in the province. Sulu is along the southern border of the Sulu Sea and the northern boundary of the Celebes Sea. History Pre-Spanish and Spanish eras Prior to the arrival of Islam in Sulu, the province used to adhere to local animist religions; this later changed to Hindu and Buddhist belief systems. Throughout this time, the Kingdom of Lupah Sug had been established centuries before Islam arrived. The advent of Islam around 1138 through merchants and traders had a distinct influence on Southeast Asia. The coming of Arabs, Persians and other Muslims paved the way for the arrival of religious missionaries, traders, scholars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sama-Bajau People
The Sama-Bajau include several Austronesian ethnic groups of Maritime Southeast Asia. The name collectively refers to related people who usually call themselves the Sama or Samah (formally A'a Sama, "Sama people"); or are known by the exonym Bajau (, also spelled Badjao, Bajaw, Badjau, Badjaw, Bajo or Bayao). They usually live a seaborne lifestyle and use small wooden sailing vessels such as the '' perahu'' (''layag'' in Meranau), ''djenging'' (''balutu''), '' lepa'', and ''vinta'' (''pilang''). Some Sama-Bajau groups native to Sabah are also known for their traditional horse culture. The Sama-Bajau are the dominant ethnic group of the islands of Tawi-Tawi in the Philippines. They are also found in other islands of the Sulu Archipelago, coastal areas of Mindanao, northern and eastern Borneo, Sulawesi, and throughout the eastern Indonesian islands. In the Philippines, they are grouped with the religiously similar Moro people. Within the last fifty years, many of the Filipi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garay (ship)
''Garay'' were traditional native warships of the Banguingui people in the Philippines. In the 18th and 19th centuries, they were commonly used for piracy by the Banguingui and Iranun people against unarmed trading ships and raids on coastal settlements in the regions surrounding the Sulu Sea. History Most ''garay'' were built in the shipyards of Parang, Sulu in the late 18th century. During the early 19th century, Banguingui ''garay'' squadrons regularly plagued the straits of southern Palawan from the months of March to November each year. They raided coastal areas in northern Borneo for slaves as well as cut off trade into the Sultanate of Brunei. These attacks severely affected the economy of Brunei, leading to its decline. The Banguingui purportedly had a saying: "It is difficult to catch fish, but easy to catch Borneans." Description ''Garay'' were smaller, faster, and more maneuverable than the Iranun ''lanong'' warships. They had a much broader beam and a somewhat round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sama-Bajau Peoples
The Sama-Bajau include several Austronesian ethnic groups of Maritime Southeast Asia. The name collectively refers to related people who usually call themselves the Sama or Samah (formally A'a Sama, "Sama people"); or are known by the exonym Bajau (, also spelled Badjao, Bajaw, Badjau, Badjaw, Bajo or Bayao). They usually live a seaborne lifestyle and use small wooden sailing vessels such as the ''perahu'' (''layag'' in Meranau), '' djenging'' (''balutu''), '' lepa'', and '' vinta'' (''pilang''). Some Sama-Bajau groups native to Sabah are also known for their traditional horse culture. The Sama-Bajau are the dominant ethnic group of the islands of Tawi-Tawi in the Philippines. They are also found in other islands of the Sulu Archipelago, coastal areas of Mindanao, northern and eastern Borneo, Sulawesi, and throughout the eastern Indonesian islands. In the Philippines, they are grouped with the religiously similar Moro people. Within the last fifty years, many of the Fili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulu Sultanate
The Sultanate of Sulu ( Tausūg: ''Kasultanan sin Sūg'', كاسولتانن سين سوڬ; Malay: ''Kesultanan Sulu''; fil, Sultanato ng Sulu; Chavacano: ''Sultanato de Sulu/Joló''; ar, سلطنة سولك) was a Muslim state that ruled the Sulu Archipelago, parts of Mindanao and certain portions of Palawan in today's Philippines, alongside parts of present-day Sabah, North and East Kalimantan in north-eastern Borneo. The sultanate was founded either on 17 November 1405 or 1457 by Johore-born explorer and religious scholar Sharif ul-Hashim. ''Paduka Mahasari Maulana al Sultan Sharif ul-Hashim'' became his full regnal name, ''Sharif-ul Hashim'' is his abbreviated name. He settled in Buansa, Sulu. After the marriage of Abu Bakr and a local ''dayang-dayang'' (princess) Paramisuli, he founded the sultanate. The sultanate gained its independence from the Bruneian Empire in 1578. At its peak, it stretched over the islands that bordered the western peninsula of Zamboanga in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of the same name that also includes its adjacent islands, notably the Sulu Archipelago. According to the 2020 census, Mindanao has a population of 26,252,442 people, while the entire island group has an estimated population of 27,021,036 according to the 2021 census. Mindanao is divided into six administrative regions: the Zamboanga Peninsula, Northern Mindanao, the Caraga region, the Davao region, Soccsksargen, and the autonomous region of Bangsamoro. According to the 2020 census, Davao City is the most populous city on the island, with 1,776,949 people, followed by Zamboanga City (pop. 977,234), Cagayan de Oro (pop. 728,402), General Santos (pop. 697,315), Butuan (pop. 372,910), Iligan (pop. 363,115) and Cotabato City (pop. 325,079). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
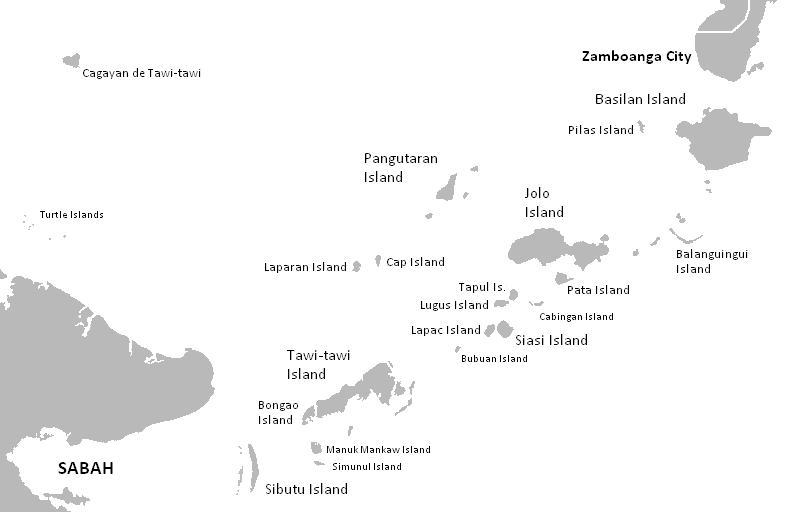
Balanguingui Island
The islands of the Philippines, also known as the Philippine Archipelago, comprises about 7,641 islands, of which only about 2,000 are inhabited.Magical Islands , Philippine Tourism, retrieved 2012 More than 5,000 islands of the archipelago are yet to be given official names. They are clustered into the three major island groups of , , and |
Bangsamoro Autonomous Region In Muslim Mindanao
ar, منطقة بانجسامورو ذاتية الحكم فى مسلمى مينداناو , native_name = , settlement_type = Autonomous regions of the Philippines, Autonomous region , anthem = Bangsamoro Hymn , image_skyline = , image_alt = , image_caption = , image_flag = Flag of Bangsamoro.svg , flag_alt = , image_seal = Seal of Bangsamoro.svg , seal_alt = , image_shield = , shield_alt = , nickname = , motto = , image_map = , map_alt = , map_caption = Location in the Philippines , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Philippines , subdivision_type1 = Island groups of the Philippine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In The Philippines
Islam was the first-recorded monotheistic religion in the Philippines. Islam reached the Philippines in the 14th century with the arrival of Muslim traders from the Persian Gulf, southern India, and their followers from several sultanates in the wider Malay Archipelago. The first missionaries then followed in the late 14th and early 15th centuries. They facilitated the formation of sultanates and conquests in mainland Mindanao and Sulu. Those who converted to Islam came to be known as the Moros, with Muslim conquest reaching as far as Tondo that was later supplanted by Bruneian Empire vassal-state of Maynila. Muslim sultanates had already begun expanding in the central Philippines by the 16th century, when the Spanish fleet led by Ferdinand Magellan arrived. The subsequent Spanish conquest led to Catholic Christianity becoming the predominant religion in most of the modern-day Philippines, with Islam becoming a significant minority religion. In the 21st century, there i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moro People
The Moro people or Bangsamoro people are the 13 Muslim-majority ethnolinguistic Austronesian groups of Mindanao, Sulu, and Palawan, native to the region known as the Bangsamoro (lit. ''Moro nation'' or ''Moro country''). As Muslim-majority ethnic groups, they form the largest non-Christian population in the Philippines, and comprise about 5% of the country's total population, or 5 million people. Most Moros are followers of Sunni Islam of the Shafiʽi school of fiqh. The Moros were once independent under a variety of local states, including the Sultanate of Sulu, the Sultanate of Maguindanao, and the Confederation of sultanates in Lanao; withstanding repeated Spanish invasions, the Moro states remained de facto independent up until the Moro Rebellion of the early 20th century. Upon Philippine independence in 1946, the Moros continued their struggle for self-determination against a predominantly–Christian Philippines, culminating in a decades-long insurgency of armed rebe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinta
The vinta is a traditional outrigger boat from the Philippine island of Mindanao. The boats are made by Sama-Bajau, Tausug and Yakan peoples living in the Sulu Archipelago, Zamboanga peninsula, and southern Mindanao. Vinta are characterized by their colorful rectangular lug sails (''bukay'') and bifurcated prows and sterns, which resemble the gaping mouth of a crocodile. Vinta are used as fishing vessels, cargo ships, and houseboats. Smaller undecorated versions of the vinta used for fishing are known as tondaan. The name "vinta" is predominantly used in Zamboanga, Basilan, and other parts of mainland Mindanao. It is also known as pilang or pelang among the Sama-Bajau of the Tawi-Tawi islands; dapang or depang among the Tausug in Sulu; and balanda or binta in Yakan in Basilan. It can also be generically referred to as ''lepa-lepa'', ''sakayan'', or '' bangka'', which are native names for small outrigger vessels. Description The vinta has a deep and narrow hull formed fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)



.jpg)