|
Banding Marbled Godwit On Bowdoin NWR (12820314955)
Banding may refer to: * Banding (medical), procedures that use elastic bands for constriction * Bird banding/ringing, the marking of individual birds with bands or rings to enable individual identification * Colour banding, an inaccuracy in computer graphics * Edge banding, a woodworking technique * G banding, a genetic technique * Minor variations in outputs from printers and photocopiers that allow forensic identification * Another name for strapping, the process of applying a strap to an item to combine, hold, reinforce, or fasten it, or the strap or band itself * Ability grouping, the educational practice of placing students into groups based on their abilities, talents or achievements * Flow banding, a geological term to describe bands or layers in rocks * Occupational exposure banding Occupational exposure banding, also known as hazard banding, is a process intended to quickly and accurately assign chemicals into specific categories (bands), each corresponding to a range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banding (medical)
Banding is a medical procedure which uses elastic bands for constriction. Banding may be used to tie off blood vessels in order to stop bleeding, as in the treatment of bleeding esophageal varices. The band restricts blood flow to the ligated tissue, so that it eventually dies and sloughs away from the supporting tissue. This same principle underlies banding as treatment for hemorrhoids. Banding may also be used to restrict the function of an organ without killing it. In gastric banding to treat obesity, the size of the stomach is reduced so that digestion is slowed and the patient feels full more quickly. Banding as a medical procedure is commonly used in livestock for male castration of sheep and cattle. Banding is also commonly done in tail docking of lambs to prevent flystrike, and less commonly, used to dock tails of dairy cattle and draft horses. The bands are applied at the base of the scrotum or desired tail site, restricting blood flow to the scrotum or tail tissue, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Ringing
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colour Banding
Colour banding is a subtle form of posterization in digital images, caused by the colour of each pixel being rounded to the nearest of the digital colour levels. While posterization is often done for artistic effect, colour banding is an undesired artifact. In 24-bit colour modes, 8 bits per channel is usually considered sufficient to render images in Rec. 709 or sRGB. However the eye can see the difference between the colour levels, especially when there is a sharp border between two large areas of adjacent color levels. This will happen with gradual gradients (like sunsets, dawns or clear blue skies), and also when blurring an image a large amount. Colour banding is more noticeable with fewer bits per pixel (BPP) at 16–256 colours (4–8 BPP), where there are fewer shades with a larger difference between them. Possible solutions include the introduction of dithering and increasing the number of bits per colour channel. Because the banding comes from limitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge Banding
Edge banding or edgebanding is the name of both a process and an associated narrow strip of material used to create durable and aesthetically pleasing trim edges during finish carpentry. Edge banding is used to cover the exposed sides of materials such as plywood, particle board or MDF, increasing durability and giving the appearance of a solid or more valuable material. Common substitutes for edge banding include face frames or molding. Edge banding can be made of different materials including PVC, ABS, acrylic, melamine, wood or wood veneer. Traditional edge banding was a manual process requiring ordinary carpentry tools and materials. In modern applications, particularly for high-volume, repetitive manufacturing steps such as cabinet doors, edge banding is applied to the substrate by an automated process using a hot-melt adhesive. Hot melt adhesives may consist of various raw materials including EVA, PUR, PA, APOA, and PO. A substrate primer may also be used as a bonding a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Banding
G-banding, G banding or Giemsa banding is a technique used in cytogenetics to produce a visible karyotype by staining condensed chromosomes. It is the most common chromosome banding method. It is useful for identifying genetic diseases through the photographic representation of the entire chromosome complement.Speicher, Michael R. and Nigel P. Carter. "The New Cytogenetics: Blurring the Boundaries with Molecular Biology." ''Nature'' Reviews Genetics, Vol 6. Oct 2005. The metaphase chromosomes are treated with trypsin (to partially digest the chromosome) and stained with Giemsa stain. Heterochromatic regions, which tend to be rich with adenine and thymine (AT-rich) DNA and relatively gene-poor, stain more darkly in G-banding. In contrast, less condensed chromatin ( Euchromatin)—which tends to be rich with guanine and cytosine ( GC-rich) and more transcriptionally active—incorporates less Giemsa stain, and these regions appear as light bands in G-banding. The pattern of ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forensic Identification
Forensic identification is the application of forensic science, or "forensics", and technology to identify specific objects from the trace evidence they leave, often at a crime scene or the scene of an accident. Forensic means "for the courts". Human identification People can be identified by their fingerprints. This assertion is supported by the philosophy of friction ridge identification, which states that friction ridge identification is established through the agreement of friction ridge formations, in sequence, having sufficient uniqueness to individualize. Friction ridge identification is also governed by four premises or statements of facts: # Friction ridges develop on the fetus in their definitive form prior to birth. # Friction ridges are persistent throughout life except for permanent scarring, disease, or decomposition after death. # Friction ridge paths and the details in small areas of friction ridges are unique and never repeated. # Overall, friction ridge patte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strapping
Strapping, also known as bundling and banding, is the process of applying a strap to an item to combine, stabilize, hold, reinforce, or fasten it. The strap may also be referred to as ''strapping''. Strapping is most commonly used in the packaging industry. Types of strap Strap is a flexible flat material, most commonly made from steel or various plastics. Steel Steel is the oldest and highest tensile strength strapping. It is available in a variety of widths and thicknesses as well as variations in the grade of steel. Steel is used for heavy duty holding where high strength and minimal stretch are desired. Surface finishes for steel strap include: paint, paint and wax, bluing or zinc and wax. The wax is used to better transmit the tension around the bundle and for use with certain types of tensioners. Common applications include steel coils, bundles of metal, baling wire, bricks and pavers, and roll end-binding. Steel Strapping is sold by weight rather than length, due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ability Grouping
Ability grouping is the educational practice of grouping students by potential or past achievement for a relevant activity. Ability groups are usually small, informal groups formed within a single classroom. It differs from tracking by being less pervasive, involving much smaller groups, and by being more flexible and informal. In a mixed-ability classroom, ability groups allow the teacher to target review, direct instruction, and advanced work to the needs of a small group, rather than attempting to meet the divergent needs of the entire class simultaneously. Assignment to an ability group is often short-term (never lasting longer than one school year), and varies by subject. Assignment to an ability group is made by (and can be changed at any time by) the individual teacher, and is usually not recorded in student records. For example, a teacher may divide a typical mixed-ability classroom into three groups for a mathematics lesson: those who need to review basic facts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow Banding
Flow banding is a geological term to describe bands or layers that can sometimes be seen in rock that formed from magma (molten rock). Flow banding is caused by friction of the viscous magma that is in contact with a solid rock interface, usually the wall rock to an intrusive chamber or, if the magma is erupted, the surface of the earth across which the lava is flowing. The friction and viscosity of the magma causes phenocrysts and xenoliths within the magma or lava to slow down near the interface and become trapped in a viscous layer. This forms laminar flow, which manifests as a banded, streaky appearance. Flow banding also results from the process of fractional crystallization that occurs by convection if the crystals that are caught in the flow-banded margins are removed from the melt. This can change the composition of the melt in large intrusions, leading to differentiation. In layered intrusions, flow banding can occur with crystal accumulation, forming pseudo-sedimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
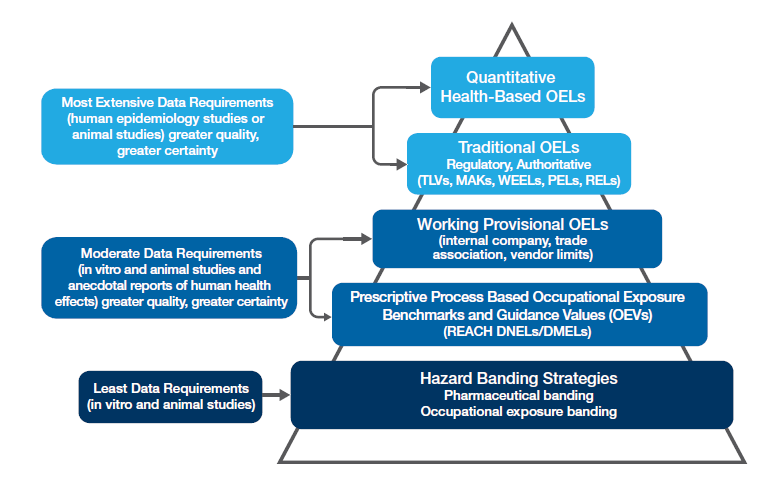
Occupational Exposure Banding
Occupational exposure banding, also known as hazard banding, is a process intended to quickly and accurately assign chemicals into specific categories (bands), each corresponding to a range of exposure concentrations designed to protect worker health. These bands are assigned based on a chemical’s toxicological potency and the adverse health effects associated with exposure to the chemical. The output of this process is an occupational exposure band (OEB). Occupational exposure banding has been used by the pharmaceutical sector and by some major chemical companies over the past several decades to establish exposure control limits or ranges for new or existing chemicals that do not have formal OELs. Furthermore, occupational exposure banding has become an important component of the Hierarchy of Occupational Exposure Limits (OELs). The U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has developed a process that could be used to apply occupational exposure bandin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



_ready_for_transport.jpg)