|
Banburismus
Banburismus was a cryptanalytic process developed by Alan Turing at Bletchley Park in Britain during the Second World War. It was used by Bletchley Park's Hut 8 to help break German ''Kriegsmarine'' (naval) messages enciphered on Enigma machines. The process used sequential conditional probability to infer information about the likely settings of the Enigma machine. It gave rise to Turing's invention of the '' ban'' as a measure of the weight of evidence in favour of a hypothesis. This concept was later applied in Turingery and all the other methods used for breaking the Lorenz cipher. Overview The aim of Banburismus was to reduce the time required of the electromechanical Bombe machines by identifying the most likely right-hand and middle wheels of the Enigma. Hut 8 performed the procedure continuously for two years, stopping only in 1943 when sufficient bombe time became readily available. Banburismus was a development of the " clock method" invented by the Polish cryptanalyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer. He is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science and artificial intelligence. Born in Maida Vale, London, Turing was raised in southern England. He graduated at King's College, Cambridge, with a degree in mathematics. Whilst he was a fellow at Cambridge, he published a proof demonstrating that some purely mathematical yes–no questions can never be answered by computation and defined a Turing machine, and went on to prove that the halting problem for Turing machines is undecidable. In 1938, he obtained his PhD from the Department of Mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock (cryptography)
In cryptography, the clock was a method devised by Polish mathematician-cryptologist Jerzy Różycki, at the Polish General Staff's Cipher Bureau, to facilitate decrypting German Enigma ciphers. The method determined the rightmost rotor in the German Enigma by exploiting the different turnover positions. For the Poles, learning the rightmost rotor reduced the rotor-order search space by a factor of 3 (the number of rotors). The British improved the method, and it allowed them to use their limited number of bombes more effectively (the British confronted 5 to 8 rotors). Method This method sometimes made it possible to determine which of the Enigma machine's rotors was at the far right, that is, in the position where the rotor always revolved at every depression of a key. The clock method was developed by Jerzy Różycki during 1933–1935. Marian Rejewski's grill method could determine the right-hand rotor, but that involved trying each possible rotor permutation (there wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hut 8
Hut 8 was a section in the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park (the British World War II codebreaking station, located in Buckinghamshire) tasked with solving German naval (Kriegsmarine) Enigma messages. The section was led initially by Alan Turing. He was succeeded in November 1942 by his deputy, Hugh Alexander. Patrick Mahon succeeded Alexander in September 1944. Hut 8 was partnered with Hut 4, which handled the translation and intelligence analysis of the raw decrypts provided by Hut 8. Located initially in one of the original single-story wooden huts, the name "Hut 8" was retained when Huts 3, 6 & 8 moved to a new brick building, Block D, in February 1943. After 2005, the first Hut 8 was restored to its wartime condition, and it now houses the " HMS Petard Exhibition". Operation In 1940, a few breaks were made into the naval "Dolphin" code, but Luftwaffe messages were the first to be read in quantity. The German navy had much tighter procedures, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turingery
Turingery in ''Testery Methods 1942–1944'' or Turing's method (playfully dubbed Turingismus by Peter Ericsson, Peter Hilton and Donald Michie) was a manual codebreaking method devised in July 1942 by the mathematician and cryptanalyst Alan Turing at the British Government Code and Cypher School at Bletchley Park during World War II. It was for use in cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher produced by the Lorenz cipher, SZ40 and SZ42 teleprinter Rotor machine, rotor stream cipher machines, one of the Germans' ''Geheimschreiber'' (secret writer) machines. The British codenamed non-Morse code, Morse traffic Fish (cryptography), "Fish", and that from this machine "Tunny" (another word for the tuna fish). Reading a Tunny message required firstly that the logical structure of the system was known, secondly that the periodically changed pattern of active cams on the wheels was derived, and thirdly that the starting positions of the scrambler wheels for this message—the Key (cryptography) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequential Analysis
In statistics, sequential analysis or sequential hypothesis testing is statistical analysis where the sample size is not fixed in advance. Instead data are evaluated as they are collected, and further sampling is stopped in accordance with a pre-defined stopping rule as soon as significant results are observed. Thus a conclusion may sometimes be reached at a much earlier stage than would be possible with more classical hypothesis testing or estimation, at consequently lower financial and/or human cost. History The method of sequential analysis is first attributed to Abraham Wald with Jacob Wolfowitz, W. Allen Wallis, and Milton Friedman while at Columbia University's Statistical Research Group as a tool for more efficient industrial quality control during World War II. Its value to the war effort was immediately recognised, and led to its receiving a "restricted" classification. At the same time, George Barnard led a group working on optimal stopping in Great Britain. Ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Foss
Hugh Rose Foss (13 May 1902 – 23 December 1971) was a British cryptanalyst. At Bletchley Park during World War II he made significant contributions both to the breaking of the German Enigma code and headed the section tasked with breaking Japanese Naval codes. Early life and education Foss was born in Kobe, Japan, one of five children of the Rt Revd Hugh Foss, Bishop of Osaka and his wife Janet Ovans. As a child of a missionary family stationed in Japan he developed fluency in Japanese from an early age. Foss was later educated at Marlborough College and graduated from Christ's College, Cambridge in 1924. Foss's elder brother Charles Calveley Foss was awarded the Victoria Cross in the First World War. Career as a cryptanalyst In December 1924 he joined the Government Code and Cipher School. He recalled learning of two models of the Enigma machine in 1926: the large non-reciprocal typing B model, and the small index C model. In 1927 Edward Travis gave him a small (recipro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ban (unit)
The hartley (symbol Hart), also called a ban, or a dit (short for decimal digit), is a logarithmic unit that measures information or entropy, based on base 10 logarithms and powers of 10. One hartley is the information content of an event if the probability of that event occurring is . It is therefore equal to the information contained in one decimal digit (or dit), assuming ''a priori'' equiprobability of each possible value. It is named after Ralph Hartley. If base 2 logarithms and powers of 2 are used instead, then the unit of information is the shannon or bit, which is the information content of an event if the probability of that event occurring is . Natural logarithms and powers of e define the nat. One ban corresponds to ln(10) nat = log2(10) Sh, or approximately 2.303 nat, or 3.322 bit (3.322 Sh). A deciban is one tenth of a ban (or about 0.332 Sh); the name is formed from ''ban'' by the SI prefix ''deci-''. Though there is no associated SI unit, information entrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
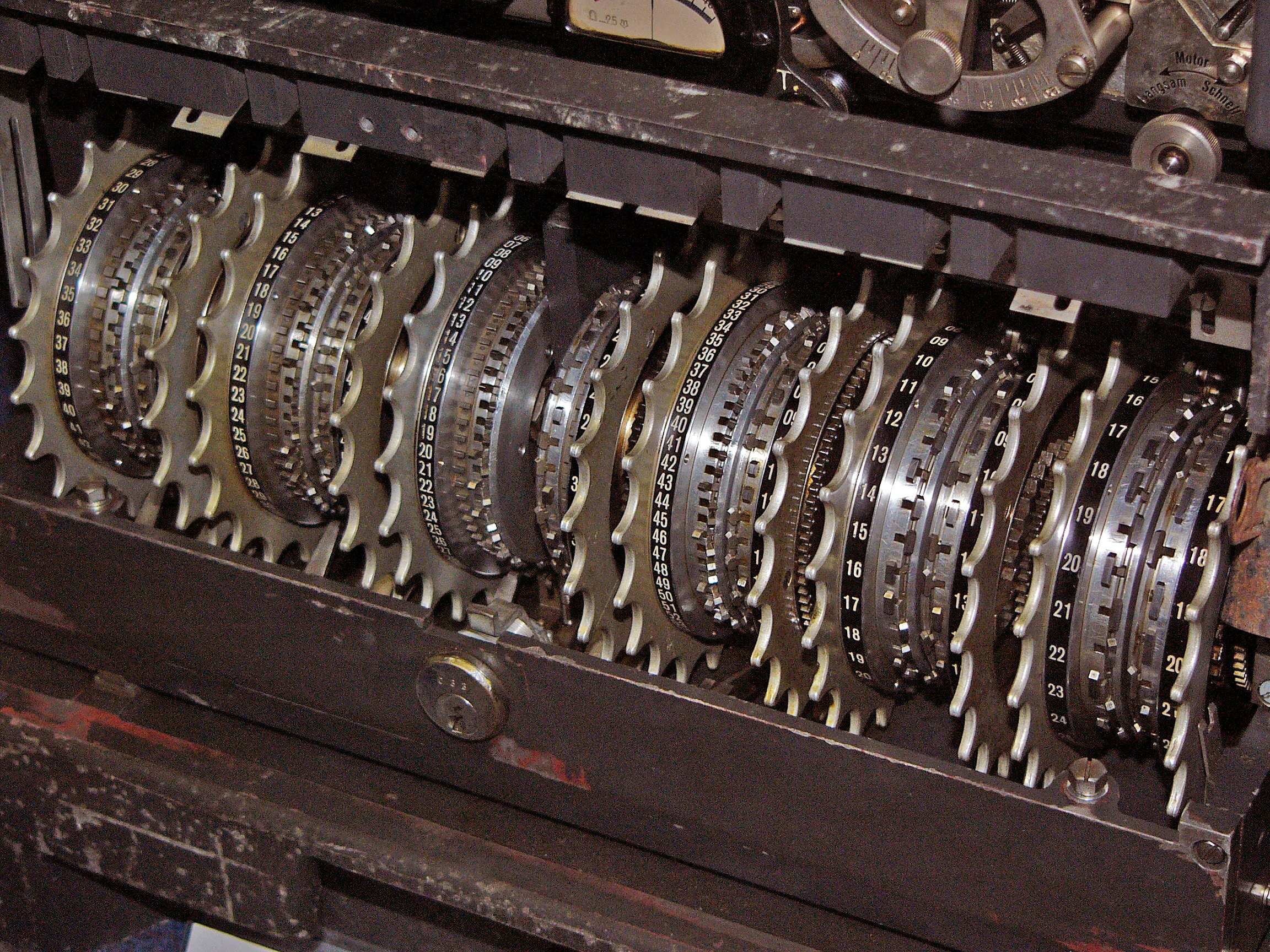
Bombe
The bombe () was an electro-mechanical device used by British cryptologists to help decipher German Enigma-machine-encrypted secret messages during World War II. The US Navy and US Army later produced their own machines to the same functional specification, albeit engineered differently both from each other and from Polish and British bombes. The British bombe was developed from a device known as the " bomba" ( pl, bomba kryptologiczna), which had been designed in Poland at the Biuro Szyfrów (Cipher Bureau) by cryptologist Marian Rejewski, who had been breaking German Enigma messages for the previous seven years, using it and earlier machines. The initial design of the British bombe was produced in 1939 at the UK Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park by Alan Turing, with an important refinement devised in 1940 by Gordon Welchman. The engineering design and construction was the work of Harold Keen of the British Tabulating Machine Company. The first bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
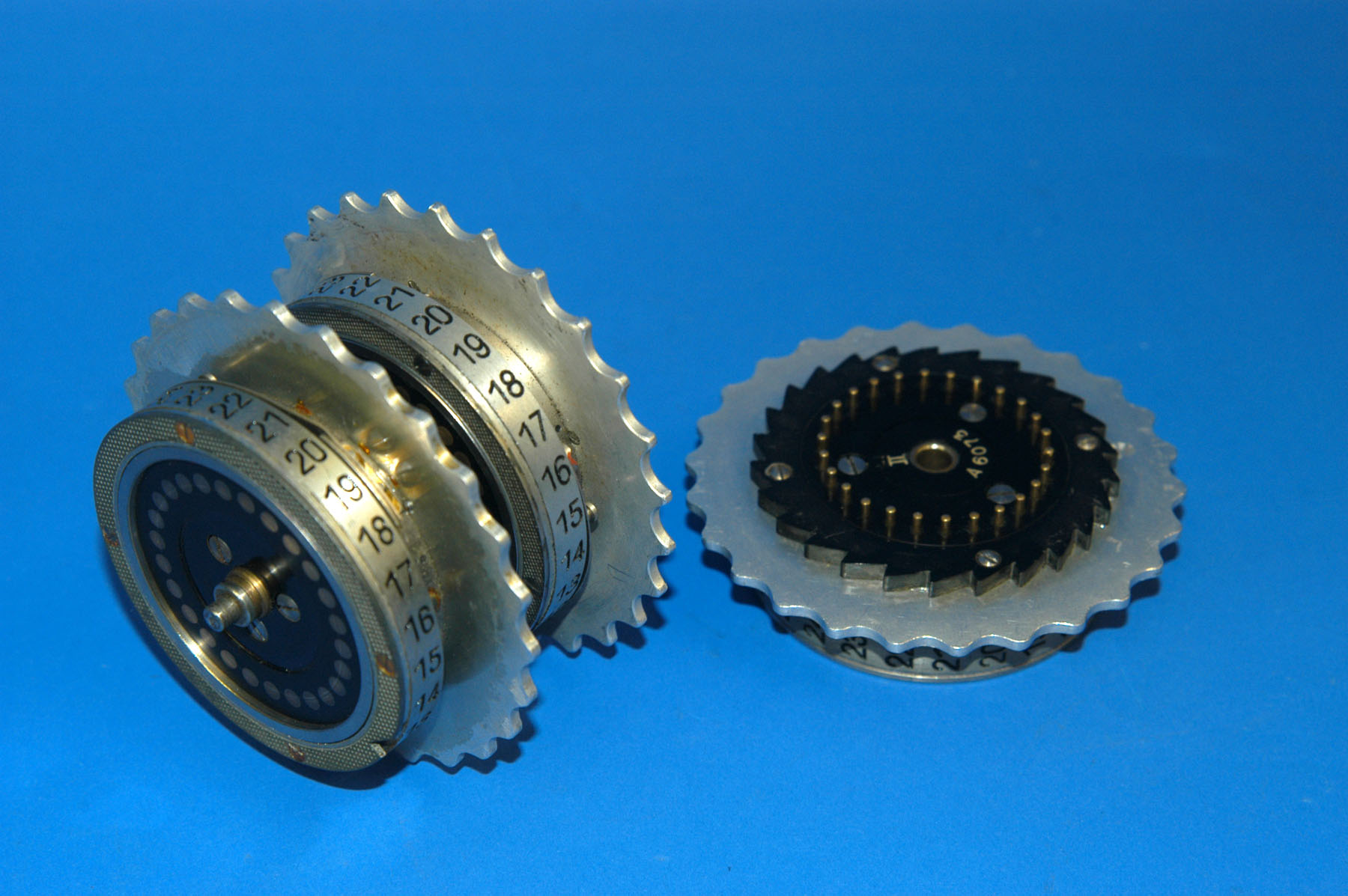
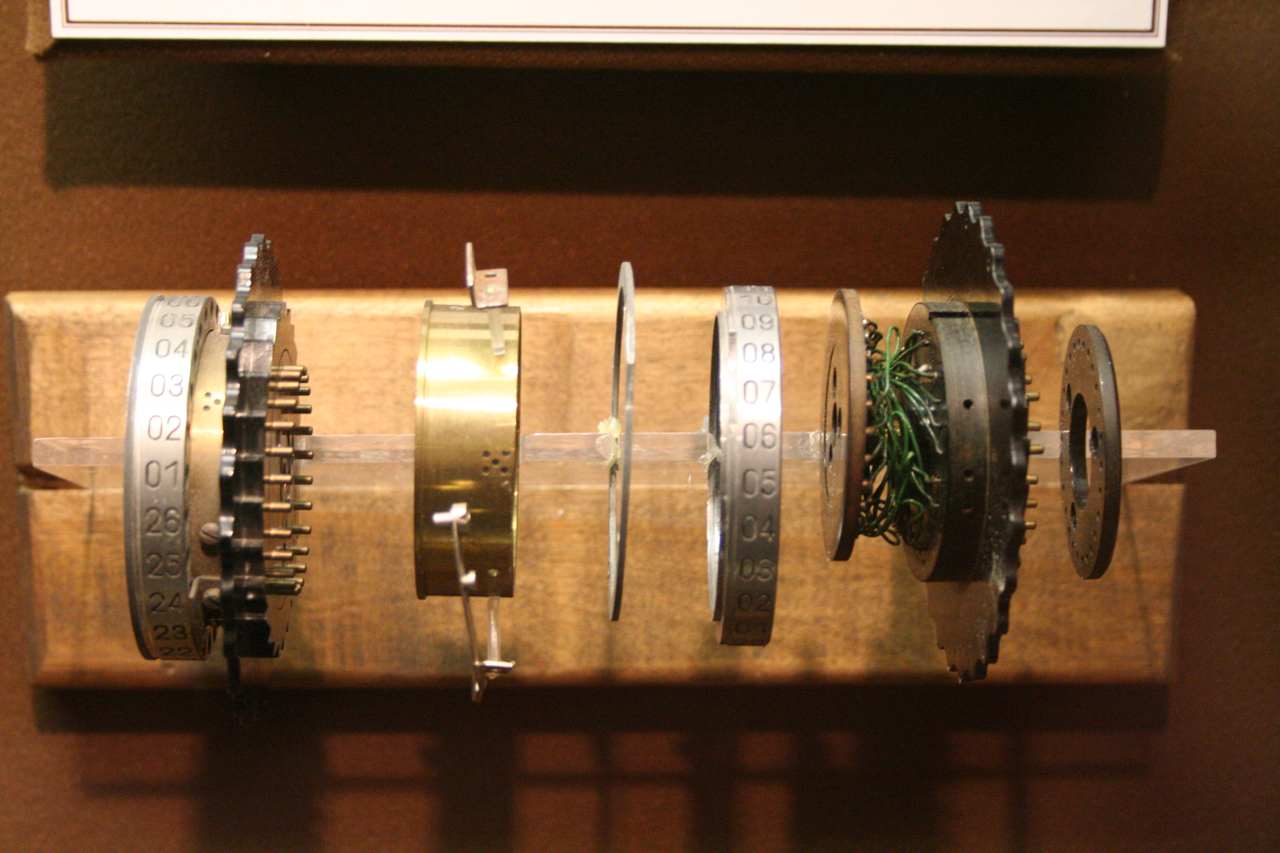
Wheels Of The Enigma
This article contains technical details about the rotors of the Enigma machine. Understanding the way the machine encrypts requires taking into account the current position of each rotor, the ring setting and its internal wiring. Physical design of rotors Image:Enigma-rotor-pin-contacts.jpg, The right side of a rotor, showing the pin electrical contacts. The Roman numeral V identifies the wiring of the rotor. Image:Enigma-rotor-flat-contacts.jpg, The left side of an Enigma rotor, showing the flat (plate) electrical contacts. A single turnover notch is visible on the left edge of the rotor. Rotor electrical view No letter can map to itself, a cryptographic weakness caused by the same wires being used for forwards and backwards legs. Rotor offset The effect of rotation on the rotors can be demonstrated with some examples. As an example, let us take rotor type I of Enigma I (see table below) without any ring setting offset. It can be seen that an is encoded as an , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerzy Różycki
Jerzy Witold Różycki (; Vilshana, Ukraine, 24 July 1909 – 9 January 1942, Mediterranean Sea, near the Balearic Islands) was a Polish mathematician and cryptologist who worked at breaking German Enigma-machine ciphers before and during World War II. Life Różycki was born in what is now Ukraine, the fourth and youngest child of Zygmunt Różycki, a pharmacist and graduate of Saint Petersburg University, and Wanda, née Benita. He attended a Polish school in Kyiv before moving with his family to Poland in 1918. In 1926 he completed secondary school at Wyszków on eastern Poland's Bug River. Różycki studied mathematics from 1927 to 1932 in western Poland, at Poznań University's Mathematics Institute, graduating with a master's degree on February 19, 1932. He would later earn a second master's degree from Poznań University, in geography, on December 13, 1937. In 1929, while still a student, Różycki, proficient in German, was one of twenty-odd Poznań University mathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic security systems and gain access to the contents of encrypted messages, even if the cryptographic key is unknown. In addition to mathematical analysis of cryptographic algorithms, cryptanalysis includes the study of side-channel attacks that do not target weaknesses in the cryptographic algorithms themselves, but instead exploit weaknesses in their implementation. Even though the goal has been the same, the methods and techniques of cryptanalysis have changed drastically through the history of cryptography, adapting to increasing cryptographic complexity, ranging from the pen-and-paper methods of the past, through machines like the British Bombes and Colossus computers at Bletchley Park in World War II, to the mathematically advanced comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conel Hugh O'Donel Alexander
Conel Hugh O'Donel Alexander (19 April 1909 – 15 February 1974), known as Hugh Alexander and C. H. O'D. Alexander, was an Irish-born British cryptanalyst, chess player, and chess writer. He worked on the German Enigma machine at Bletchley Park during the Second World War, and was later the head of the cryptanalysis division at GCHQ for 25 years. He was twice British chess champion and earned the title of International Master. Early life Hugh Alexander was born into an Anglo-Irish family on 19 April 1909 in Cork, Ireland, the eldest child of Conel William Long Alexander, an engineering professor at University College, Cork (UCC), and Hilda Barbara Bennett.Harry Golombek, revised by Ralph Erskine, "Alexander, (Conel) Hugh O'Donel (1909-1974), chess player and cryptanalyst" in the Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, 2004 His father died in 1920 (during the Irish War of Independence), and the family moved to Birmingham, England, where he attended King Edw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |