|
Bakers Pit
Bakers Pit is a phreatic maze cave system near Buckfastleigh, Devon, England. It was first opened in 1847 by quarrying activities. Bakers Pit is entered via a vertical descent of 16 metres. It has of passage contained within an area of and a small stream, flowing to the River Dart, that is still actively developing the cave. It was once connected to Reeds cave, however, only "voice" connection is currently possible, and only in a few locations. Connections between the two systems have been filled in with concrete to protect the beautiful formations in the Reeds cave. The cave was much frequented between the wars by local people during which time many of the calcite formations were destroyed, although some formations have now naturally regenerated. In the early 1960s an upper series was discovered significantly extending the known cave by as much as 50 per cent by climbing a vertical slot in the roof. This extension is better known as the Plymouth Extension and this area conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buckfastleigh
Buckfastleigh is a market town and civil parish in Devon, England situated beside the Devon Expressway ( A38) at the edge of the Dartmoor National Park. It is part of Teignbridge and, for ecclesiastical purposes, lies within the Totnes Deanery. It is 18 miles (29 km) east-northeast of Plymouth, 20 miles (32 km) southwest of Exeter and has a population of 3,661. It is a centre of tourism and is home to Buckfast Abbey, the South Devon Railway, the Buckfastleigh Butterfly Farm and Otter Sanctuary, the Tomb of Squire Richard Cabell and The Valiant Soldier. With 13 letters, Buckfastleigh is one of the longest place names in England with no repeated letters, tied with Buslingthorpe, Leeds and Buslingthorpe, Lincolnshire, but exceeded by Bricklehampton in Worcestershire with 14 letters. Geography Geographically, Buckfastleigh straddles the confluence of two small streams from Dartmoor which feed into the River Dart just to the east of the town. About one mile to the north lies Buckf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is a coastal county with cliffs and sandy beaches. Home to the largest open space in southern England, Dartmoor (), the county is predominately rural and has a relatively low population density for an English county. The county is bordered by Somerset to the north east, Dorset to the east, and Cornwall to the west. The county is split into the non-metropolitan districts of East Devon, Mid Devon, North Devon, South Hams, Teignbridge, Torridge, West Devon, Exeter, and the unitary authority areas of Plymouth, and Torbay. Combined as a ceremonial county, Devon's area is and its population is about 1.2 million. Devon derives its name from Dumnonia (the shift from ''m'' to ''v'' is a typical Celtic consonant shift). During the Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phreatic
''Phreatic'' is a term used in hydrology to refer to aquifers, in speleology to refer to cave passages, and in volcanology to refer to a type of volcanic eruption. Hydrology The term phreatic (the word originates from the Greek , meaning "well" or "spring") is used in hydrology and the earth sciences to refer to matters relating to ground water (an aquifer) below the water table. The term 'phreatic surface' indicates the location where the pore water pressure is under atmospheric conditions (i.e. the pressure head is zero). This surface normally coincides with the water table. The slope of the phreatic surface is assumed to indicate the direction of ground water movement in an unconfined aquifer. The phreatic zone, below the phreatic surface where rock and soil is saturated with water, is the counterpart of the vadose zone, or unsaturated zone, above. Unconfined aquifers are also referred to as phreatic aquifers because their upper boundary is provided by the phreatic surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorgani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Dart
The River Dart is a river in Devon, England, that rises high on Dartmoor and flows for to the sea at Dartmouth. Name Most hydronyms in England derive from the Brythonic language (from which the river's subsequent names ultimately derive from an original Celtic etymology. As the lower stretches of the river are still covered in ancient oak woodlands, it is accepted that the first element derives from *Dar-, meaning oak (derow'', Welsh ''derw''). However the second element (evident in the hard consonantal termination of ''Dar-t'') is less certain, with postulated etymologies from ''Darwent'' / ''Derventio'' (Sacred place of Oak) or ''Darnant'' / ''Darant'' (Oak stream). The Ravenna Cosmography records a number of Latinised names for the area, ''Devionisso Statio'' and ''Deventiasteno'' may represent corrupted doublets of a ''Statio'' (Station) on a river named ''Derventio''. Although the name ''Derventio'' is otherwise unattested for the river, it is an established etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reeds Cave
Reed's cave is a cave in Higher Kiln Quarry near Buckfastleigh, Dartmoor, Devon. It has many formations including the unique Little Man formation, which is beyond Easter Chamber. Devon's only true troglobite collembolan ''Pseudosinella dobati'' is recorded from this cave. People are generally not allowed to enter Reed's Cave, but some entries are permitted during the summer months. Reed's Cave was once connected to Bakers pit but the connection has been filled in with concrete. Because of entry restrictions, the cave has become an important roosting site for Greater Horseshoe Bats. Easter Chamber Near the entrance, there is a long crawl followed by a squeeze that leads to a grotto followed by Easter Chamber. Easter Chamber has many boulders and a few pools and formations. From here, some passages lead to the "little man" formation Formation may refer to: Linguistics * Back-formation, the process of creating a new lexeme by removing or affixes * Word formation, the crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
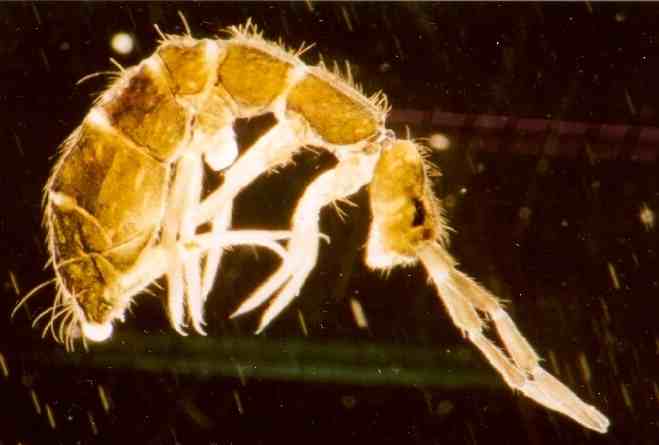
Collembola
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called Entognatha because they have internal mouthparts, they do not appear to be any more closely related to one another than they are to all insects, which have external mouthparts. Collembolans are omnivorous, free-living organisms that prefer moist conditions. They do not directly engage in the decomposition of organic matter, but contribute to it indirectly through the fragmentation of organic matter and the control of soil microbial communities. The word ''Collembola'' is from the ancient Greek "glue" and "peg"; this name was given due to the existence of the collophore, which was previously thought to stick to surfaces to stabilize the creature. Some DNA sequence studies suggest that Collembola represent a separate evolutionary line fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |