|
Badejo Field
Badejo Field is an offshore oil field in Brazil. It is a mature oil field located in the southwest part of the Campos Basin off the coast. Above of it is laying partly the Membro Siri (sometimes referred just as Siri) extra heavy crude oil field with and 12.8° API gravity. Oil was discovered in the Membro Siri reservoir in 1975, but was considered uneconomical to develop this time. In 2008 the FPSO A floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) unit is a floating vessel used by the offshore oil and gas industry for the production and processing of hydrocarbons, and for the storage of oil. An FPSO vessel is designed to receive ... '' Petrojarl Cidade de Rio das Ostras'' started test production of the Siri crude. Part of the process equipment on the FPSO is an electrostatic coalescer with the VIEC technology from Hamworthy. The process system was delivered by Expro. It consists of two separator stages and the electrostatic coalescer. Using high processi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the seventh most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 States of Brazil, states and the Federal District (Brazil), Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese language, Portuguese as an List of territorial entities where Portuguese is an official language, official language and the only one in the Americas; one of the most Multiculturalism, multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass Immigration to Brazil, immigration from around the world; and the most populous Catholic Church by country, Roman Catholic-majority country. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a Coastline of Brazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campos Basin
The Campos Basin is one of 12 coastal sedimentary basins of Brazil. It spans both onshore and offshore parts of the South Atlantic with the onshore part located near Rio de Janeiro. The basin originated in Neocomian stage of the Cretaceous period 145–130 million years ago during the breakup of Gondwana. It has a total area of about , with the onshore portion small at only . Etymology The basin is named after the Campos dos Goytacazes city. Description The Campos Basin is bound on the south by the Cabo Frio High, separating the basin from the Santos Basin and on the north by the Vitória High, forming the boundary with the Espírito Santo Basin. Campos Basin contains the Paraiba do Sul River delta. Tectonic history The South Atlantic margin developed on Archean stable cratons consisting of hard and resistant rocks and partly on the Neoproterozoic mobile belts composed of less resistant metamorphic rocks.Clemente, 2013, p.3 The Precambrian basement of the Santos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
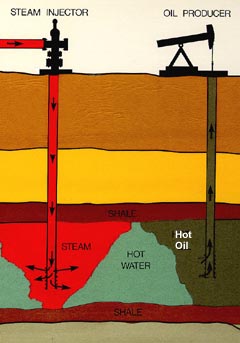
Heavy Crude Oil
Heavy crude oil (or extra heavy crude oil) is highly-viscous oil that cannot easily flow from production wells under normal reservoir conditions. It is referred to as "heavy" because its density or specific gravity is higher than that of light crude oil. Heavy crude oil has been defined as any liquid petroleum with an API gravity less than 20°. Physical properties that differ between heavy crude oils and lighter grades include higher viscosity and specific gravity, as well as higher molecular weight hydrocarbon composition. In 2010, the World Energy Council defined extra heavy oil as crude oil having a gravity of less than 10° and a reservoir viscosity of more than 10,000 centipoises. When reservoir viscosity measurements are not available, extra-heavy oil is considered by the WEC to have a lower limit of 4° API. In other words, oil with a density greater than 1000 kg/m3 (or a specific gravity greater than 1) and a reservoir viscosity of more than 10,000 centipois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
API Gravity
The American Petroleum Institute gravity, or API gravity, is a measure of how heavy or light a petroleum liquid is compared to water: if its API gravity is greater than 10, it is lighter and floats on water; if less than 10, it is heavier and sinks. API gravity is thus an inverse measure of a petroleum liquid's density relative to that of water (also known as specific gravity). It is used to compare densities of petroleum liquids. For example, if one petroleum liquid is less dense than another, it has a greater API gravity. Although API gravity is mathematically a dimensionless quantity (see the formula below), it is referred to as being in 'degrees'. API gravity is graduated in degrees on a hydrometer instrument. API gravity values of most petroleum liquids fall between 10 and 70 degrees. In 1916, the U.S. National Bureau of Standards accepted the Baumé scale, which had been developed in France in 1768, as the U.S. standard for measuring the specific gravity of liquids less den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
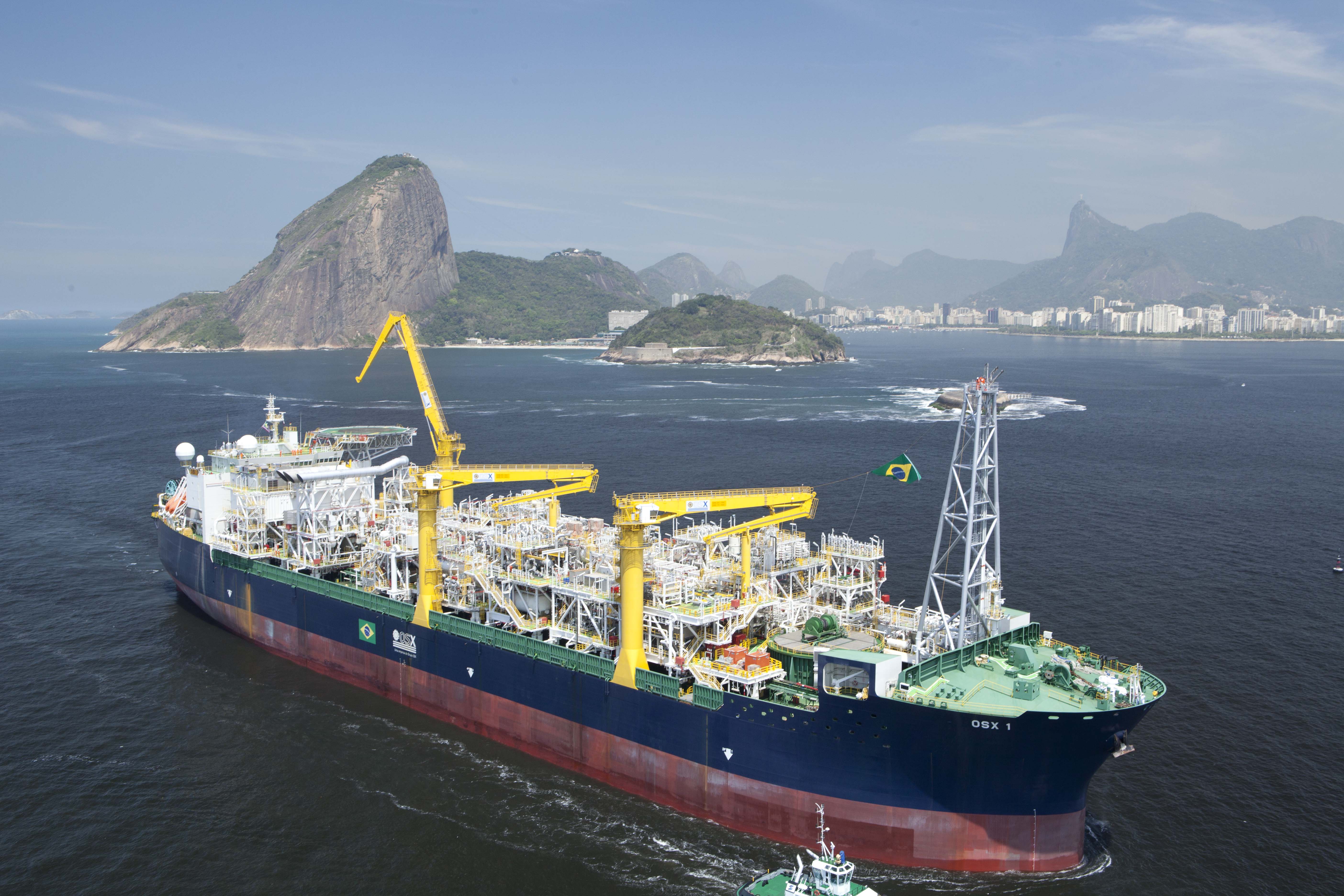
FPSO
A floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) unit is a floating vessel used by the offshore oil and gas industry for the production and processing of hydrocarbons, and for the storage of oil. An FPSO vessel is designed to receive hydrocarbons produced by itself or from nearby platforms or subsea template, process them, and store oil until it can be offloaded onto a tanker or, less frequently, transported through a pipeline. FPSOs are preferred in frontier offshore regions as they are easy to install, and do not require a local pipeline infrastructure to export oil. FPSOs can be a conversion of an oil tanker (like the ''Seawise Giant'') or can be a vessel built specially for the application. A vessel used only to store oil (without processing it) is referred to as a floating storage and offloading (FSO) vessel. The first of a related type, floating liquefied natural gas vessels, went into service in 2016. Types FPSOs are classified into the following types. * F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrojarl Cidade De Rio Das Ostras
Teekay Petrojarl was the largest Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) operator in the North Sea with a daily production of 339,000 barrels of oil A barrel is one of several units of volume applied in various contexts; there are dry barrels, fluid barrels (such as the U.K. beer barrel and U.S. beer barrel), oil barrels, and so forth. For historical reasons the volumes of some barrel units ... per day and a storage capacity of of crude oil. Teekay Petrojarl operated five FPSO vessels, two shuttle tankers and one storage oil tanker, tanker. It was owned by Teekay, a large operator of tankers until purchased by Brookfield Asset Management, becoming Altera Infrastructure. Operations History Teekay Petrojarl started off as Golar Nor Offshore and was part of Petroleum Geo-Services (PGS) in 1998 when it acquired Golar-Nor and two Floating Production Storage and Offloading, FPSO vessels, Petrojarl I and Foinaven oilfield, Petrojarl Foinaven. Within a year two more ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)
