|
BL 9.2-inch Mk IX – X Naval Gun
The BL 9.2-inch Mk IX and Mk X gunsMk IX = Mark 9, Mk X = Mark 10. Britain used Roman numerals to denote Marks (models) of ordnance until after World War II. Hence these were the ninth and tenth models of BL 9.2-inch gun. were British breech loading guns of 46.7 calibre, in service from 1899 to the 1950s as naval and coast defence guns. They had possibly the longest, most varied and successful service history of any British heavy ordnance. History The Mk IX/X guns succeeded the BL 9.2-inch Mk VIII naval gun and increased the bore length from 40 to 46.7 calibres, increasing the muzzle velocity from . The Mk IX was designed as a coast defence gun, with a three-motion breech. Only fourteen were built and the Mk X, introduced in 1900 and incorporating a single-motion breech and changed rifling, succeeded them. As coastal artillery, the Mk X remained in service in Britain until 1956, and in Portugal until 1998. A total of 284 of the Mark X version were built by Vickers, of whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakneck Battery
Breakneck Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located on Ministry of Defence property at the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, north of Lord Airey's Battery. It is one of a dozen batteries in Gibraltar that had 9.2-inch (233.7 mm) guns installed around the turn of the twentieth century. The emplacement features a 9.2-inch Mark X breech-loading gun on a Mark V mounting. The battery was refurbished by 10 Signal Regiment in 2012 and 2016 whilst being on Ceremonial duties whilst the Gibraltar Regiment where on exercise and is one of three surviving 9.2-inch gun emplacements at the Upper Ridge of the Rock of Gibraltar. By the late twentieth century, the 9.2-inch guns in Gibraltar, Bermuda (also known affectionately as "the Rock", and the former site of a Royal Naval Dockyard, and once considered "the Gibraltar of the West"), Portugal, South Africa, and Australia were the remaining examples of an emplacement that at one point had b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Cruiser Georgios Averof
''Georgios Averof'' ( el, Θ/Κ Γεώργιος Αβέρωφ) is a modified armored cruiser built in Italy for the Royal Hellenic Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. The ship served as the Greek flagship during most of the first half of the century. Although popularly known as a battleship () in Greek, she is in fact an armored cruiser (), the only ship of this type still in existence. The ship was initially ordered by the Italian Regia Marina, but budgetary constraints led Italy to offer it for sale to international customers. With the bequest of the wealthy benefactor George Averoff as down payment, Greece acquired the ship in 1909. Launched in 1910, ''Averof'' arrived in Greece in September 1911. The most modern warship in the Aegean at the time, she served as the flagship of admiral Pavlos Kountouriotis in the First Balkan War, and played a major role in the establishment of Greek predominance over the Ottoman Navy and the incorporation of many Aegean islands to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elswick Ordnance Company
The Elswick Ordnance Company (sometimes referred to as Elswick Ordnance Works, but usually as "EOC") was a British armaments manufacturing company of the late 19th and early 20th century History Originally created in 1859 to separate William Armstrong's armaments business from his other business interests, to avoid a conflict of interest as Armstrong was then Engineer of Rifled Ordnance for the War Office and the company's main customer was the British Government. Armstrong held no financial interest in the company until 1864 when he left Government service, and Elswick Ordnance was re-united with the main Armstrong businesses to form Sir W.G. Armstrong & Company. EOC was then the armaments branch of W.G. Armstrong & Company and later of Armstrong Whitworth. EOC's main customer in its early years was the British Government, but the Government abandoned "Armstrong guns" in the mid-1860s due to dissatisfaction with Armstrong's breech mechanism, and instead built its own rifled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M15-class Monitor
The ''M15'' class comprised fourteen monitors of the Royal Navy, all built and launched during 1915. Design The ships of this class were ordered in March, 1915, as part of the Emergency War Programme of ship construction. They were designed to use the 9.2 inch Mk VI gun turrets removed from the and the Mk X turrets held in stock for the and s. This resulted in the first four of the class, which were built by William Gray & Company of Hartlepool, receiving the Mk X mounting. The remaining ten ships, all built by Sir Raylton Dixon & Co., Middlesbrough, all received the Mk VI mounting. During September 1915, the 9.2 inch guns of HMS ''M24'', ''M25'', ''M26'' and ''M27'' were removed for use as artillery. These were replaced by 7.5-inch guns. ''M24'' and ''M25'' received the spare guns reserved for the recently sunk pre-dreadnought battleship , ''M26'' received one of ''Swiftsure''s spare guns. ''M27'' received 6-inch (M27) guns. ''M21'' and ''M23'' also had th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Edward VII-class Battleship
The ''King Edward VII'' class was a class of eight pre-dreadnought battleships launched by the Royal Navy between 1903 and 1905. The class comprised , the lead ship, , , , , , , and . They marked the first major development of the basic pre-dreadnought type that had been developed with the type of the mid-1890s, all of which had been designed by the Director of Naval Construction, William Henry White, with the primary innovation being the adoption of a heavy secondary battery of four guns to supplement the standard main battery of four guns. The ''King Edward VII''s were among the last pre-dreadnoughts built for the Royal Navy before the construction and launch of the revolutionary battleship HMS ''Dreadnought'' in 1906, which immediately rendered them obsolescent. The ships served with the Atlantic Fleet from 1905 to 1907, when they were transferred to the Channel Fleet, though this service lasted only until 1908–1909, when they were reassigned to the Home Fleet. Dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
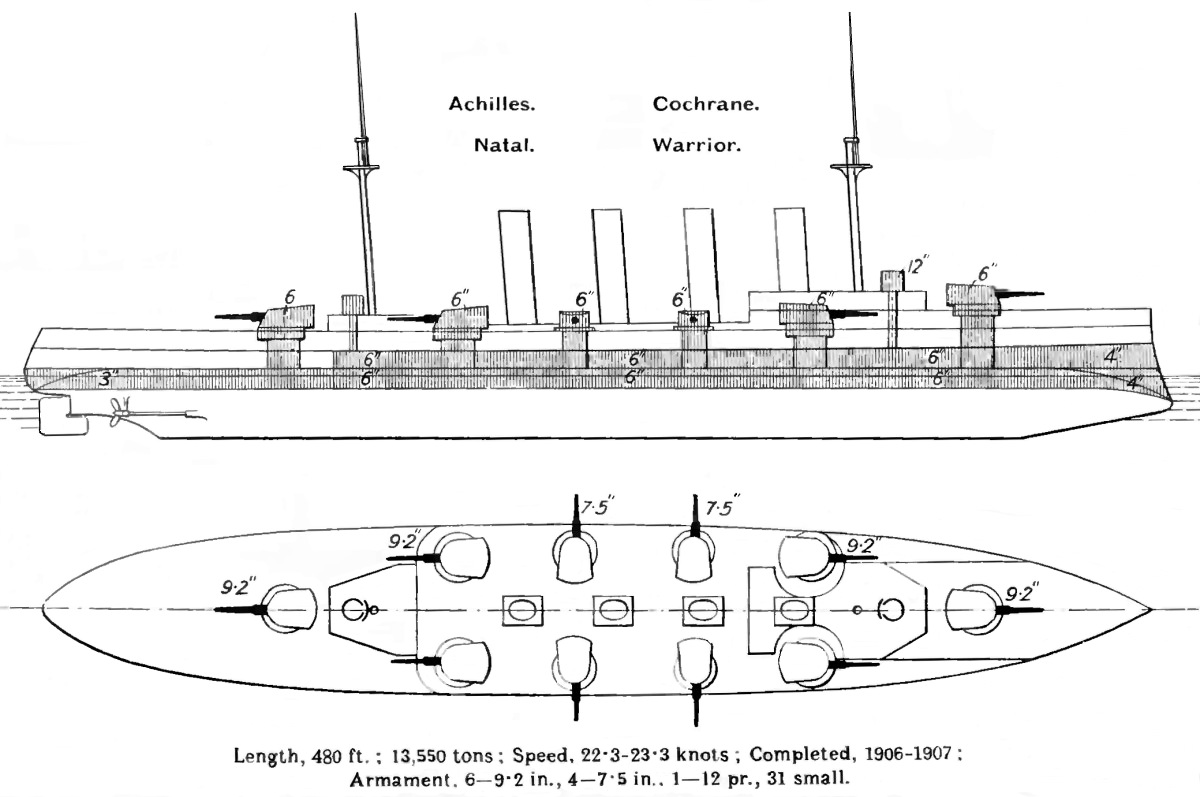
Warrior-class Cruiser
The ''Warrior'' class consisted of four armoured cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. After commissioning, all four sister ships were assigned to the Channel and Home Fleets until 1913 when was transferred to the Mediterranean Fleet. After the start of World War I in August 1914, ''Warrior'' participated in the pursuit of the German battlecruiser and light cruiser and her three sisters were assigned to the 2nd Cruiser Squadron of the Grand Fleet. ''Warrior'' joined the 1st Cruiser Squadron of the Grand Fleet in late 1914. Neither squadron participated in any of the naval battles in the North Sea in 1915. was destroyed by a magazine explosion in late 1915 and only two of the ships participated in the Battle of Jutland in 1916. was not engaged during the battle, but ''Warrior'' was heavily damaged and sank the following morning. was assigned to blockade duty after the battle and sank a German commerce raider in early 1917. Both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Edinburgh-class Cruiser
The ''Duke of Edinburgh''-class cruiser was a class of two armoured cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. They were the first British armoured cruisers designed to work with the battlefleet rather than protect merchant shipping. After commissioning, they were assigned to the Atlantic, Channel and Home Fleets until 1913 when they were transferred to the Mediterranean Fleet. After the start of World War I in August 1914, the sister ships participated in the pursuit of the German battlecruiser and light cruiser . After the German ships reached their refuge in Ottoman Turkey, the ships were ordered to the Red Sea for convoy escort duties. They captured three German merchant ships before they returned to home at the end of the year. The sisters participated in the Battle of Jutland in May 1916 where was sunk with all hands. spent the next year on blockade duties in the North Sea before she was transferred to the Atlantic Ocean on convo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
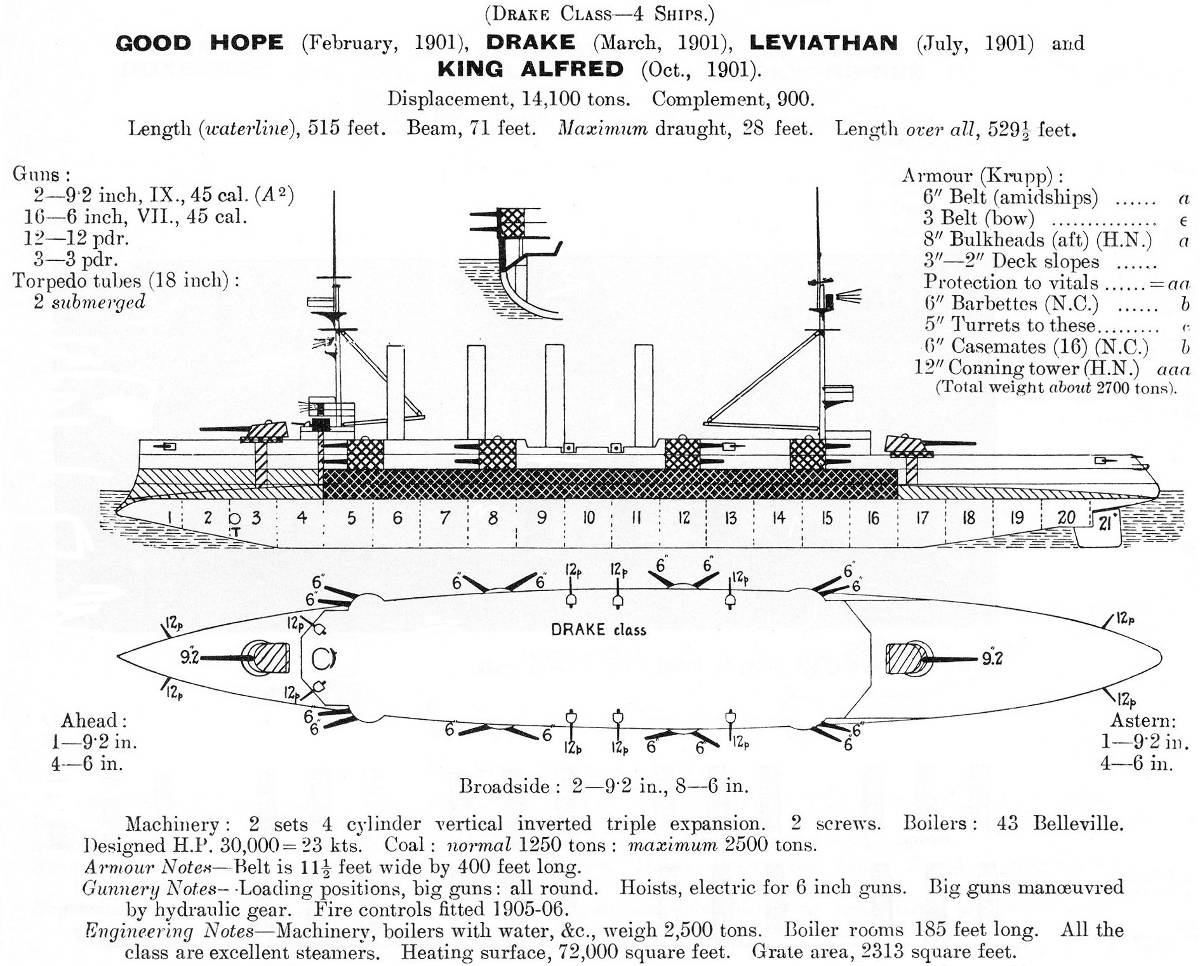
Drake-class Cruiser
The ''Drake'' class was a four-ship class of armoured cruisers built around 1900 for the Royal Navy. Design and description The ''Drake'' class were enlarged and improved versions of the designed by Sir William White, Chief Constructor of the Royal Navy, to counter the new French armoured cruiser . The ships had an overall length of , a beam of and a deep draught of . They displaced and proved to be good seaboats in service. Their crew consisted of 900 officers and other ranks. The ships were powered by two 4-cylinder triple-expansion steam engines, each driving one shaft, using steam provided by 43 Belleville boilers. The engines produced a total of and the ''Drake''s easily reached their designed speed of .Chesneau & Kolesnik, p. 69 They carried a maximum of of coal.Friedman 2012, p. 336 The main armament of the ''Drake''-class ships consisted of two breech-loading (BL) Mk X guns in single gun turrets, one each fore and aft of the superstructure. They fired she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cressy-class Cruiser
The ''Cressy''-class cruiser was a class of six armoured cruisers built for the Royal Navy around 1900. Their design’s incorporation of a pair of 9.2-inch guns and armoured sides served to address criticism directed against the previous — advances made possible by their 1,000 ton increase in displacement over their predecessors. The ships were notably stable, except for a susceptibility to pitching. Service Until 1908, the ships served in Home waters, the Mediterranean and the Far East. On the outbreak of the First World War ''Cressy'', ''Aboukir'', ''Hogue'', ''Bacchante'' and ''Euryalus'' formed the Seventh Cruiser Squadron. Due to the obsolescence of the ships and because they were crewed by inexperienced reservists the squadron was known as the " Live Bait Squadron". This epithet proved prophetic when ''Cressy'', ''Hogue'' and ''Aboukir'' were sunk in a single action on 22 September 1914 by the German submarine ''U-9'' near the Dutch coast. After the first cruise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |