|
BFW M.27
The BFW M.27, sometimes known as the Messerschmitt M.27, was a German two-seat sports plane with a low, cantilever wing, open cockpits and a fixed undercarriage sold in small numbers at the start of the 1930s. Development In the late 1920s and early 1930s, Willy Messerschmitt, working at '' Bayerische Flugzeugwerke'' (BFW) produced a series of low-wing sports monoplanes with either one or two seats. These were the M.19, M.23, M.27, M.31 and M.35 with the M.23, the only one with sales of much over double figures. The ''M'' stood for ''Messerschmitt''. The M.27 was a two-seater, very similar to the M.23b but with a more rounded fin and rudder assembly, a fuselage stretched by about 1,400 mm (55 in) to accommodate luggage and a new, spatted undercarriage. Pilot and passenger sat in tandem in separate open cockpits. It was successfully raced, winning the Deutschland Competition in 1932 and coming second in the Zugspitz Circuit in 1933. Nonetheless, it was not sold i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Fairing
An aircraft fairing is a structure whose primary function is to produce a smooth outline and reduce drag.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, Third Edition'', page 206. Aviation Supplies & Academics Inc, Newcastle Washington, 1997. These structures are covers for gaps and spaces between parts of an aircraft to reduce form drag and interference drag, and to improve appearance.Bingelis, Tony: ''The Sportplane Builder'', pages 261-265. Experimental Aircraft Association Aviation Foundation, 1979. Types On aircraft, fairings are commonly found on: ; Belly fairing : Also called a "ventral fairing", it is located on the underside of the fuselage between the main wings. It can also cover additional cargo storage or fuel tanks. ; Cockpit fairing : Also called a "cockpit pod", it protects the crew on ultralight trikes. Commonly made from fiberglass, it may also incorporate a windshield.Cliche, Andre: ''Ultralight Aircraft Shopper's Guide'' 8th Edition, page C-17. Cybair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-wing Aircraft
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration with a single mainplane, in contrast to a biplane or other types of multiplanes, which have multiple planes. A monoplane has inherently the highest efficiency and lowest drag of any wing configuration and is the simplest to build. However, during the early years of flight, these advantages were offset by its greater weight and lower manoeuvrability, making it relatively rare until the 1930s. Since then, the monoplane has been the most common form for a fixed-wing aircraft. Characteristics Support and weight The inherent efficiency of the monoplane is best achieved in the cantilever wing, which carries all structural forces internally. However, to fly at practical speeds the wing must be made thin, which requires a heavy structure to make it strong and stiff enough. External bracing can be used to improve structural efficiency, reducing weight and cost. For a wing of a given size, the weight reduction allows it to fly slower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BFW Aircraft
{{disambiguation ...
BFW may refer to: * Bayerische Flugzeugwerke AG, later Messerschmitt AG, German aircraft manufacturer * Bleed from Within, Scottish heavy metal band * Boiler feedwater Boiler feedwater is an essential part of boiler operations. The feed water is put into the steam drum from a feed pump. In the steam drum the feed water is then turned into steam from the heat. After the steam is used it is then dumped to the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1930s German Sport Aircraft
Year 193 ( CXCIII) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sosius and Ericius (or, less frequently, year 946 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 193 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * January 1 – Year of the Five Emperors: The Roman Senate chooses Publius Helvius Pertinax, against his will, to succeed the late Commodus as Emperor. Pertinax is forced to reorganize the handling of finances, which were wrecked under Commodus, to reestablish discipline in the Roman army, and to suspend the food programs established by Trajan, provoking the ire of the Praetorian Guard. * March 28 – Pertinax is assassinated by members of the Praetorian Guard, who storm the imperial palace. The Empire is auctioned off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
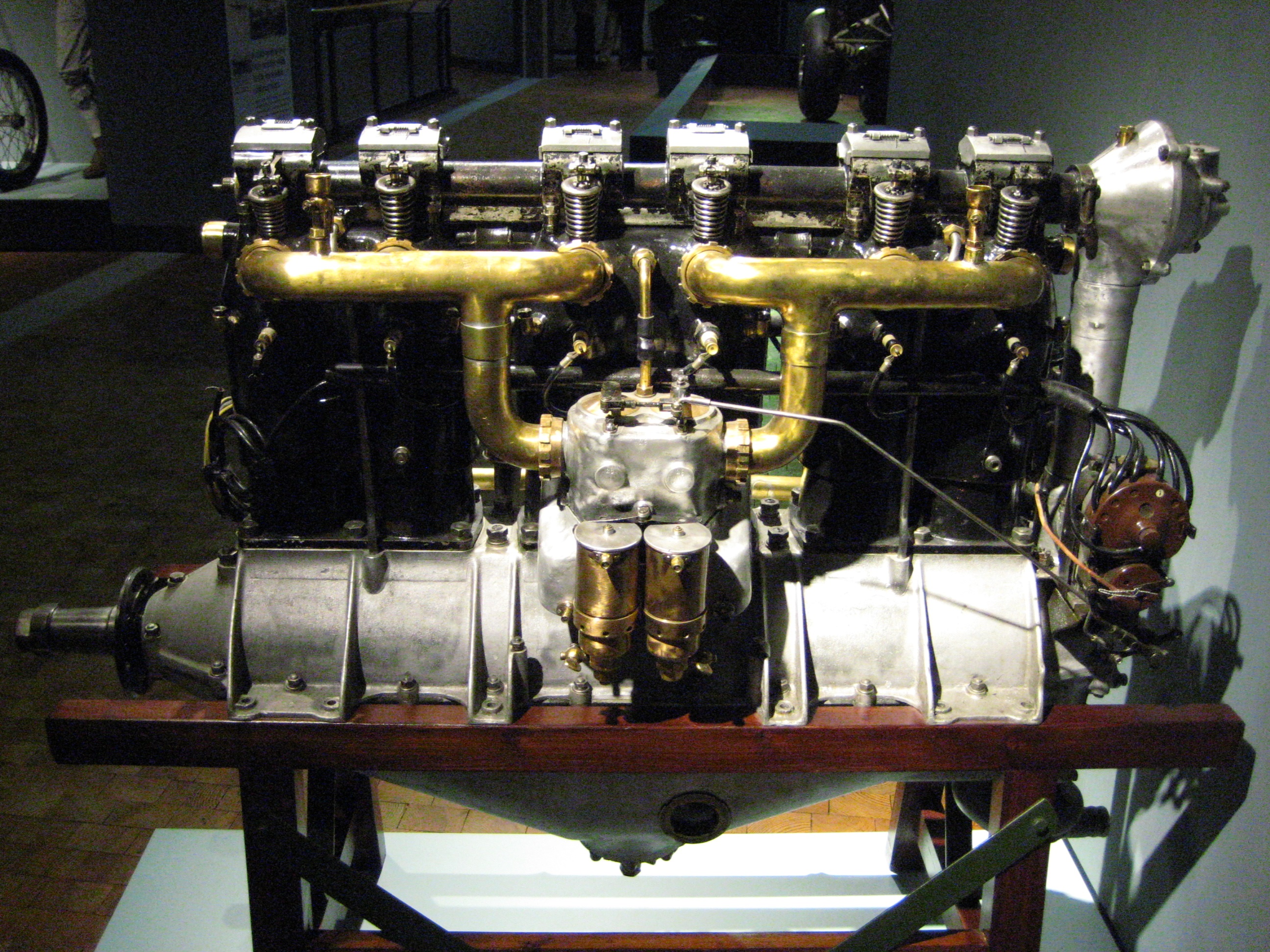
Argus As 8R
The Argus As 8 was a four-cylinder, air-cooled, inverted inline aircraft engine produced in Germany by Argus Motoren in the 1930s. Variants ;As 8A:Initial production version maximum for 5 minutes, continuous. ;As 8B:A more powerful variant developing maximum for 5 minutes, continuous. ;As 8R:A variant produced for sport aircraft, particularly for competition use, developing for take-off. Featuring: :*Increased compression ratio, from 5.36 to 5.8 :*Improved cooling by increasing the numbers of cooling fins at the cylinder head and the cylinder body :*Increasing the heat dispersing area of the pistons :*Improved crankcase and oil cooling :*Improved cylinder charging :*Modified valve timing Applications *Albatros L 100 *Albatros Al 101 *Arado L II (As 8A) *Arado L IIa (As 8R) * Baumgärtl Heliofly III *BFW M.23 * BFW M.27 * BFW M.29 *BFW M.35 * Blohm & Voss Ha 136 *Comte AC-12 Moskito *Darmstadt D-22 * DFS 40 *Focke-Wulf Fw 44 *Heinkel He 64 *Heinkel He 72 * Klemm L 25E *Klemm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inline Engine (aviation)
In aviation, an inline engine is a reciprocating engine with banks of cylinders, one behind another, rather than rows of cylinders, with each bank having any number of cylinders, although more than six is uncommon. The major reciprocating-engine alternative configuration is the radial engine, where the cylinders are placed in a circular or "star" arrangement. The term "inline" is used somewhat differently for aircraft engines than automotive engines. For automotive engines, the term ‘inline’ refers only to straight engines (those with a single bank of cylinders). But for aircraft, ‘inline’ can also refer to engines which are not of the straight configuration, such as V, H, or horizontally opposed. Inline engine configurations ;Straight: Engines with a single bank of cylinders which can be arranged at any angle but typically upright or inverted, (e.g. upright ADC Cirrus, inverted de Havilland Gipsy Major). ; V:Engines with two banks of cylinders with less than 180° betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argus As 8B
The Argus As 8 was a four-cylinder, air-cooled, inverted inline aircraft engine produced in Germany by Argus Motoren in the 1930s. Variants ;As 8A:Initial production version maximum for 5 minutes, continuous. ;As 8B:A more powerful variant developing maximum for 5 minutes, continuous. ;As 8R:A variant produced for sport aircraft, particularly for competition use, developing for take-off. Featuring: :*Increased compression ratio, from 5.36 to 5.8 :*Improved cooling by increasing the numbers of cooling fins at the cylinder head and the cylinder body :*Increasing the heat dispersing area of the pistons :*Improved crankcase and oil cooling :*Improved cylinder charging :*Modified valve timing Applications *Albatros L 100 *Albatros Al 101 *Arado L II (As 8A) *Arado L IIa (As 8R) *Baumgärtl Heliofly III *BFW M.23 *BFW M.27 *BFW M.29 *BFW M.35 * Blohm & Voss Ha 136 *Comte AC-12 Moskito * Darmstadt D-22 *DFS 40 *Focke-Wulf Fw 44 *Heinkel He 64 *Heinkel He 72 *Klemm L 25E *Klemm Kl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating type internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. It resembles a stylized star when viewed from the front, and is called a "star engine" in some other languages. The radial configuration was commonly used for aircraft engines before gas turbine engines became predominant. Engine operation Since the axes of the cylinders are coplanar, the connecting rods cannot all be directly attached to the crankshaft unless mechanically complex forked connecting rods are used, none of which have been successful. Instead, the pistons are connected to the crankshaft with a master-and-articulating-rod assembly. One piston, the uppermost one in the animation, has a master rod with a direct attachment to the crankshaft. The remaining pistons pin their connecting rods' attachments to rings around the edge of the master rod. Extra "rows" of radial cylinders can be added i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens-Halske Sh 12
The Siemens-Halske Sh 12 was a nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft built in Germany in the 1920s. First run in 1925, it was rated at 80 kW (110 hp). The Sh 12 was also produced in the United States by Ryan Aeronautical Corp. as the Ryan-Siemens 9. Applications * Albatros L 68 * Albatros L 79 * Arado S I * Arado W 2 * BFW M.21 * BFW M.27 * Bücker Bü 133 * Command-Aire 3C3-B * Lampich BL-6 * Raab-Katzenstein KL.1 * Udet U 8 * Udet U 11 Kondor * Udet U 12 * VL Sääski VL Sääski II (English: mosquito) was the first series-produced aircraft designed in Finland. The aircraft was built by the State Aircraft Factory (''Valtion lentokonetehdas'') (abbreviated either V.L. or VL) and was a two-seat, biplane, single ... * Weiss-EM-10 Ölyv * Lóczy Hungária References bungartz.nl Aircraft air-cooled radial piston engines Siemens-Halske aircraft engines 1920s aircraft piston engines {{Aircraft-engine-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutschland Competition
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its 16 constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of . It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and Czechia to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in what is now Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |