|
Byzantine Commonwealth
The term Byzantine commonwealth was coined by 20th-century historians to refer to the area where Byzantine general influence ( Byzantine liturgical and cultural tradition) was spread during the Middle Ages by the Byzantine Empire and its missionaries. This area covers approximately the modern-day countries of Greece, Cyprus, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, Serbia, Montenegro, Romania, Moldova, Ukraine, Belarus, southwestern Russia, and Georgia (known as the region of ''Eastern Orthodoxy in Europe'' or the ''Orthodox civilization''). According to Anthony Kaldellis, the Byzantines in generally did not have a ecumenical outlook, nor did they think about the notion of an panorthodox commonwealth, which he describes as "Roman Chavinism". The Obolensky model The most important treatment of the concept is a study by Dimitri Obolensky, ''The Byzantine Commonwealth''. In his book ''Six Byzantine Portraits'' he examined the life and works of six persons mentioned in ''The Byzantine Commonwealt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
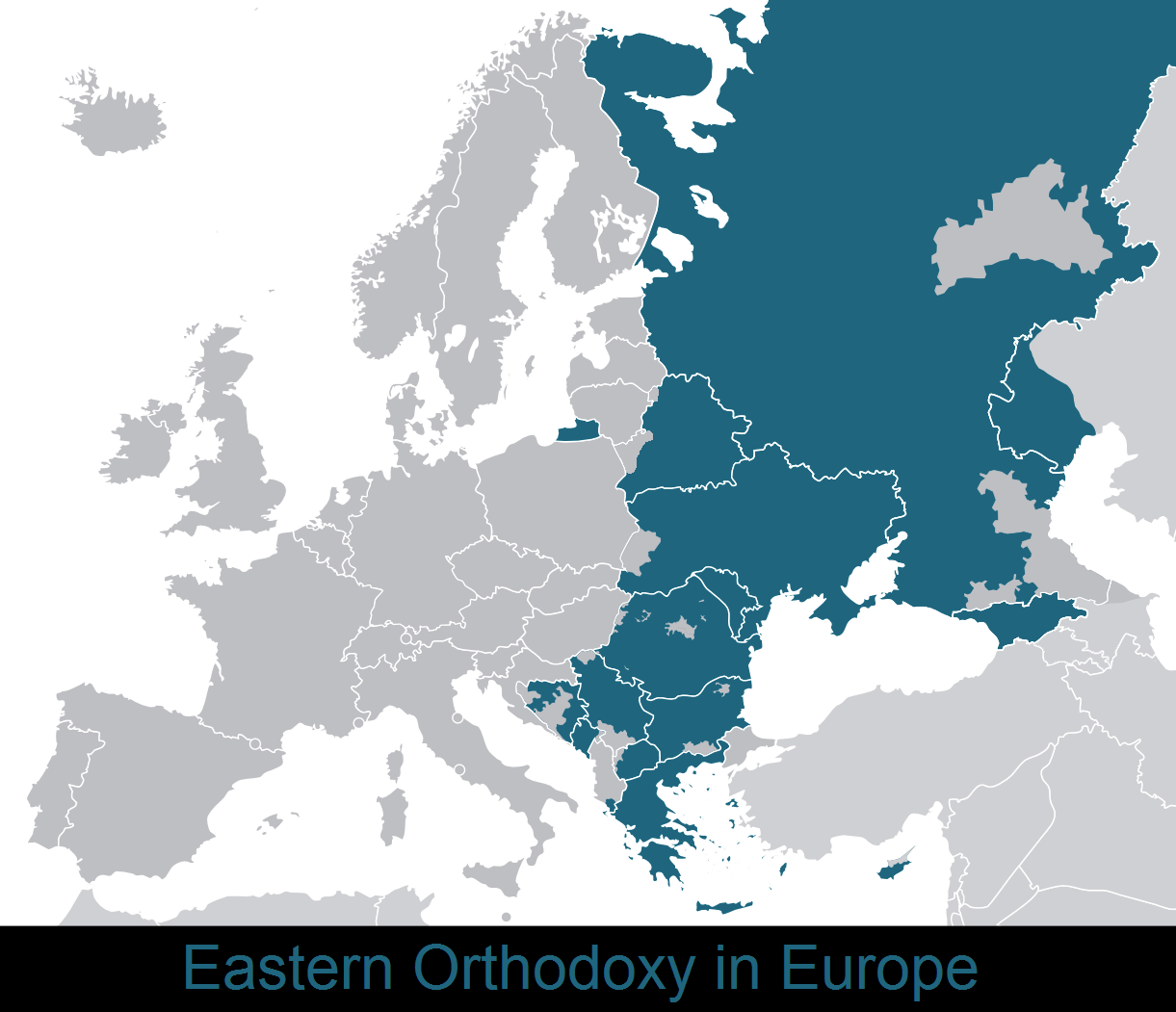
Eastern Orthodoxy In Europe
The Eastern Orthodoxy in Europe constitutes the second largest Christian denomination. European Eastern Orthodox Christians are predominantly present in Eastern and Southeastern Europe, and they are also significantly represented in diaspora throughout the Continent. The term Eastern Orthodox Europe is informally used to describe the predominantly Eastern Orthodox countries of Eastern Europe, as well as, Belarus, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Georgia, Greece, Moldova, Montenegro, Republic of North Macedonia, Romania, Russia, Serbia and Ukraine. History Almost all of Eastern Orthodox Europe became part of communist states after World War II. Eastern Orthodoxy in Orthodox majority countries *Eastern Orthodoxy in Moldova, 97.0% (2017 census) * Eastern Orthodoxy in Greece, 90% *Eastern Orthodoxy in Serbia, 84.6% (2011 census) *Eastern Orthodoxy in Romania, 81.0% (2015 census) * Eastern Orthodoxy in Georgia, 83.4% (2014 census) *Eastern Orthodoxy in Cyprus, 73.2% () [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Relations Of The Byzantine Empire
A reason for the longevity of the Byzantine Empire is how they managed their foreign relations. When excluding the Roman Empire of which the Byzantine Empire is a direct continuation of, it still stands as the longest living regime to have ruled in Europe (and second in the world only to Japan). Armed combat was the primary method with the evolved traditions of the Roman Empire, however Byzantine diplomacy which eventuated with their many treaties was used extensively as well. A lot of what we know of the world (and Europe in particular) during the Middle Ages comes from the records of Byzantine scholars, which were detailing the Empire's interactions. Byzantine and Persian-Turk relations Göktürk relations: 6th–7th centuries The Göktürks of the First Turkic Khaganate, which came to prominence in 552 CE, were the first Turkic state to use the name Türk politically. They played a major role with the Byzantine Empire's relationship with the Persian Sasanian Empire. The first co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miliana Kaimakamova
Miliana Vasileva Kaimakamova (; born 22 January 1951) is a Bulgarian medieval historian, whose work on Bulgarian medieval historiography is foundational to the discipline. She is Professor of History at Sofia University. Biography Kaymakamova was born on 22 January 1951 in Smolyan.Review by Prof. Vasilka Tapkova-Zaimova . // uni-sofia.bg, July 29, 2011. Accessed July 17, 2016. In 1973 she graduated with a degree in History & Archaeology from . In 1985 she was awarded the scientific title of associate professor. From 1972 to 1979 she was an assistant professor of medieval Bulgari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succession Of The Roman Empire
The continuation, succession and revival of the Roman Empire is a running theme of the history of Europe and the Mediterranean Basin. It reflects the lasting memories of power and prestige associated with the Roman Empire itself. Several polities have claimed immediate continuity with the Roman Empire, using its name or a variation thereof as their own exclusive or non-exclusive self-description. As centuries went by and more political ruptures occurred, the idea of institutional continuity became increasingly debatable. The most enduring and significant claimants of continuation of the Roman Empire have been, in the East, the Ottoman Empire and Russian Empire which both claimed succession of the Byzantine Empire after 1453; and in the West, the Holy Roman Empire from 800 to 1806. Separately from claims of continuation, the view that the Empire had ended has led to various attempts to revive it or appropriate its legacy, notably in the case of Orthodox Russia. The vocabulary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
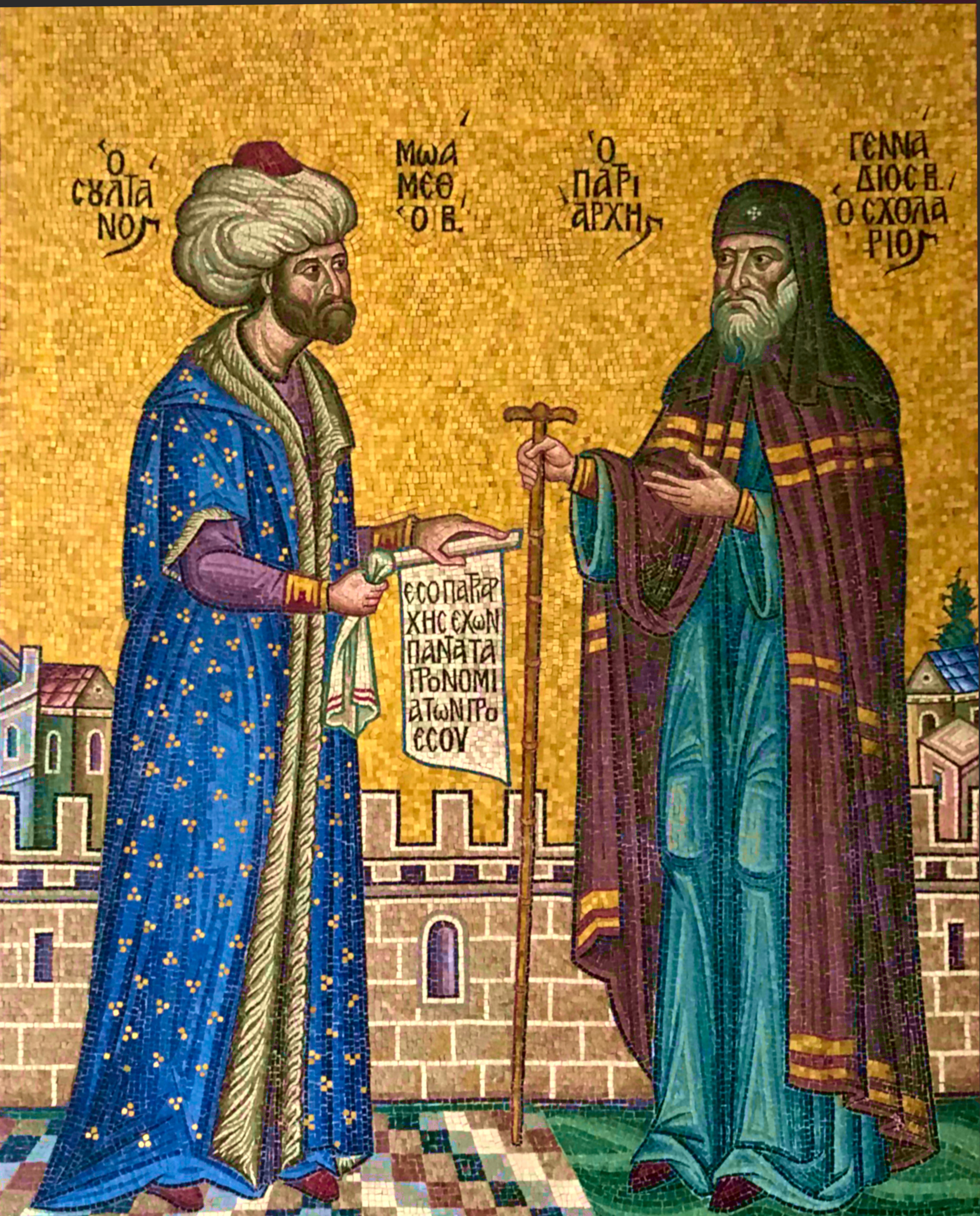
Rum Millet
Rūm millet (millet-i Rûm), or "''Roman nation''", was the name of the Eastern Orthodox Christian community in the Ottoman Empire. Despite being subordinated within the Ottoman political system, the community maintained a certain internal autonomy. Establishment and development After the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453, all Orthodox Christians were treated as a lower class of people. The Rum millet was instituted by Sultan Mehmet II who set himself to reorganise the state as the conscious heir of the East Roman Empire. The Orthodox congregation was included in a specific ethno-religious community under ''Graeco-Byzantine'' domination. Its name was derived from the former Eastern Roman (a.k.a. ''Byzantine'') subjects of the Ottoman Empire, but all Orthodox Greeks, Bulgarians, Albanians, Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians and Serbs, as well as Georgians and Middle Eastern Christians, were considered part of the same millet in spite of their differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodoxy By Country
Based on the numbers of adherents, the Eastern Orthodox Church (also known as Eastern Orthodoxy) is the second largest Christian communion in the world, after the Roman Catholic Church, with the most common estimates of baptised members being approximately 220 million. The numerous Protestant groups in the world, if taken all together, substantially outnumber the Eastern Orthodox, but they differ theologically and do not form a single communion. Overview Eastern Orthodoxy is the predominant religion in Russia (77%), where roughly half the world's Eastern Orthodox Christians live. The religion is also heavily concentrated in the rest of Eastern Europe, where it is the majority religion in Ukraine (65.4% [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Culture
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantinism
Byzantinism, or Byzantism, is the political system and culture of the Byzantine Empire, and its spiritual successors the Orthodox Christian Balkan countries of Greece and Bulgaria especially, and to a lesser extent Serbia and some other Orthodox countries in Eastern Europe like Belarus, Georgia, Russia and Ukraine.Dimiter G. Angelov, ''Byzantinism: The Imaginary and Real Heritage of Byzantium in Southeastern Europe'', in Dimitris Keridis, Ellen Elias-Bursać, Nicholas Yatromanolakis, ''New approaches to Balkan studies'', Brassey's, 2003, Google Print, p.3/ref>Angelov 2003p.11/ref> The term ''byzantinism'' itself was coined in the 19th century.Angelov 2003p.8/ref> The term has primarily negative associations, implying complexity and autocracy. This negative reputation stressed the confusing complexities of the Empire's ministries and the elaborateness of its court ceremonies. Likewise, the "Byzantine system" also suggests a penchant for intrigue, plots and assassinations and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellen Elias-Bursać
Ellen Elias-Bursać (born 1952) is an American scholar and literary translator. Specializing in South Slavic literature, she has translated numerous works from Bosnian, Croatian, and Serbian. Early life Ellen Elias was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Her parents were Peter and Marjorie (née Forbes) Elias. She has two brothers. Her aunt was Barbara Elias, a poet. She studied at the Commonwealth School in Boston, graduating in 1970. She attended Macalester College, receiving a Bachelor of Arts degree in Russian literature and language in 1974. During her undergraduate studies, she attended a study abroad programme in Yugoslavia. She worked as a freelance translator, and studied towards a master's degree at the University of Zagreb. In 1999, she received a PhD from University of Zagreb in philology; her dissertation was titled ''Augustina-Tina Ujevića prijevodi iz anglo-američke književnosti: komparativno/kontrastivna lingvo-stilistička analiza''. Career Elias-Bursać ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, Българско царство, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between the twelfth and the fourteenth centuries. The two "Bulgarian Empires" are treated not as separate entities but rather as one state that was restored after a period of Byzantine rule over its territory. First Bulgarian Empire Moesia was repeatedly invaded by both Slavs and Bulgars during the 5th, 6th and 7th centuries. In 499, the Bulgars crossed Danube and reached Thrace where on the banks of the river Tzurta (considered a tributary of Maritsa) defeated 15,000 men strong Roman army led by magister militum Aristus. In the 670s under the rule of Asparukh the Bulgars settled further south on territories of the Eastern Roman Empire in Scythia Minor near the Danube Delta in a region called Ongal and allied with the local Slavs. Their ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via local synods. The church has no central doctrinal or governmental authority analogous to the head of the Roman Catholic Church—the Pope—but the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople is recognized by them as '' primus inter pares'' ("first among equals"), which may be explained as a representative of the church. As one of the oldest surviving religious institutions in the world, the Eastern Orthodox Church has played a prominent role in the history and culture of Eastern and Southeastern Europe. The Eastern Orthodox Church officially calls itself the Orthodox Catholic Church. Eastern Orthodox theology is based on holy tradition, which incorporates the dogmatic decrees of the seven ecumenical councils, the Scriptures, and the teachin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |