|
Buša Cattle
The Buša or Busha is a breed or group of breeds of small short-horned cattle distributed in south-eastern Europe, principally in Albania and the countries of the former Yugoslavia – Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro and Serbia. Related breeds include the Gurgucke, Lekbibaj and Prespa of Albania, the Gacko of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Greek Shorthorn, the Metohija Red of Kosovo and the Rhodope Shorthorn of Bulgaria. History The Buša is a traditional breed or group of breeds of Albania and the countries of the former Yugoslavia – Bosnia, Croatia, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro and Serbia. It forms part of a larger group of related breeds including the Gurgucke, Lekbibaj and Prespa of Albania, the Gacko or Gatacko of Bosnia and Herzegovina (after the Gatačko Polje), the Greek Shorthorn, the Metohija Red of Kosovo and the Rodopi of Bulgaria. The Anatolian Black of Turkey is also related, but more distantly, as it has some zebuine herit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bijela Gora
Bijela Gora (Montenegrin Cyrillic , Бијела Гора, , lit. "White Mountain") is a karstic high plateau between 1200–1500 m on the northern side of Mount Orjen in Montenegro. At 1862 m, Velika Jastrebica is the highest summit. It bears heavy glacial traces as a huge ice cap covered it during the last ice age. Sparsely inhabited pastures and vast virgin beech-fir forests are major resources. Also, endemic Dinaric calcareous Silver Fir forests are found at Bijela Gora with rare endemic plants, such as Bosnian pine. Fauna of Bijela Gora includes brown bears, wolves, deer, boars, and a small population of chamois The chamois (''Rupicapra rupicapra'') or Alpine chamois is a species of goat-antelope native to mountains in Europe, from west to east, including the Alps, the Dinarides, the Tatra and the Carpathian Mountains, the Balkan Mountains, the Ril .... Bijela Gora is inhabited by Montenegrin tribes who belong to the Katun clans. Fir trees of Bijela Gora are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-bred
A crossbreed is an organism with purebred parents of two different breeds, varieties, or populations. ''Crossbreeding'', sometimes called "designer crossbreeding", is the process of breeding such an organism, While crossbreeding is used to maintain health and viability of organisms, irresponsible crossbreeding can also produce organisms of inferior quality or dilute a purebred gene pool to the point of extinction of a given breed of organism. A domestic animal of unknown ancestry, where the breed status of only one parent or grandparent is known, may also be called a crossbreed though the term "mixed breed" is technically more accurate. Outcrossing is a type of crossbreeding used within a purebred breed to increase the genetic diversity within the breed, particularly when there is a need to avoid inbreeding. In animal breeding, ''crossbreeds'' are crosses within a single species, while '' hybrids'' are crosses between different species. In plant breeding terminology, the term ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus (; el, Όλυμπος, Ólympos, also , ) is the highest mountain in Greece. It is part of the Olympus massif near the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea, located in the Olympus Range on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia, between the regional units of Larissa and Pieria, about southwest from Thessaloniki. Mount Olympus has 52 peaks and deep gorges. The highest peak, Mytikas (Μύτικας ''Mýtikas''), meaning "nose", rises to . It is one of the highest peaks in Europe in terms of topographic prominence. In Greek mythology, Olympus is the home of the Greek gods, on Mytikas peak. The mountain has exceptional biodiversity and rich flora. It has been a National Park, the first in Greece, since 1938. It is also a World Biosphere Reserve. Every year, thousands of visitors admire its fauna and flora, tour its slopes, and climb its peaks. Organized mountain refuges and various mountaineering and climbing routes are available. The usual starting point for cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avala
Avala ( sr-cyr, Авала, ) is a mountain in Serbia, overlooking Belgrade. It is situated in the south-eastern corner of the city and provides a great panoramic view of Belgrade, Vojvodina and Šumadija, as the surrounding area on all sides is mostly lowlands. It stands at above sea level, which means that it enters the locally defined mountain category just by . Location Avala is located south-east of downtown Belgrade. The entire area of the mountain belongs to the Belgrade City area, the majority of it being in the municipality of Voždovac, with the eastern slopes being in the municipality of Grocka, and the southernmost extension in the municipality of Sopot. It is possible that in the future the entire area of Avala will create a separate municipality of Belgrade, named Avalski Venac. Geography Avala is a low type of the Pannonian island mountain, though it is actually the northernmost mountain in Šumadija. Until 600,000 years ago, when the surrounding low area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine before draining into the Black Sea. Its drainage basin extends into nine more countries. The largest cities on the river are Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade and Bratislava, all of which are the capitals of their respective countries; the Danube passes through four capital cities, more than any other river in the world. Five more capital cities lie in the Danube's basin: Bucharest, Sofia, Zagreb, Ljubljana and Sarajevo. The fourth-largest city in its basin is Munich, the capital of Bavaria, standing on the Isar River. The Danube is the second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through much of Central and Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sava (river)
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally through Serbia, feeding into the Danube in its capital, Belgrade. The Sava forms the main northern limit of the Balkan Peninsula, and the southern edge of the Pannonian Plain. The Sava is long, including the Sava Dolinka headwater rising in Zelenci, Slovenia. It is the largest tributary of the Danube by volume of water, and second-largest after the Tisza in terms of catchment area () and length. It drains a significant portion of the Dinaric Alps region, through the major tributaries of Drina, Bosna, Kupa, Una, Vrbas, Lonja, Kolubara, Bosut and Krka. The Sava is one of the longest rivers in Europe and among the longest tributaries of another river. The population in the Sava River basin is estimated at 8,176,000, and is shared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yurino (cattle)
The Yurino ( Russian: Юpинcкaя, Yurinskaya) is a dual purpose cattle breed from the Russian Federation, particularly the Mari Republic. References Cattle breeds originating in Ukraine {{cattle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Gorbatov
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondary color (made from magenta and yellow) in the CMYK color model, and is the complementary color of cyan. Reds range from the brilliant yellow-tinged scarlet and vermillion to bluish-red crimson, and vary in shade from the pale red pink to the dark red burgundy. Red pigment made from ochre was one of the first colors used in prehistoric art. The Ancient Egyptians and Mayans colored their faces red in ceremonies; Roman generals had their bodies colored red to celebrate victories. It was also an important color in China, where it was used to color early pottery and later the gates and walls of palaces. In the Renaissance, the brilliant red costumes for the nobility and wealthy were dyed with kermes and cochineal. The 19th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simmental (cattle)
The Simmental or Swiss Fleckvieh is a Swiss breed of dual-purpose cattle. It is named after the Simmental – the valley of the Simme river – in the Bernese Oberland, in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It is reddish in colour with white markings, and is raised for both milk and meat. History European origin Among the older and most widely distributed of all breeds of cattle in the world, and recorded since the Middle Ages, the Simmental breed has contributed to the creation of several other famous European breeds, including the Montbéliarde (France), the Pezzata Rossa d'Oropa (Italy), and the Fleckvieh (Germany and Austria). Africa Namibia (1893) and South Africa (1905) were the first countries outside Europe where the breed was successfully established. Here the breed is known as Simmentaler and is mainly used for beef cattle production under suckler cow systems. The Simmentaler breeders' society is, as far as registered animals are concerned, by far the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsatellite
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. They have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA leading to high genetic diversity. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists and in genetic genealogy, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name "satellite" DNA refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying "satellite" layers of repetitive DNA. They are widely used for DNA profiling in cancer diagnosis, in kinship analysis (especially paternity testing) and in forensic identific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y-chromosomal
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes ( allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers male development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs, making it similar in size to chromosome 19. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest-evolving parts of the human genome. The human Y chromosome carries an estimated 100–200 genes, with between 45 and 73 of these being protein-coding. All single-copy Y-linked genes are hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XX ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
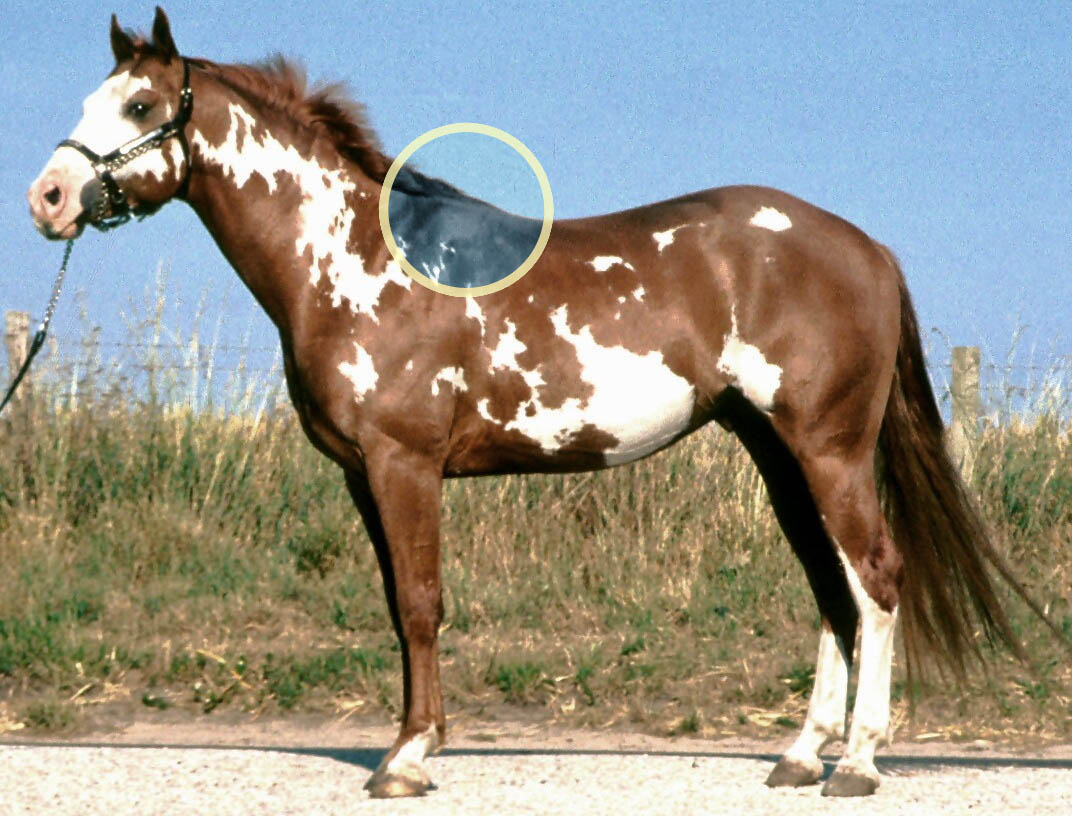
Withers
The withers is the ridge between the shoulder blades of an animal, typically a quadruped. In many species, it is the tallest point of the body. In horses and dogs, it is the standard place to measure the animal's height. In contrast, cattle are often measured to the top of the hips. The term (pronounced ) derives from Old English ''wither'' (“against”), because it is the part of a draft animal that pushes against a load. Horses The withers in horses are formed by the dorsal spinal processes of roughly the 3rd through 11th thoracic vertebrae, which are unusually long in this area. Most horses have 18 thoracic vertebrae. The processes at the withers can be more than long. Since they do not move relative to the ground as the horse's head does, the withers are used as the measuring point for the height of a horse. Horses are sometimes measured in hands – one hand is . Horse heights are extremely variable, from small pony breeds to large draft breeds. The height at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |