|
Buya, Eritrea
Buya or Buia is an archaeological site in the Danakil Depression of Eritrea. It is known for the discovery of Madam Buya, a one Myr, million-year-old fossil of a ''Homo erectus'' skull. Two other expeditions in 2011 and 2012 also unearthed ancient hominid fossils at the site. Archaeologists have uncovered large quantities of animal fossils and Lithic core, lithic tools in the area. Archaeology Surveys and excavations of the region have led to the identification of hundreds of fossils and artifacts. Much of the artifacts found in the area are acheulean or oldowan. Following a 1994 prospection of the region, surveys were carried out in 1995. These surveys were conducted by the Asmara Department of Mines, the Department of Earth science, Earth Sciences, the Eritrean Ministry of Energy and Mines, and the University of Florence. Buya was excavated from 1995 to 1997 by a team of Eritrean and Italian Paleontology, paleontologists from the National Museum of Eritrea, and the Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or recorded history, historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort, although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition, such as a hoard or burial, can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension (chemistry), suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone (sedimentary rocks) through lithification. Sediments are most often transported by water (fluvial, fluvial processes), but also wind (aeolian processes) and glaciers. Beach sands and stream channel, river channel deposits are examples of fluvial transport and deposition (geology), deposition, though sediment also often settles out of slow-moving or standing water in lakes and oceans. Desert sand dunes and loess are examples of aeolian transport and deposition. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Size
The size of the brain is a frequent topic of study within the fields of anatomy, biological anthropology, animal science and evolution. Measuring brain size and cranial capacity is relevant both to humans and other animals, and can be done by weight or volume via MRI scans, by Cranial capacity#Humans, skull volume, or by neuroimaging intelligence testing. The relationship between brain size and intelligence has been a controversial and frequently investigated question. In 2021 scientists from Stony Brook University and the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior published findings showing that the brain size to body size ratio of different species has changed over time in response to a variety of conditions and events. As Kamran Safi, researcher at the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior and the study’s senior author writes: “Sometimes, relatively big brains can be the end result of a gradual decrease in body size to suit a new habitat or way of moving—in other word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-orbital Constriction
In physical anthropology, post-orbital constriction is the narrowing of the cranium (skull) just behind the eye sockets (the orbits, hence the name) found in most non-human primates and early hominins. This constriction is very noticeable in non-human primates, slightly less so in Australopithecines, even less in Homo erectus and completely disappears in modern Homo sapiens. Post-orbital constriction index in non-human primates and hominin range in category from increased constriction, intermediate, reduced constriction and disappearance. The post-orbital constriction index is defined by either a ratio of minimum frontal breadth (MFB), behind the supraorbital torus, divided by the maximum upper facial breadth (BFM), bifrontomalare temporale, or as the maximum width behind the orbit of the skull. Cranial evolution Measurement of cranial capacity in hominis has been long used to examine the evolutionary development of increased brain size, allowing for comparing and contrasting amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'. The occipital lobe is the Visual perception, visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area, Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1 (visual one). Human V1 is located on the Anatomical terms of location#Left and right (lateral), and medial, medial side of the occipital lobe within the calcarine sulcus; the full extent of V1 often continues onto the cerebral hemisphere#Poles, occipital pole. V1 is often also called striate cortex because it can be identified by a large stripe of myelin, the stria of Gennari. Visually driven regions outside V1 are called Extrastriate, extrastriate cortex. There are many extrastriate regions, and these are specialized for different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enamel Organ
The enamel organ, also known as the dental organ, is a cellular aggregation seen in a developing tooth and it lies above the dental papilla. The enamel organ which is differentiated from the primitive oral epithelium lining the stomodeum. The enamel organ is responsible for the formation of enamel, initiation of dentine formation, establishment of the shape of a tooth's crown, and establishment of the dentoenamel junction. The enamel organ has four layers; the inner enamel epithelium, outer enamel epithelium, stratum intermedium, and the stellate reticulum. The dental papilla, the differentiated ectomesenchyme deep to the enamel organ, will produce dentin and the dental pulp. The surrounding ectomesenchyme tissue, the dental follicle, is the primitive cementum, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone beneath the tooth root. The site where the internal enamel epithelium and external enamel epithelium coalesce is the cervical root, important in proliferation of the dental root ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
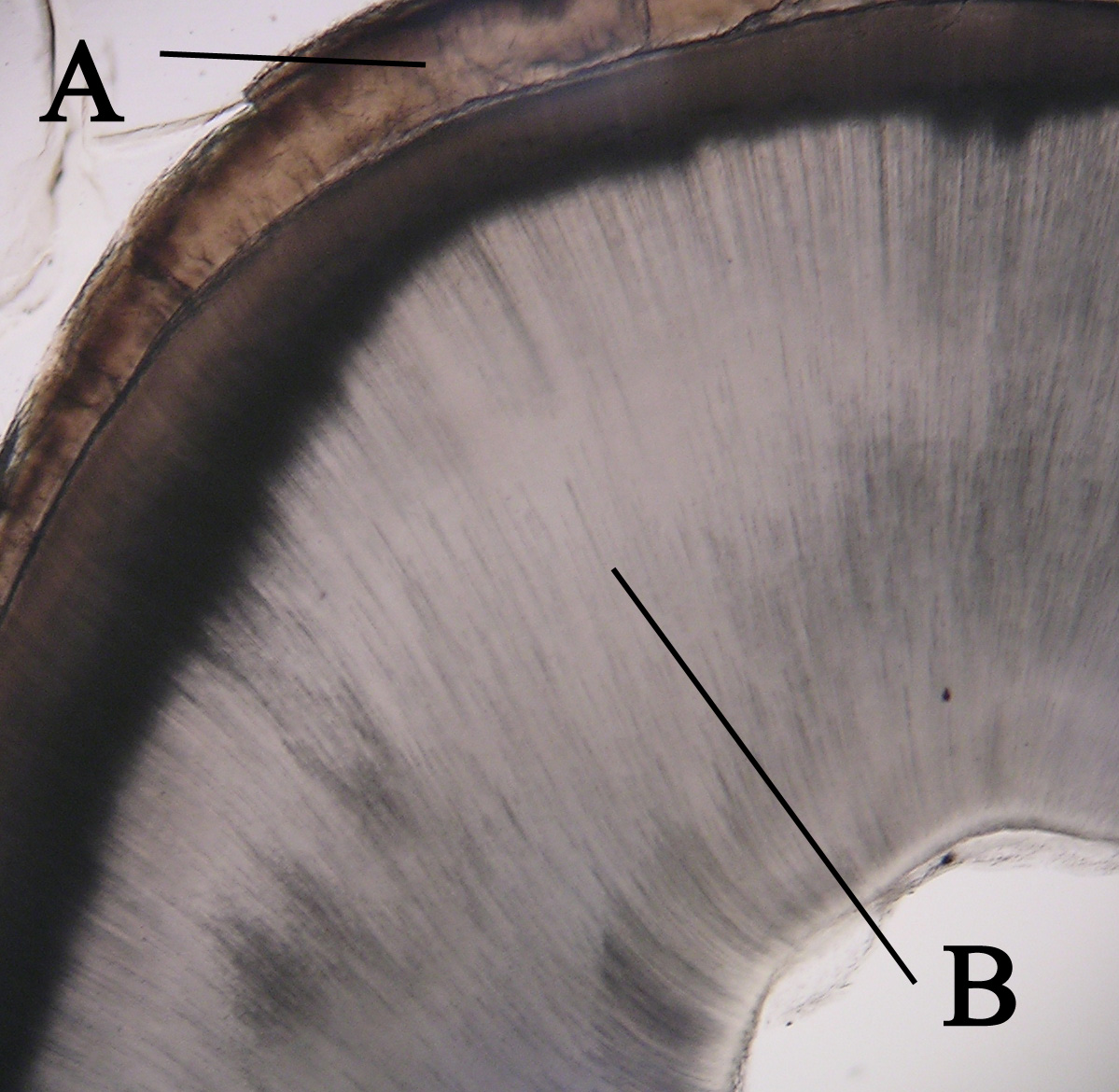
Dentin
Dentin ( ) (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) () is a calcified tissue (biology), tissue of the body and, along with tooth enamel, enamel, cementum, and pulp (tooth), pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occlusion (dentistry)
Occlusion, in a dental context, means simply the contact between teeth. More technically, it is the relationship between the maxillary (upper) and mandibular (lower) teeth when they approach each other, as occurs during chewing or at rest. Static occlusion refers to contact between teeth when the jaw is closed and stationary, while dynamic occlusion refers to occlusal contacts made when the jaw is moving. The masticatory system also involves the periodontium, the TMJ (and other skeletal components) and the neuromusculature, therefore the tooth contacts should not be looked at in isolation, but in relation to the overall masticatory system. Anatomy of Masticatory System One cannot fully understand occlusion without an in depth understanding of the anatomy including that of the teeth, TMJ, musculature surrounding this and the skeletal components. The Dentition and Surrounding Structures The human dentition consists of 32 permanent teeth and these are distributed between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Anatomy Structure The maxilla is a paired bone - the two maxillae unite with each other at the intermaxillary suture. The maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla: pyramid-shaped; has an orbital, a nasal, an infratemporal, and a facial surface; contains the maxillary sinus. * Four processes: ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process It has three surfaces: * the anterior, posterior, medial Features of the maxilla include: * t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Canal
A root canal is the naturally occurring anatomic space within the root of a tooth. It consists of the pulp chamber (within the coronal part of the tooth), the main canal(s), and more intricate anatomical branches that may connect the root canals to each other or to the surface of the root. Structure At the center of every tooth is a hollow area that houses soft tissues, such as the nerve, blood vessels, and connective tissue. This hollow area contains a relatively wide space in the coronal portion of the tooth called the pulp chamber. These canals run through the center of the roots, similar to the way graphite runs through a pencil. The pulp receives nutrition through the blood vessels, and sensory nerves carry signals back to the brain. A tooth can be relieved from pain if there is irreversible damage to the pulp, via root canal treatment. Root canal anatomy consists of the pulp chamber and root canals. Both contain the dental pulp. The smaller branches, referred to as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown (tooth)
In dentistry, the crown is the visible part of the tooth above the gingival margin and is an essential component of dental anatomy. Covered by Tooth enamel, enamel, the crown plays a crucial role in cutting, tearing, and grinding food. Its shape and structure vary depending on the type and function of the tooth (incisors, Canine tooth, canines, premolars, or Molar (tooth), molars), and differ between Deciduous teeth, primary dentition and Permanent teeth, permanent dentition. The crown also contributes to facial aesthetics, speech, and oral health. Anatomical crown vs clinical crown The anatomical crown refers to the portion of the tooth covered by enamel, regardless of whether it is visible. The clinical crown is the part of the tooth that is visible in the mouth. In a healthy young adult, the gums typically follow the contour where enamel meets the root, so the clinical and anatomical crowns are similar in size. However, with age or periodontal disease, this may change. Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla). The jawbone is the skull's only movable, posable bone, sharing Temporomandibular joint, joints with the cranium's temporal bones. The mandible hosts the lower Human tooth, teeth (their depth delineated by the alveolar process). Many muscles attach to the bone, which also hosts nerves (some connecting to the teeth) and blood vessels. Amongst other functions, the jawbone is essential for chewing food. Owing to the Neolithic Revolution, Neolithic advent of agriculture (), human jaws evolved to be Human jaw shrinkage, smaller. Although it is the strongest bone of the facial skeleton, the mandible tends to deform in old age; it is also subject to Mandibular fracture, fracturing. Surgery allows for the removal of jawbone fragments (or its entirety) as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |