|
Burushaski Language
Burushaski (; ) is a language isolate spoken by Burusho people, who reside almost entirely in northern Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan, with a few hundred speakers in northern Jammu and Kashmir, India. In Pakistan, Burushaski is spoken by people in Hunza District, Nagar District, northern Gilgit District, the Yasin valley in the Gupis-Yasin District and the Ishkoman valley of the northern Ghizer District. Their native region is located in northern Gilgit–Baltistan and borders with the Pamir corridor to the north. In India, Burushaski is spoken in Botraj Mohalla of the Hari Parbat region in Srinagar. Other names for the language are ''Biltum'', ''Khajuna'', ''Kunjut'', ''Brushaski'', ''Burucaki'', ''Burucaski'', ''Burushaki'', ''Burushki'', ''Brugaski'', ''Brushas'', ''Werchikwar'' and ''Miśa:ski''. Classification Attempts have been made to establish links between Burushaski and several different language families, although none has been accepted by a majority of linguists. Foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's Islam by country#Countries, second-largest Muslim population just behind Indonesia. Pakistan is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 33rd-largest country in the world by area and 2nd largest in South Asia, spanning . It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south, and is bordered by India to India–Pakistan border, the east, Afghanistan to Durand Line, the west, Iran to Iran–Pakistan border, the southwest, and China to China–Pakistan border, the northeast. It is separated narrowly from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in the north, and also shares a maritime border with Oman. Islamabad is the nation's capital, while Karachi is its largest city and fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamir Corridor
The Wakhan Corridor ( ps, واخان دهلېز, translit=wāxān dahléz, fa, دالان واخان, translit=dâlân vâxân) is a narrow strip of territory in Badakhshan Province of Afghanistan, extending to Xinjiang in China and separating the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region of Tajikistan from the Gilgit-Baltistan region of Pakistan-administered Kashmir.International Boundary Study of the Afghanistan–USSR Boundary (1983) by the US Pg. 7 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
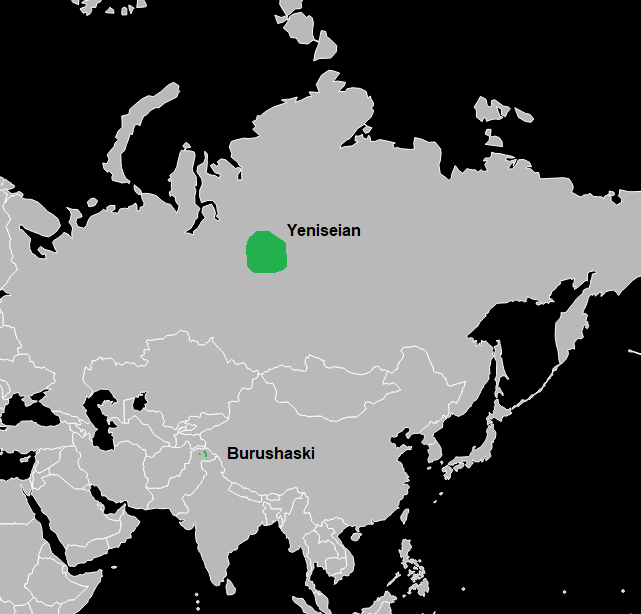
Karasuk Languages
Karasuk is a hypothetical language family that links the Yeniseian languages of central Siberia with the Burushaski language of northern Pakistan. History of proposals Hyde Clarke (1870) first noted a possible connection between the Yeniseian and Burushaski languages. The name ''Karasuk'' was proposed by George van Driem of the University of Leiden The family is named after the Karasuk culture, which existed in Central Asia during the Bronze Age in second millennium BCE. Van Driem postulates the Burusho people took part in the Indo-Aryan migration out of Central Asia and into the northern part of the Indian sub-continent, while other Karasuk peoples migrated northwards to become the Yeniseians. These claims have been picked up by anthropologist and linguist Roger Blench (1999). Václav Blažek (2019) places the linguistic homeland of Proto-Yeniseian close to where Burushaski is now spoken today. He argues that based on hydronomic evidence, Yeniseian languages were originally spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bengtson
John D. Bengtson (born 1948) is an American historical and anthropological linguist. He is past president and currently vice-president of the Association for the Study of Language in Prehistory, and has served as editor (or co-editor) of the journal '' Mother Tongue'' (1996–2003, 2007–present). Since 2001 he has been a member/researcher of Evolution of Human Languages, an international project on the linguistic prehistory of humanity coordinated by the Santa Fe Institute. His areas of specialization include Scandinavian languages and linguistics, Indo-European linguistics, Dené–Caucasian (Sino-Caucasian) languages, and paleolinguistics (the study of human prehistory through linguistic evidence). Publications * Bengtson, John D. 1994. (with Merritt Ruhlen) Global Etymologies. In M. Ruhlen, ''On the Origin of Languages: Studies in Linguistic Taxonomy''. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. * 1994. Edward Sapir and the 'Sino-Dene' Hypothesis. ''Anthropological Science'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dené–Caucasian Languages
Dené–Caucasian is a proposed language family that includes widely-separated language groups spoken in the Northern Hemisphere: Sino-Tibetan languages, Yeniseian languages, Burushaski and North Caucasian languages in Asia; Na-Dené languages in North America; and the Vasconic languages from Europe (including Basque). A narrower connection specifically between North American Na-Dené and Siberian Yeniseian (the Dené–Yeniseian languages hypothesis) was proposed by Edward Vajda in 2008, and has met with some acceptance within the community of professional linguists. The validity of the rest of the family, however, is viewed as doubtful or rejected by nearly all historical linguists. History of the hypothesis Classifications similar to Dené–Caucasian were put forward in the 20th century by Alfredo Trombetti, Edward Sapir, Robert Bleichsteiner, Karl Bouda, E. J. Furnée, René Lafon, Robert Shafer, Olivier Guy Tailleur, Morris Swadesh, Vladimir N. Toporov, and other scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrofamily
In historical linguistics, a macrofamily, also called a superfamily or phylum, is a proposed genetic relationship grouping together language families (also isolates) in a larger scale classification.Campbell, Lyle and Mixco, Mauricio J. (2007), ''A Glossary of Historical Linguistics'', University of Utah Press/Edinburgh University Press. However, CampbellCampbell, Lyle (2004), ''Historical Linguistics: An Introduction'', Edinburgh University Press. regards this term as superfluous, preferring "language family" for those classifications for which there is consensus and "distant genetic relationship" for those for which there is no, or not yet, consensus, whether due to lack of documentation or scholarship of the constituent languages, or to an estimated time depth thought by many linguists to be too great for reconstruction. More rarely, the term has also been applied to an exceptionally old, large and diverse language family, such as Afro-Asiatic. Diakonoff, Igor M. (1996), "Some r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeniseian Languages
The Yeniseian languages (sometimes known as Yeniseic or Yenisei-Ostyak;"Ostyak" is a concept of areal rather than genetic linguistics. In addition to the Yeniseian languages it also includes the Uralic languages Khanty and Selkup. occasionally spelled with -ss-) are a family of languages that are spoken by the Yeniseian people in the Yenisei River region of central Siberia. As part of the proposed Dené–Yeniseian language family, the Yeniseian languages have been argued to be part of "the first demonstration of a genealogical link between Old World and New World language families that meets the standards of traditional comparative-historical linguistics". The only surviving language of the group today is Ket. From hydronymic and genetic data, it is suggested that the Yeniseian languages were spoken in a much greater area in ancient times, including parts of northern China and Mongolia.Vajda, Edward J. (2013). Yeniseian Peoples and Languages: A History of Yeniseian Studies w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kartvelian Languages
The Kartvelian languages (; ka, ქართველური ენები, tr; also known as South Caucasian, Kartvelic, and Iberian languagesBoeder (2002), p. 3) are a language family indigenous to the South Caucasus and spoken primarily in Georgia. There are approximately 5.2 million Kartvelian speakers worldwide, with large groups in Russia, Iran, the United States, the European Union, Israel, and northeastern Turkey. The Kartvelian family has no known relation to any other language family, making it one of the world's primary language families. The most widely spoken of these languages is Georgian. The earliest literary source in any Kartvelian language is the Old Georgian Bir el Qutt inscriptions, written in ancient Georgian ''Asomtavruli'' script at the once-existing Georgian monastery near Bethlehem,Lang (1966), p. 154 dated to c. 430 AD. The Georgian script is used to write all Kartvelian languages. Social and cultural status Georgian is the official language of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Caucasian Languages
The North Caucasian languages, sometimes called simply Caucasic, is a proposed language family consisting of a pair of well established language families spoken in the Caucasus, predominantly in the north, consisting of the Northwest Caucasian family (also called ''Pontic, Abkhaz–Adyghe, Circassian,'' or ''West Caucasian'') and the Northeast Caucasian family (also called ''Nakh–Dagestanian'', ''Caspian'' or ''East Caucasian''). The Kartvelian languages, including Georgian, Zan and Svan, were once known as South Caucasian. However, they are no longer considered genetically related to the North Caucasian languages and are classified as an independent language family. Some linguists, notably Sergei Starostin and Sergei Nikolaev, believe that the two groups sprang from a common ancestor about five thousand years ago.Nikolayev, S., and S. Starostin. 1994 ''North Caucasian Etymological Dictionary''. Moscow: Asterisk PressAvailable online However, this proposal is difficult to ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE or its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result. PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from 4500 BC to 2500 BC during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, ''Malus sieversii'', is still found today. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Asia and Europe and were brought to North America by European colonization of the Americas, European colonists. Apples have Religion, religious and mythology, mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse mythology, Norse, Greek mythology, Greek, and Christianity in Europe, European Christian tradition. Apples grown from seed tend to be very different from those of their parents, and the resultant fruit frequently lacks desired characteristics. Generally, apple cultivars are propagated by clonal grafting onto rootstocks. Apple trees grown without rootstocks tend to be larger and much slower to fruit after plantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)