|
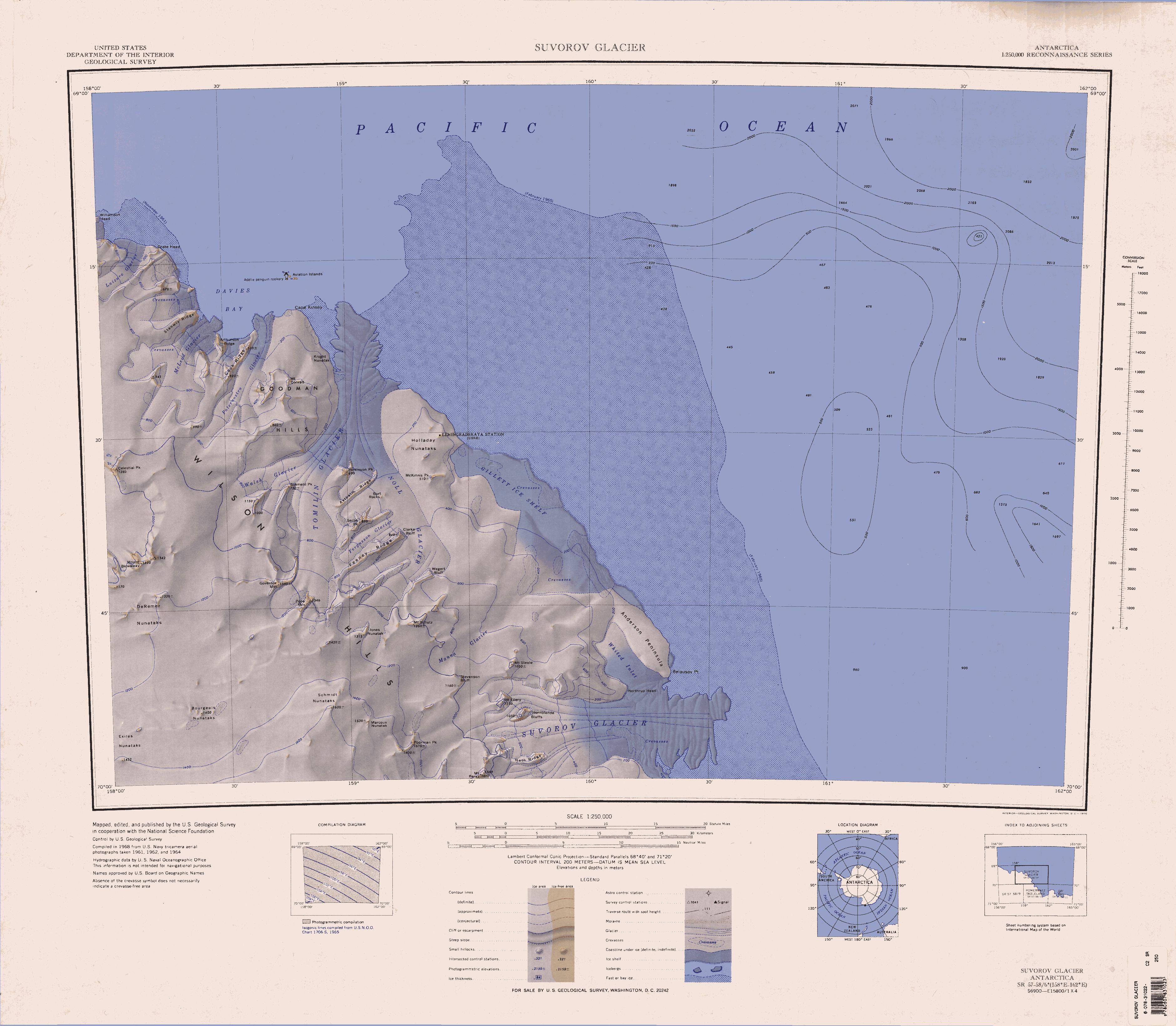
Burt Rocks
The Burt Rocks () are a cluster of rocks at the western margin of Noll Glacier, south of Axthelm Ridge, in the Wilson Hills. The rocks were mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–64, and were named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for DeVere E. Burt, a United States Antarctic Research Program biologist at Hallett Station Cape Hallett is a snow-free area (Antarctic oasis) on the northern tip of the Hallett Peninsula on the Ross Sea coast of Victoria Land, East Antarctica. Cape Adare lies to the north. History In 1956, during Operation Deep Freeze II, was dam ..., 1968–69. References Rock formations of Oates Land {{OatesLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noll Glacier
Noll Glacier () is a glacier, nearly 20 nautical miles (37 km) long, draining northeast from Jones Nunatak in central Wilson Hills. The glacier turns northwest at Wegert Bluff and enters the lower part of Tomilin Glacier before the latter debouches into the sea. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–64. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Maj. Edmund P. Noll, United States Marine Corps (USMC), Cargo Officer and LC-130 Aircraft Commander with U.S. Navy Squadron VX-6 during Operation Deep Freeze 1968. Returning from the war in Vietnam in June 1966 he deployed to Antarctica in October that year completing deployments with VX6 for the 1966–67 and 1967–68 season on the ice. He commanded the winter fly-in in 1967 and was co-pilot on the rescue flight from the U,S, base at McMurdo to Haley Bay, the British base across the continent for which he was awarded a single mission AIR Medal. Major Noll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axthelm Ridge
The Tomilin Glacier () is a glacier over long, draining north from Pope Mountain in the central Wilson Hills. It enters the sea east of Goodman Hills and Cape Kinsey, forming a substantial glacier tongue. Discovery and naming The Tomilin Glacier was photographed from aircraft of the United States Navy Operation Highjump in 1947, and by the Soviet Antarctic Expedition 1958. It was named by the latter for Soviet polar aviator Mikhail N. Tomilin (1908-52), who perished in the Arctic. Location The Tomilin Glacier forms in the Wilson Hills, flowing north or northeast from Governor Mountain and Pope Mountain, and passing Feeney Ridge, Serba Peak, Axthelm Ridge and Parkinson Peak to the east. It is joined from the west by Walsh Glacier, just north of Schmehl Peak, and flows north past the Goodman Hills to enter the ocean in an ice tongue. It is joined from the southeast by Noll Glacier, which forms near Wegert Bluff and flows northwest past Clarke Bluff, where it is joined by Fergu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson Hills
Wilson Hills () is a group of scattered hills, nunataks and ridges that extend NW-SE for about between Matusevich Glacier and Pryor Glacier in Antarctica. They were discovered by Lieutenant Harry Pennell, Royal Navy, on the Terra Nova Expedition in February 1911 during Robert Falcon Scott's last expedition, and named after Edward Adrian Wilson, a zoologist with the expedition, who perished with Scott on the return journey from the South Pole. Geological features Axthelm Ridge Axthelm Ridge () is a narrow ridge, 4 miles (6 km) long, 1.5 miles (2.4 km) southeast of Parkinson Peak. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–63. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Commander Charles E. Axthelm, U.S. Navy, Flag Secretary to the Commander of the U.S. Naval Support Force, Antarctica, during Operation Deep Freeze 1969 and 1970; executive officer on the USS ''Glacier'' during Operation Deep Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Antarctic Research Program
The United States Antarctic Program (or USAP; formerly known as the United States Antarctic Research Program or USARP and the United States Antarctic Service or USAS) is an organization of the United States government which has presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. scientific research and related logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean. United States Antarctic Program The United States established the U.S. Antarctic Research Program (USARP) in 1959—the name was later changed to the U.S. Antarctic Program—immediately following the success of the International Geophysical Year (IGY). Today, the National Science Foundation (NSF) has a Presidential Mandate to manage the United States Antarctic Program, through which it operates three year-round research stations and two research vessels, coordinates all U.S. science on the southernmost continent, and works with other federal agencies, the U.S. military, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallett Station
Cape Hallett is a snow-free area (Antarctic oasis) on the northern tip of the Hallett Peninsula on the Ross Sea coast of Victoria Land, East Antarctica. Cape Adare lies to the north. History In 1956, during Operation Deep Freeze II, was damaged by an ice floe at Cape Hallett. Hallett Station The cape was the location of a joint scientific base, Hallett Station, between the United States and New Zealand during the International Geophysical Year of 1957, and was manned permanently until 1964, when there was a major fire. It was then used as a summer only base until 1973. The site is currently being remediated by removing hazardous materials: fuel, and oil stored in several large tanks. This is an ongoing project which will take several years to complete. Antarctic Specially Protected Area An area of 74 ha is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.106 because it contains habitats with a rich and diverse range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |