|
Burst Lobe
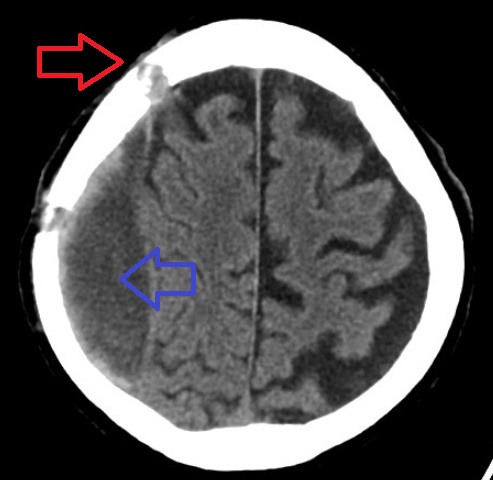
A burst lobe is an intracranial hemorrhage affecting a brain lobe (part of the cerebral hemispheres) and characterized by an intracerebral hemorrhage in continuity with a subdural hemorrhage and contusion. On a CT scan, it is shown as an irregular area of increased density which corresponds to a blood clot. This is surrounded by a low density area of oedema Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma .... References Neurotrauma {{neuroscience-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracranial Hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), also known as intracranial bleed, is bleeding within the skull. Subtypes are intracerebral bleeds (intraventricular bleeds and intraparenchymal bleeds), subarachnoid bleeds, epidural bleeds, and subdural bleeds. More often than not it ends in a lethal outcome. Intracerebral bleeding affects 2.5 per 10,000 people each year. Signs and symptoms Intracranial hemorrhage is a serious medical emergency because the buildup of blood within the skull can lead to increases in intracranial pressure, which can crush delicate brain tissue or limit its blood supply. Severe increases in intracranial pressure (ICP) can cause brain herniation, in which parts of the brain are squeezed past structures in the skull. Causes Trauma is the most common cause of intracranial hemorrhage. It can cause epidural hemorrhage, subdural hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Other condition such as hemorrhagic parenchymal contusion and cerebral microhemorrhages can also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special senses such as vision, hearing and olfaction. Being the most specialized organ, it is responsible for receiving information from the sensory nervous system, processing those information (thought, cognition, and intelligence) and the coordination of motor control (muscle activity and endocrine system). While invertebrate brains arise from paired segmental ganglia (each of which is only responsible for the respective body segment) of the ventral nerve cord, vertebrate brains develop axially from the midline dorsal nerve cord as a vesicular enlargement at the rostral end of the neural tube, with centralized control over all body segments. All vertebrate brains can be embryonically divided into three parts: the forebrain (prosencep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobe (anatomy)
In anatomy, a lobe is a clear anatomical division or extension of an organ (as seen for example in the brain, lung, liver, or kidney) that can be determined without the use of a microscope at the gross anatomy level. This is in contrast to the much smaller lobule, which is a clear division only visible under the microscope. Interlobar ducts connect lobes and interlobular ducts connect lobules. Examples of lobes *The four main lobes of the brain **the frontal lobe **the parietal lobe **the occipital lobe **the temporal lobe *The three lobes of the human cerebellum **the flocculonodular lobe **the anterior lobe **the posterior lobe *The two lobes of the thymus *The two and three lobes of the lungs ** Left lung: superior and inferior ** Right lung: superior, middle, and inferior *The four lobes of the liver ** Left lobe of liver ** Right lobe of liver ** Quadrate lobe of liver ** Caudate lobe of liver *The renal lobes of the kidney * Earlobes Examples of lobules *the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter, the cerebral cortex, that is supported by an inner layer of white matter. In eutherian (placental) mammals, the hemispheres are linked by the corpus callosum, a very large bundle of nerve fibers. Smaller commissures, including the anterior commissure, the posterior commissure and the fornix, also join the hemispheres and these are also present in other vertebrates. These commissures transfer information between the two hemispheres to coordinate localized functions. There are three known poles of the cerebral hemispheres: the '' occipital pole'', the '' frontal pole'', and the '' temporal pole''. The central sulcus is a prominent fissure which separates the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), also known as cerebral bleed, intraparenchymal bleed, and hemorrhagic stroke, or haemorrhagic stroke, is a sudden bleeding into the tissues of the brain, into its ventricles, or into both. It is one kind of bleeding within the skull and one kind of stroke. Symptoms can include headache, one-sided weakness, vomiting, seizures, decreased level of consciousness, and neck stiffness. Often, symptoms get worse over time. Fever is also common. Causes include brain trauma, aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, and brain tumors. The biggest risk factors for spontaneous bleeding are high blood pressure and amyloidosis. Other risk factors include alcoholism, low cholesterol, blood thinners, and cocaine use. Diagnosis is typically by CT scan. Other conditions that may present similarly include ischemic stroke. Treatment should typically be carried out in an intensive care unit. Guidelines recommend decreasing the blood pressure to a systo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdural Hemorrhage
A subdural hematoma (SDH) is a type of bleeding in which a collection of blood—usually but not always associated with a traumatic brain injury—gathers between the inner layer of the dura mater and the arachnoid mater of the meninges surrounding the brain. It usually results from tears in bridging veins that cross the subdural space. Subdural hematomas may cause an increase in the pressure inside the skull, which in turn can cause compression of and damage to delicate brain tissue. Acute subdural hematomas are often life-threatening. Chronic subdural hematomas have a better prognosis if properly managed. In contrast, epidural hematomas are usually caused by tears in arteries, resulting in a build-up of blood between the dura mater and the skull. The third type of brain hemorrhage, known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage, causes bleeding into the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. __TOC__ Signs and symptoms The symptoms of a subdural hematoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contusion
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur close enough to the epidermis such that the bleeding causes a visible discoloration. The bruise then remains visible until the blood is either absorbed by tissues or cleared by immune system action. Bruises which do not blanch under pressure can involve capillaries at the level of skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle, or bone. Bruises are not to be confused with other similar-looking lesions. (Such lesions include petechia (less than , resulting from numerous and diverse etiologies such as adverse reactions from medications such as warfarin, straining, asphyxiation, platelet disorders and diseases such as ''cytomegalovirus''), purpura (, classified as palpable purpura or non-palpable purpura and indicates various pathologic conditions such as thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Computed Tomography
X-rays (or rarely, ''X-radiation'') are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895 and named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. There is no universally accepted, strict definition of the bounds of the X-ray band. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 nanometers to 10 picometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range of 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oedema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area may feel heavy, and joint stiffness. Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause. Causes may include venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis, infections, angioedema, certain medications, and lymphedema. It may also occur after prolonged sitting or standing and during menstruation or pregnancy. The condition is more concerning if it starts suddenly, or pain or shortness of breath is present. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. If the underlying mechanism involves sodium retention, decreased salt intake and a diuretic may be used. Elevating the legs and support stockings may be useful for edema of the legs. Older people are more commonly affected. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_-_inferiror_view.png)