|
Buraiha
The were a group of dissolute writers who expressed the aimlessness and identity crisis of post-World War II Japan. While not comprising a true literary school, the Buraiha writers were linked together by a similar approach to the subject matter and literary style. The main characters in works of the Buraiha feature anti-heroes that are dissolute and aimless. Their work was based on criticism of the complete body of pre-war Japanese literature as well as American social values that were introduced into Japanese society with the occupation. Their work did not appeal to any one particular group, and their range was not well defined. Writers The term mainly applied to Ango Sakaguchi, Osamu Dazai and Sakunosuke Oda, however, it also often referred to others, such as Jun Ishikawa, Itō Sei, Jun Takami, Tanaka Hidemitsu and Kazuo Dan. Further, according to Takeo Okuno, the group also included Miyoshi Jūrō and Taiko Hirabayashi. Lifestyle Buraiha writers are sometimes referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
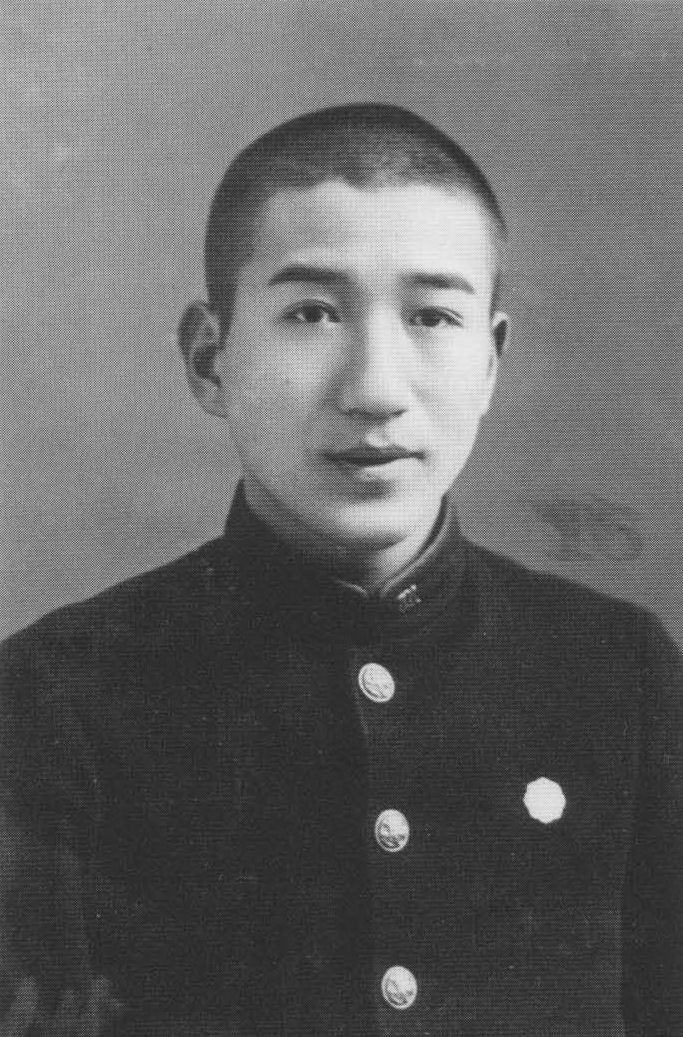
Tanaka Hidemitsu
was a novelist of the ''Buraiha'' genre in Shōwa period Japan. His name was also pronounced "Tanaka Eiko" on occasion. Biography Tanaka was born in the uptown Akasaka, Tokyo, Akasaka district of Tokyo as the son of a historian; however, he was listed under his mother's maiden name of “Tanaka” in the family register rather than his father's surname of Iwasaki. He grew up in Kamakura, Kanagawa, Kamakura and was a graduate of Waseda University’s School of Political Science and Economics. While still a student, he was influenced by his newspaper journalist brother towards a literary career, and towards membership in the Japan Communist Party. However, he was discouraged by the corruption of the senior leadership of the party, and left before graduation. Shortly after graduation, he met Dazai Osamu, who became his mentor. Also while still a university student, Tanaka was a member of the Japan at the 1932 Summer Olympics, Japanese Olympic team to the 1932 Summer Olympics, 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakunosuke Oda
was a Japanese writer. He is often grouped together with Osamu Dazai and Ango Sakaguchi as the '' Buraiha.'' Literally meaning ruffian or hoodlum faction, this label was not a matter of a stylistic school but one bestowed upon them by conservative critics disparaging the authors' attitudes and subject matter. Life and Writings Oda's writing career spans both prewar and postwar Japan. A native of Osaka, he wrote mostly of life in that city and the customs and manners of the common people there. In 1939, his story ''Zokushu'' (, Vulgarity) was a candidate for the Akutagawa Prize. The following year, Oda published ''Meoto Zenzai'' (). Named after an Osaka sweet shop, it follows the life of a couple whose relationship survives despite the persistent wastefulness, debauchery, and unkept promises of the erring man. Oda's characters usually did not fit into what were traditionally considered appropriate forms, either in their frank humanness or in their stubborn individuality, as in ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jun Ishikawa
was the pen name of a modernism, modernist author, translator and literary critic active in Shōwa period Japan. His real name (written in the same ''kanji'') was Ishikawa Kiyoshi. Early life Ishikawa was born in the Asakusa district of Tokyo as the son of a banker. He graduated from the Tokyo School of Foreign Languages (, later Tokyo University of Foreign Studies) with a degree in French literature. After graduation, he served a tour of duty in the Imperial Japanese Navy from 1922 to 1923, following which he was hired by Fukuoka University as a professor of French literature. His early career involved translating works such as Anatole France's ''Le lys rouge'' and author André Gide's ''L'Immoraliste'' into Japanese. The next year, he was resigned from the university due to controversy over his participation in student protest movements. He returned to Tokyo and began a bohemian existence, living out of cheap pensions while translating André Gide's ''Les Caves du Vatican'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decadent
The word decadence, which at first meant simply "decline" in an abstract sense, is now most often used to refer to a perceived decay in social norm, standards, morality, morals, dignity, religion, religious faith, honor, discipline, or competence (human resources), skill at governing among the members of the elite of a very large social structure, such as an empire or nation state. By extension, it may refer to a decline in art, literature, science, technology, and workforce productivity, work ethics, or (very loosely) to libertinism, self-indulgent behavior. Usage of the term sometimes implies moral censure, or an acceptance of the idea, met with throughout the world since ancient times, that such declines are objectively observable and that they inevitably precede the destruction of the society in question; for this reason, modern historians use it with caution. The word originated in Medieval Latin ''(dēcadentia)'', appeared in 16th-century French language, French, and enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazuo Dan
was a Japanese novelist and poet. Biography Dan was born in what is now part of Tsuru, Yamanashi Prefecture, to a family originally from Kyūshū. His father's work required frequent changes of residence, so Dan grew up with his grandparents in Yanagawa from age 6 onwards. His parents were divorced when Dan was nine, and he subsequently moved to live with his father in Ashikaga, Tochigi Prefecture, where he led a solitary life, walking over hills and fields. In 1928, at age 16, he entered Fukuoka City High School, where he began his literary life by publishing poems, novels and plays in the school magazine. In 1932 he entered the Tokyo Imperial University from which he received a degree in economics. After graduation, Dan dedicated himself entirely to writing, and in 1944 won the Noma Prize while serving as a newspaper war correspondent. Returning to Japan at the end of World War II, he married his wife Yosoko in Yanagawa. They moved to Tokyo, where he resumed his literary activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decadence
The word decadence, which at first meant simply "decline" in an abstract sense, is now most often used to refer to a perceived decay in standards, morals, dignity, religious faith, honor, discipline, or skill at governing among the members of the elite of a very large social structure, such as an empire or nation state. By extension, it may refer to a decline in art, literature, science, technology, and work ethics, or (very loosely) to self-indulgent behavior. Usage of the term sometimes implies moral censure, or an acceptance of the idea, met with throughout the world since ancient times, that such declines are objectively observable and that they inevitably precede the destruction of the society in question; for this reason, modern historians use it with caution. The word originated in Medieval Latin ''(dēcadentia)'', appeared in 16th-century French, and entered English soon afterwards. It bore the neutral meaning of decay, decrease, or decline until the late 19th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osamu Dazai
was a Japanese author. A number of his most popular works, such as '' The Setting Sun'' (''Shayō'') and ''No Longer Human'' (''Ningen Shikkaku''), are considered modern-day classics. His influences include Ryūnosuke Akutagawa, Murasaki Shikibu and Fyodor Dostoyevsky. While Dazai continues to be widely celebrated in Japan, he remains relatively unknown elsewhere, with only a handful of his works available in English. His last book, ''No Longer Human'', is his most popular work outside of Japan. Early life , who was later known as Osamu Dazai, was born on June 19, 1909, the eighth surviving child of a wealthy landowner in Kanagi, a remote corner of Japan at the northern tip of Tōhoku in Aomori Prefecture. At the time of his birth, the huge, newly-completed Tsushima mansion where he would spend his early years was home to some thirty family members. The Tsushima family was of obscure peasant origins, with Dazai's great-grandfather building up the family's wealth as a moneyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ango Sakaguchi
was a Japanese writer of short stories and novels and an essayist. His real name was . Biography Born in Niigata, Sakaguchi was one of a group of young Japanese writers to rise to prominence in the years immediately following Japan's defeat in World War II. As such, Ango Sakaguchi was associated with the Buraiha or "Decadent School" (無頼派 buraiha, the school of irresponsibility and decadence), which designated a group of dissolute writers who expressed their perceived aimlessness and identity crisis of post-World War II Japan. In 1946 he wrote his most famous essay, titled "Darakuron" ("Discourse on Decadence"), which examined the role of bushido during the war. It is widely argued that he saw postwar Japan as decadent, yet more truthful than a wartime Japan built on illusions like bushido. (The work itself does not make any claims about the meaning of decadence.) Ango was born in 1906 and was the 12th child of 13. He was born in the middle of a Japan perpetually at war. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Literature
Japanese literature throughout most of its history has been influenced by cultural contact with neighboring Asian literatures, most notably China and its literature. Early texts were often written in pure Classical Chinese or , a Chinese-Japanese creole language. Indian literature also had an influence through the spread of Buddhism in Japan. During the Heian period, Japan's original culture () developed and literature also established its own style, with the significant usage and development of to write Japanese literature. Following the Perry Expedition which led to the end of the policy and the forced reopening of foreign trade, Western literature has also made influences to the development of modern Japanese writers, while Japanese literature has in turn become more recognized internationally, leading to two Japanese Nobel laureates in literature, namely Yasunari Kawabata and Kenzaburō Ōe. History Nara-period literature (before 794) Before the introduction of kanji f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itō Sei
Itō may refer to: *Itō (surname), a Japanese surname *Itō, Shizuoka, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan *Ito District, Wakayama Prefecture, Japan See also *Itô's lemma, used in stochastic calculus *Itoh–Tsujii inversion algorithm, in field theory *Itô calculus, an extension of calculus to stochastic processes, named after Kiyoshi Itô *Ito (other) *ITO (other) Ito may refer to: Places * Ito Island, an island of Milne Bay Province, Papua New Guinea * Ito Airport, an airport in the Democratic Republic of the Congo * Ito District, Wakayama, a district located in Wakayama Prefecture, Japan * Itō, Shizuok ..., for the three-letter acronym {{DEFAULTSORT:Ito es:Ito fr:Ito nl:Ito ja:いとう pt:Ito ru:Ито ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jun Takami
was the pen-name of a Japanese novelist and poet active in Shōwa period Japan. His real name was Takami Yoshio. Early life Takami was born in Mikuni, Fukui (part of the present-day city of Sakai), Fukui Prefectural Library as the illegitimate son of the prefecture's governor and a young woman who had been assigned to entertain him on a visit to her town. The famous writer was his half-brother. Literary career Takami was interested in literature from youth, and was particularly attracted to the expressed by the '' |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |