|
Bumhpa Bum Wildlife Sanctuary
Bumhpa Bum Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area in Myanmar, covering an area of . It was established in 2004. It ranges in elevation from and harbours evergreen forest in Kachin State. Bumhpa Bum Wildlife Sanctuary is contiguous with Khakaborazi National Park and Hukaung Valley Wildlife Sanctuary. Together with Hponkanrazi Wildlife Sanctuary, they form a large continuous expanse of natural forest stretching over an area of , called the Northern Forest Complex. It was established in 1996 with the objective to conserve the biodiversity of the Ayeyarwady and Chindwin river basins. It is managed by the Forest Department. Biodiversity Bumhpa Bum Wildlife Sanctuary harbours tropical evergreen forest along with pine hill forest. Wildlife recorded during a camera trap survey in 2001 included binturong (''Arctictis binturong''), yellow-throated marten (''Martes flavigula''), spotted linsang (''Prionodon pardicolor''), Asian palm civet (''Paradoxurus hermaphroditus''), masked palm ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumprabum Township
Sumprabum Township ( my, ဆွမ်ပရာဘွမ်မြို့နယ်) is a township of Putao District in the Kachin State of Burma. The principal town is Sumprabum Sumprabum ( my, ဆွမ်ပရာဘွမ်မြို့) is a town in the Kachin State of the northernmost part of the Myanmar. Climate Sumprabum has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification The Köppen climate clas .... Townships of Kachin State {{Kachin-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian Palm Civet
The Asian palm civet (''Paradoxurus hermaphroditus''), also called common palm civet, toddy cat and musang, is a viverrid native to South and Southeast Asia. Since 2008, it is IUCN Red Listed as Least Concern as it accommodates to a broad range of habitats. It is widely distributed with large populations that in 2008 were thought unlikely to be declining. In Indonesia, it is threatened by poaching and illegal wildlife trade; buyers use it for the increasing production of kopi luwak. Characteristics The Asian palm civet's long, stocky body is covered with coarse, shaggy hair that is usually greyish in colour. It has a white mask across the forehead, a small white patch under each eye, a white spot on each side of the nostrils, and a narrow dark line between the eyes. The muzzle, ears, lower legs, and distal half of the tail are black, with three rows of black markings on the body. Its head-to-body length is about with a long unringed tail. It weighs . Its anal scent glands e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Goral
The red goral (''Naemorhedus baileyi'') is a species of even-toed ungulate in the subfamily Caprinae in the family Bovidae. It is found in India, Tibet and Myanmar. Its natural habitats are seasonal mountainous areas 1,000 to 2,000 meters above sea level. It is threatened by habitat loss and hunting. Origin and discovery The genus name ''Naemorhedus'' is derived from the Latin words ''nemus'' (genitive ''nemoris''), meaning "forest", and ''haedus'', meaning a young goat. Reports dating back to 1912 of a remarkable foxy-red coloured goral or goat-antelope (Nemorhaedus) from S.E. Tibet and N.E. Assam have been investigated. One of the earliest recorded references to their existence was made in 1863, however it was not until 1961 that the red goral was identified as its own species. Red goral are endemic to the region where the borders of India, Myanmar, and China meet. Appearance and morphology The red goral is a bright foxy-red animal with long, soft, shaggy hair. A thin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainland Serow
The mainland serow (''Capricornis sumatraensis'') is a serow species native to the Himalayas, Southeast Asia and China. The mainland serow is related closely to the red serow, Himalayan serow, Sumatran serow, and the Chinese serow (''C. milneedwardsii)''. Taxonomy In 1831, Brian Houghton Hodgson first described a goat-like animal with short annulated horns occurring in montane regions between the Sutlej and Teesta Rivers under the name "Bubaline Antelope". As "Bubaline" was preoccupied, he gave it the scientific name ''Antelope thar'' a few months later. When William Ogilby described the genus '' Capricornis'' in 1838, he determined the Himalayan serow as type species of this genus. Teeth from ''C. sumatraensis'' were found in a dig from Khok Sung, estimated to originate from the Middle Pleistocene. Characteristics The mainland serow possesses guard hairs on its coat that are bristly or coarse and cover the layer of fur closest to its skin to varying degrees. The animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaur
The gaur (''Bos gaurus''; ), also known as the Indian bison, is a bovine native to South Asia and Southeast Asia, and has been listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List since 1986. The global population was estimated at a maximum of 21,000 mature individuals in 2016, with the majority of those existing in India. It has declined by more than 70% during the last three generations, and is extirpated from Sri Lanka and most likely Bangladesh. Populations in well-protected areas are stable and increasing. It is the largest species among the wild cattle and the Bovidae. The domesticated form of the gaur is called ''gayal'' (''Bos frontalis'') or ''mithun''. Taxonomy ''Bison gaurus'' was the scientific name proposed by Charles Hamilton Smith in 1827. Later authors subordinated the species under either ''Bos'' or ''Bibos''. To date, three gaur subspecies have been recognized: * ''B. g. gaurus'' ranges in India, Nepal and Bhutan; * ''B. g. readei'' described by Richard Lydekk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
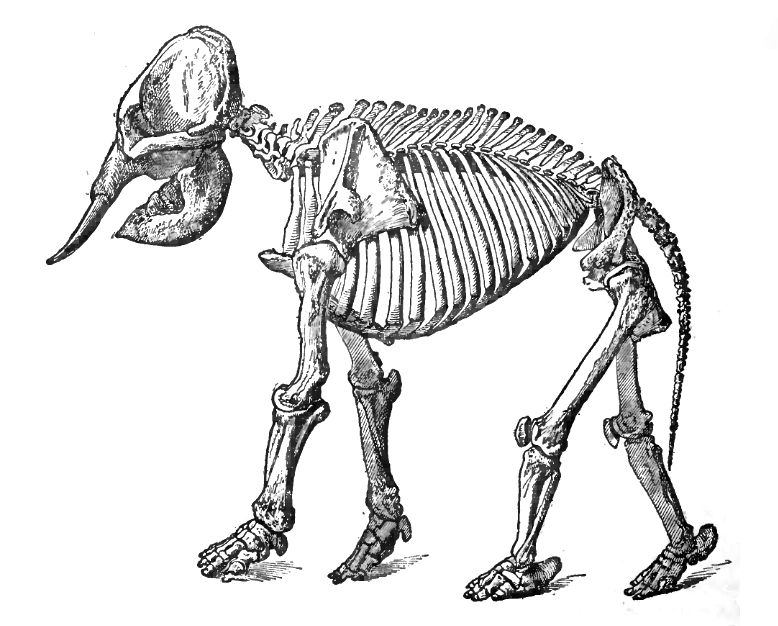
Asian Elephant
The Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is the only living species of the genus ''Elephas'' and is distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, Nepal in the north, Sumatra in the south, and to Borneo in the east. Three subspecies are recognised—'' E. m. maximus'' from Sri Lanka, ''E. m. indicus'' from mainland Asia and '' E. m. sumatranus'' from the island of Sumatra. Formerly, there was also the Syrian elephant or Western Asiatic elephant (''Elephas maximus asurus'') which was the westernmost population of the Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''). This subspecies became extinct in ancient times. Skeletal remains of ''E. m. asurus'' have been recorded from the Middle East: Iran, Iraq, Syria, and Turkey from periods dating between at least 1800 BC and likely 700 BC. It is one of only three living species of elephants or elephantids anywhere in the world, the others being the African bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marbled Cat
The marbled cat (''Pardofelis marmorata'') is a small wild cat native from the eastern Himalayas to Southeast Asia, where it inhabits forests up to an elevation of . As it is present in a large range, it has been listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List since 2015. The marbled cat is closely related to the Asian golden cat (''Catopuma temminckii'') and the bay cat (''C. badia''), all of which diverged from other felids about 9.4 million years ago. Characteristics The marbled cat is similar in size to a domestic cat, but has rounded ears and a very long tail that is as long as the cat's head and body. The ground colour of its long fur varies from brownish-grey to ochreous brown above and greyish to buff below. It is patterned with black stripes on the short and round head, on the neck and back. On the tail, limbs and underbelly it has solid spots. On the flanks it has irregular dark-edged blotches that fuse to dark areas and look like a 'marbled' pattern. Its paws are webbed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
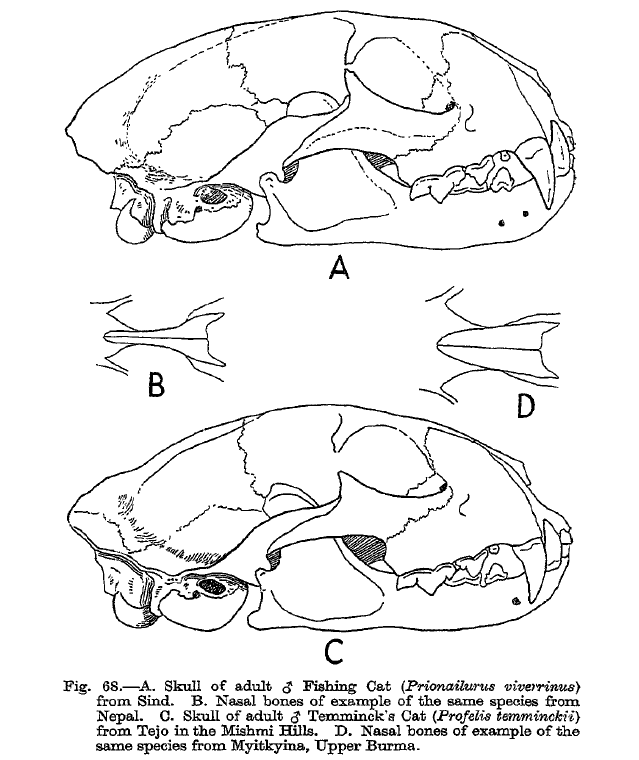
Leopard Cat
The leopard cat (''Prionailurus bengalensis'') is a small wild cat native to continental South, Southeast, and East Asia. Since 2002 it has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List as it is widely distributed although threatened by habitat loss and hunting in parts of its range. Historically, the leopard cat of continental Asia was considered the same species as the Sunda leopard cat. As of 2017, the latter is recognised as a distinct species, with the taxonomic name ''Prionailurus javanensis''. Leopard cat subspecies differ widely in fur colour, tail length, skull shape and size of carnassials. Archaeological evidence indicates that the leopard cat was the first cat species domesticated in Neolithic China about 5,000 years ago in Shaanxi and Henan Provinces. Characteristics A leopard cat is about the size of a domestic cat, but more slender, with longer legs and well-defined webs between its toes. Its small head is marked with two prominent dark stripes and a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asiatic Golden Cat
The Asian golden cat (''Catopuma temminckii'') is a medium-sized wild cat native to the northeastern Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia and China. It has been listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List since 2008, and is threatened by poaching and habitat destruction, since Southeast Asian forests are undergoing the world's fastest regional deforestation. The Asian golden cat's scientific name honours Coenraad Jacob Temminck. It is also called Temminck's cat and Asiatic golden cat. Taxonomy ''Felis temmincki'' was the scientific name used in 1827 by Nicholas Aylward Vigors and Thomas Horsfield who described a reddish brown cat skin from Sumatra. ''Felis moormensis'' proposed by Brian Houghton Hodgson in 1831 was a young male cat caught alive by Moormi hunters in Nepal. ''Felis tristis'' proposed by Alphonse Milne-Edwards in 1872 was a spotted Asian golden cat from China. It was subordinated to the genus ''Catopuma'' proposed by Nikolai Severtzov in 1853. Two subspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clouded Leopard
The clouded leopard (''Neofelis nebulosa''), also called the mainland clouded leopard, is a wild cat inhabiting dense forests from the foothills of the Himalayas through mainland Southeast Asia into South China. In the early 19th century, a clouded leopard was brought to London from China and described in 1821. It has large dusky-grey blotches and irregular spots and stripes reminiscent of clouds. Its head-and-body length ranges from with a long tail. It uses its tail for balancing when moving in trees and is able to climb down vertical tree trunks head first. It rests in trees during the day and hunts by night on the forest floor. The clouded leopard is the first cat that genetically diverged 9.32 to 4.47 million years ago from the common ancestor of the pantherine cats. Today, the clouded leopard is locally extinct in Singapore, Taiwan, and possibly Hainan Island and Vietnam. Its total population is suspected to be fewer than 10,000 mature individuals, with a decreasing pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crab-eating Mongoose
The crab-eating mongoose (''Urva urva'') is a mongoose species ranging from the northeastern Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia to southern China and Taiwan. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List. Taxonomy ''Gulo urva'' was the scientific name introduced by Brian Houghton Hodgson in 1836 who first described the type specimen that originated in central Nepal. It was later classified in the genus ''Herpestes'', but all Asian mongooses are now thought to belong in the genus ''Urva'', of which ''U. urva'' is the type species. Characteristics The crab-eating mongoose is grey on the sides and dusky brown on neck, chest, belly and limbs. It has a broad white stripe on the sides of the neck extending from the cheeks to the shoulder. It has white specks on the top of the head, its chin is white and its throat gray. Its iris is yellow. Its ears are short and rounded. It has webs between the digits. In head-to-body length it ranges from with a long bushy tail. Its wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masked Palm Civet
The masked palm civet (''Paguma larvata''), also called the gem-faced civet, is a palm civet species native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It has been listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008 as it occurs in many protected areas, is tolerant to some degree of habitat modification, and widely distributed with presumed large populations that are unlikely to be declining. The genus ''Paguma'' was first named and described by John Edward Gray in 1831. All described forms are regarded as a single species. In 2003, masked palm civets at a wildlife market in China were found to have been infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Characteristics The masked palm civet's fur is grayish to ochraceous, black on the head, shoulders and neck, and blackish brown on the tail and feet. It has a white blaze on the forehead; white marks above and below the eyes extend to the ears, forming a half-collar. In morphology the masked palm cive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |