|
Bumbita-Muhian Rural LLG
Bumbuita/Muhiang Rural LLG is a local-level government (LLG) of East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea. The Muhian language and Bumbita language, which are both Torricelli languages belonging to the Arapesh The Arapesh languages are several closely related Torricelli languages of the 32,000 Arapesh people of Papua New Guinea. They are spoken in eastern Sandaun Province and northern East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea. The Arapesh languages are a ... group, are spoken in this LLG. Wards *01. Albinama 1 *02. Timigir *03. Balif 1 *04. Salata *05. Bonohol *06. Urita *07. Malohum *08. Kamanakor *09. Sunuhu 1 *10. Mui 1 *11. Utamup *12. Ilahita 1 *13. Ilahita 3 *14. Albinama 2 *15. Ilahita 4 *16. Numangu *17. Taunangas References * * {{EastSepikProvince-geo-stub Local-level governments of East Sepik Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia (a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia). Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of . At the national level, after being ruled by three external powers since 1884, including nearly 60 years of Australian administration starting during World War I, Papua New Guinea established its sovereignty in 1975. It became an independent Commonwealth realm in 1975 with Elizabeth II as its queen. It also became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations in its own right. There are 839 known languages of Papua New Guinea, one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Papua New Guinea
For administrative purposes, Papua New Guinea is divided into administrative divisions Administrative division, administrative unit,Article 3(1). country subdivision, administrative region, subnational entity, constituent state, as well as many similar terms, are generic names for geographical areas into which a particular, ind ... called provinces. There are 22 provincial-level divisions, which include #List of provinces, 20 provinces, the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, and the National Capital District (Papua New Guinea), National Capital District of Port Moresby. In 2009, the National Parliament of Papua New Guinea created two additional provinces, that officially came into being on 17 May 2012. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Sepik Province
East Sepik is a province in Papua New Guinea. Its capital is Wewak. East Sepik has an estimated population of 433,481 people (2010 census) and is 43,426 km square in size. History Cherubim Dambui was appointed as East Sepik's first premier by Prime Minister Michael Somare upon the creation of the provincial government in 1976. Dambui remained interim premier until 1979, when he became East Sepik's permanent premier with a full term. He remained in office until 1983. Geography Wewak, the provincial capital, is located on the coast of East Sepik. There are a scattering of islands off shore, and coastal ranges dominate the landscape just inland of the coast. The remainder of the province's geography is dominated by the Sepik River, which is one of the largest rivers in the world in terms of water flow and is known for flooding—the river's level can alter by as much as five metres in the course of the year as it rises and falls. The southern areas of the province are taken up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Papua New Guinea
This page is a list of districts of Papua New Guinea. Administrative divisions On the highest level, Papua New Guinea is divided into 4 regions, which are Highlands, Islands, Momase, and Southern regions. Below, Papua New Guinea has 22 province-level divisions: 20 integrated provinces, the autonomous province of North Solomons (Bougainville) and the National Capital District. Each province has one or more districts, and each district has one or more local-level government (LLG) areas. For census purposes, the LLG areas are subdivided into wards and those into census units. Wards typically consist of a few hundred to a few thousand individuals, and are the lowest level of government administration under local-level governments (LLGs). List of districts by region and province Highlands Region Chimbu Province * Chuave District * Gumine District *Karimui-Nomane District *Kerowagi District * Kundiawa-Gembogl District * Sina Sina-Yonggomugl District (Sinasina-Yonggomugl Distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, a sovereign state in Oceania, is the most linguistically diverse country in the world. According to Ethnologue, there are 839 living languages spoken in the country. In 2006, Papua New Guinea Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare stated that "Papua New Guinea has 832 living languages (languages, not dialects)." Languages with statutory recognition are Tok Pisin, English, Hiri Motu, and Papua New Guinean Sign Language.There is no specific legislation proclaiming official languages in Papua New Guinea. In the constitution of Papua New Guinea, section 2(11) (literacy) of its preamble mentions '...all persons and governmental bodies to endeavour to achieve universal literacy in Pisin, Hiri Motu or English' as well as "tok ples" and "ita eda tano gado". In addition, section 67 (2)(c) mentions "speak and understand Pisin or Hiri Motu, or a vernacular of the country, sufficiently for normal conversational purposes" as a requirement for citizenship by nationalisation; this i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Code
A postal code (also known locally in various English-speaking countries throughout the world as a postcode, post code, PIN or ZIP Code) is a series of letters or digits or both, sometimes including spaces or punctuation, included in a postal address for the purpose of sorting mail. the Universal Postal Union lists 160 countries which require the use of a postal code. Although postal codes are usually assigned to geographical areas, special codes are sometimes assigned to individual addresses or to institutions that receive large volumes of mail, such as government agencies and large commercial companies. One example is the French CEDEX system. Terms There are a number of synonyms for postal code; some are country-specific; * CAP: The standard term in Italy; CAP is an acronym for ''codice di avviamento postale'' (postal expedition code). * CEP: The standard term in Brazil; CEP is an acronym for ''código de endereçamento postal'' (postal addressing code). * Eircode: Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
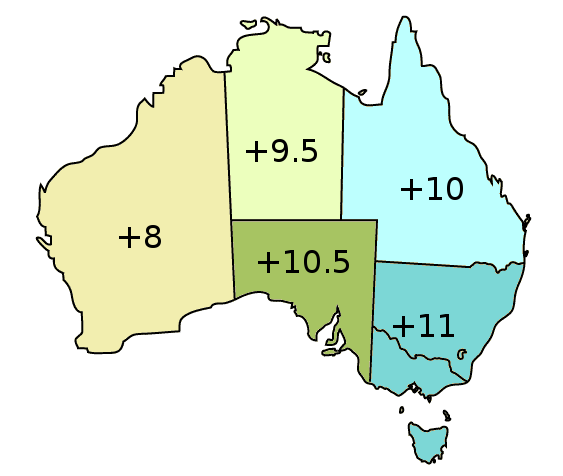
Time In Australia
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones. Standard time was introduced in the 1890s when all of the Australian colonies adopted it. Before the switch to standard time zones, each local city or town was free to determine its local time, called local mean time. Now, Western Australia uses Western Standard Time; South Australia and the Northern Territory use Central Standard Time; while New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria, Jervis Bay Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory use Eastern Standard Time. Daylight saving time (+1 hour) is used in jurisdictions in the south and south-east: South Australia, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local-level Governments Of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea has 326 local-level governments (LLGs) comprising 6,112 wards as of 2018. ''Note'': LLG names with slashes (/) are listed with dashes (-) due to technical limitations on previous versions of the Wikipedia software. Administrative divisions At the highest level, Papua New Guinea is divided into four regions, namely the Highlands, Islands, Momase, and Southern regions. Below, Papua New Guinea has 22 province-level divisions: 20 integrated provinces, the autonomous province of North Solomons (Bougainville) and the National Capital District. Each province has one or more districts, and each district has one or more local-level government (LLG) areas. For census purposes, the LLG areas are subdivided into wards and those into census units. Wards typically consist of a few hundred to a few thousand individuals, and are the lowest level of government administration under LLGs. Wards are further divided into census units (CU). List of local-level governments by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhian Language
Mufian (Muhian, Muhiang), or Southern Arapesh, is an Arapesh language ( Torricelli) of Papua New Guinea. Dialects are ''Supari, Balif, Filifita (Ilahita), Iwam-Nagalemb, Nagipaem''; Filifita speakers are half the population, at 6,000 in 1999. It is spoken in 36 villages, most of which are located within Bumbita-Muhian Rural LLG, East Sepik Province. It is also spoken in Supari ward of Albiges-Mablep Rural LLG. Phonology /ʔʷ/ is a coarticulated glottal stop with lip rounding that occurs only in final word positions. Pronouns Southern Arapesh pronouns are: : Noun classes There are 17 classes for count nouns in Mufian, plus two extra classes, i.e. proper names and place names. Noun classes are expressed in noun suffixes, adjective suffixes, and verb prefixes. Although Southern Arapesh has more than a dozen noun classes, only four noun classes are determined by semantics, while the other noun classes are determined phonologically using the final root segment (a feature t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bumbita Language
Bumbita (But Arapesh) is an Arapesh language ( Torricelli) of Papua New Guinea spoken mainly by older adults, unlike other Arapesh languages. Dialects are ''Bonahoi, Urita, Timingir, Weril, Werir.'' It is spoken in 13 villages of Bumbita-Muhian Rural LLG, East Sepik Province East Sepik is a province in Papua New Guinea. Its capital is Wewak. East Sepik has an estimated population of 433,481 people (2010 census) and is 43,426 km square in size. History Cherubim Dambui was appointed as East Sepik's first premier .... Dialects Dialects are: *Bonahoi dialect: spoken in Bonohol ward () *Urita dialect: spoken in Urita ward () *Timingir dialect: spoken in Timigir ward () *Weril dialect *Werir dialect References {{Languages of Papua New Guinea Arapesh languages Languages of East Sepik Province Vulnerable languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torricelli Languages
The Torricelli languages are a family of about fifty languages of the northern Papua New Guinea coast, spoken by about 80,000 people. They are named after the Torricelli Mountains. The most populous and best known Torricelli language is Arapesh, with about 30,000 speakers. The most promising external relationship for the Torricelli family is the Sepik languages. In reconstructions of both families, the pronouns have a plural suffix ''*-m'' and a dual suffix ''*-p''. History The Torricelli languages occupy three geographically separated areas, evidently separated by later migrations of Sepik-language speakers several centuries ago. Foley considers the Torricelli languages to be autochthonous to the Torricelli Mountains and nearby surrounding areas, having been resident in the region for at least several millennia. The current distribution of Lower Sepik-Ramu and Sepik (especially Ndu) reflects later migrations from the south and the east. Foley notes that the Lower Sepik and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arapesh Languages
The Arapesh languages are several closely related Torricelli languages of the 32,000 Arapesh people of Papua New Guinea. They are spoken in eastern Sandaun Province and northern East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea. The Arapesh languages are among the better-studied of Papuan languages and are most distinctive in their gender systems, which contain up to thirteen genders (noun classes) with noun-phrase concordance. Mufian, for example, has 17 noun classes for count nouns plus two extra noun classes, i.e. proper names and place names. (See that article for examples.) Phonology The most notable feature of the Arapesh phoneme inventory is the use of labialization as a contrastive device. Consonants Vowels Arapesh syllables have the structure (C)V(V)(C), though in monosyllables there is a requirement that the coda be filled. Normally either of the higher central vowels (ɨ, ə) is inserted to break up consonant clusters in the middle of words. Pronouns Pronouns in Arapesh an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |