|
Bull Trap
In stock market trading, a bull trap is an inaccurate signal that shows a decreasing trend in a stock or index has reversed and is now heading upwards, when in fact, the security will continue to decline. It is seen as a trap because the bullish investor purchases the stock, thinking it will increase in value, but is trapped with a poor performing stock whose value is still falling. See also *Economic bubble *Stock market bubble *Speculation *Boom and bust *Market trend *Dead cat bounce In finance, a dead cat bounce is a small, brief recovery in the price of a declining stock. Derived from the idea that "even a dead cat will bounce if it falls from a great height", the phrase, which originated on Wall Street, is also popularly ap ... References Setting the Bull Trap (investorinsight.com) {{business-stub Behavioral finance Business cycle Stock market Financial crises ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bear Market
A market trend is a perceived tendency of financial markets to move in a particular direction over time. Analysts classify these trends as ''secular'' for long time-frames, ''primary'' for medium time-frames, and ''secondary'' for short time-frames. Traders attempt to identify market trends using technical analysis, a framework which characterizes market trends as predictable price tendencies within the market when price reaches support and resistance levels, varying over time. A market trend can only be determined in hindsight, since at any time prices in the future are not known. Market terminology The terms "bull market" and "bear market" describe upward and downward market trends, respectively, and can be used to describe either the market as a whole or specific sectors and securities. The terms come from London's Exchange Alley in the early 18th century, where traders who engaged in naked short selling were called "bear-skin jobbers" because they sold a bear's skin (the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock
In finance, stock (also capital stock) consists of all the shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided.Longman Business English Dictionary: "stock - ''especially AmE'' one of the shares into which ownership of a company is divided, or these shares considered together" "When a company issues shares or stocks ''especially AmE'', it makes them available for people to buy for the first time." (Especially in American English, the word "stocks" is also used to refer to shares.) A single share of the stock means fractional ownership of the corporation in proportion to the total number of shares. This typically entitles the shareholder (stockholder) to that fraction of the company's earnings, proceeds from liquidation of assets (after discharge of all senior claims such as secured and unsecured debt), or voting power, often dividing these up in proportion to the amount of money each stockholder has invested. Not all stock is necessarily equal, as certain classe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index (economics)
In Statistics, Economics and Finance, an index is a statistical measure of change in a representative group of individual data points. These data may be derived from any number of sources, including company performance, prices, productivity, and employment. Economic indices track economic health from different perspectives. Influential global financial indices such as the Global Dow, and the NASDAQ Composite track the performance of selected large and powerful companies in order to evaluate and predict economic trends. The Dow Jones Industrial Average and the S&P 500 primarily track U.S. markets, though some legacy international companies are included. The consumer price index tracks the variation in prices for different consumer goods and services over time in a constant geographical location and is integral to calculations used to adjust salaries, bond interest rates, and tax thresholds for inflation. The GDP Deflator Index, or real GDP, measures the level of prices of all- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bull Market
A market trend is a perceived tendency of financial markets to move in a particular direction over time. Analysts classify these trends as ''secular'' for long time-frames, ''primary'' for medium time-frames, and ''secondary'' for short time-frames. Traders attempt to identify market trends using technical analysis, a framework which characterizes market trends as predictable price tendencies within the market when price reaches support and resistance levels, varying over time. A market trend can only be determined in hindsight, since at any time prices in the future are not known. Market terminology The terms "bull market" and "bear market" describe upward and downward market trends, respectively, and can be used to describe either the market as a whole or specific sectors and securities. The terms come from London's Exchange Alley in the early 18th century, where traders who engaged in naked short selling were called "bear-skin jobbers" because they sold a bear's skin (the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullish
Market sentiment, also known as investor attention, is the general prevailing attitude of investors as to anticipated Market trends, price development in a market. This attitude is the accumulation of a variety of fundamental analysis, fundamental and technical analysis, technical factors, including price history, economic reports, seasonal factors, and national and world events. If investors expect upward price movement in the stock market, the sentiment is said to be ''bullish''. On the contrary, if the market sentiment is ''bearish'', most investors expect downward price movement. Market participants who maintain a static sentiment, regardless of market conditions, are described as ''permabulls'' and ''permabears'' respectively. Market sentiment is usually considered as a contrarian indicator: what most people expect is a good thing to bet against. Market sentiment is used because it is believed to be a good predictor of market moves, especially when it is more extreme. Very bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Bubble
An economic bubble (also called a speculative bubble or a financial bubble) is a period when current asset prices greatly exceed their intrinsic valuation, being the valuation that the underlying long-term fundamentals justify. Bubbles can be caused by overly optimistic projections about the scale and sustainability of growth (e.g. dot-com bubble), and/or by the belief that intrinsic valuation is no longer relevant when making an investment (e.g. Tulip mania). They have appeared in most asset classes, including equities (e.g. Roaring Twenties), commodities (e.g. Uranium bubble), real estate (e.g. 2000s US housing bubble), and even esoteric assets (e.g. Cryptocurrency bubble). Bubbles usually form as a result of either excess liquidity in markets, and/or changed investor psychology. Large multi-asset bubbles (e.g. 1980s Japanese asset bubble and the 2020–21 Everything bubble), are attributed to central banking liquidity (e.g. overuse of the Fed put). In the early stages o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock Market Bubble
A stock market bubble is a type of economic bubble taking place in stock markets when market participants drive stock prices above their value in relation to some system of stock valuation. Behavioral finance theory attributes stock market bubbles to cognitive biases that lead to groupthink and herd behavior. Bubbles occur not only in real-world markets, with their inherent uncertainty and noise, but also in highly predictable experimental markets. In the laboratory, uncertainty is eliminated and calculating the expected returns should be a simple mathematical exercise, because participants are endowed with assets that are defined to have a finite lifespan and a known probability distribution of dividends . Other theoretical explanations of stock market bubbles have suggested that they are rational, intrinsic, and contagious. History Historically, early stock market bubbles and crashes have their roots in financial activities of the 17th-century Dutch Republic, the birth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculation
In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset (a commodity, good (economics), goods, or real estate) with the hope that it will become more valuable shortly. (It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline in value.) Many speculators pay little attention to the fundamental value of a security and instead focus purely on price movements. In principle, speculation can involve any tradable good or financial instrument. Speculators are particularly common in the markets for stocks, bond (finance), bonds, commodity futures, currency, currencies, fine art, collectibles, real estate, and derivative (finance), derivatives. Speculators play one of four primary roles in financial markets, along with hedge (finance), hedgers, who engage in transactions to offset some other pre-existing risk, arbitrageus who seek to profit from situations where Fungibility, fungible instruments trade at different prices in different market segments, and investors who s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
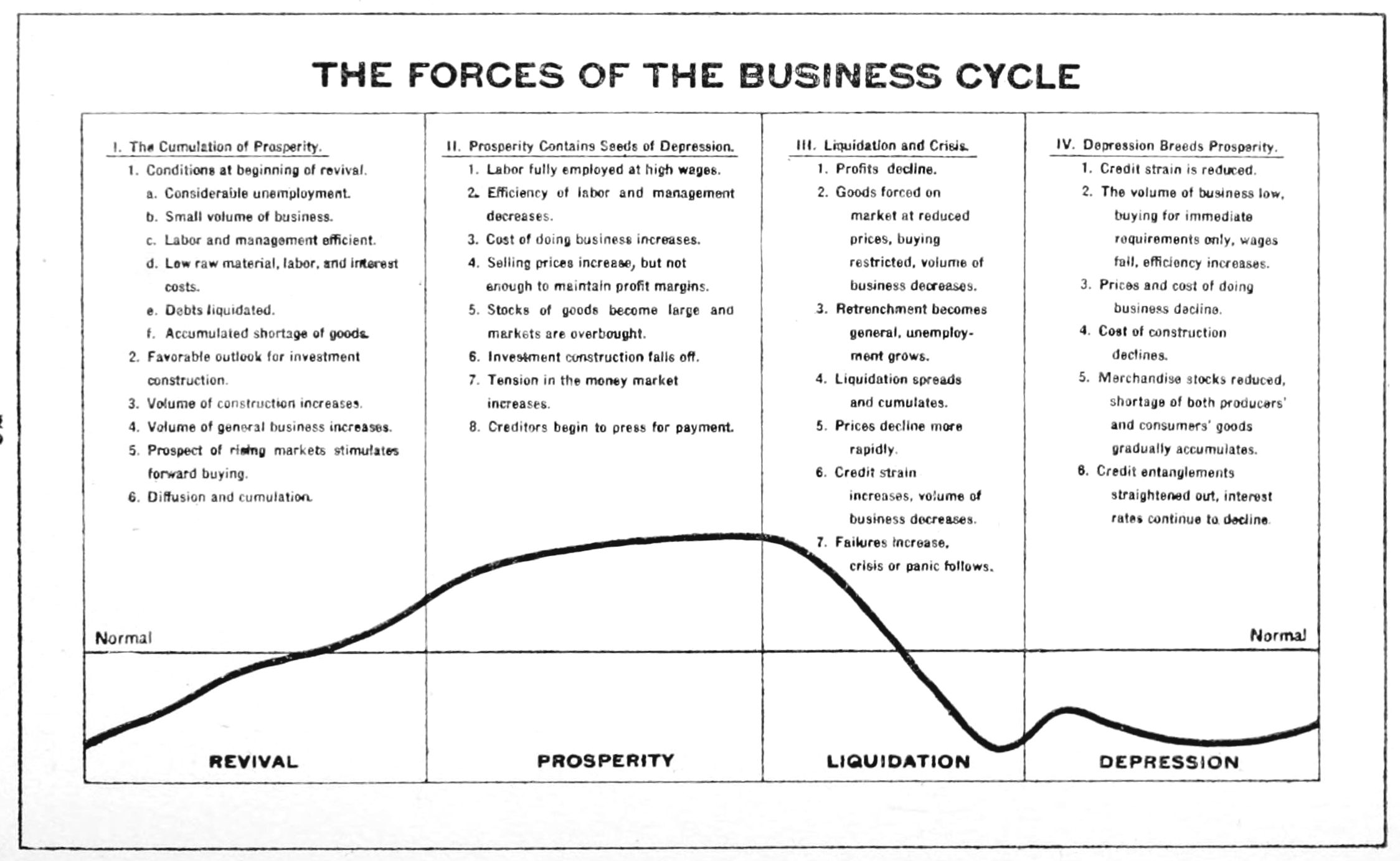
Boom And Bust
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examining trends in a broad economic indicator such as Real Gross Domestic Production. Business cycle fluctuations are usually characterized by general upswings and downturns in a span of macroeconomic variables. The individual episodes of expansion/recession occur with changing duration and intensity over time. Typically their periodicity has a wide range from around 2 to 10 years (the technical phrase "stochastic cycle" is often used in statistics to describe this kind of process.) As in arvey, Trimbur, and van Dijk, 2007, ''Journal of Econometrics'' such flexible knowledge about the frequency of business cycles can actually be included in their mathematical study, using a Bayesian statistical paradigm. There are numerous sources of business ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Trend
A market trend is a perceived tendency of financial markets to move in a particular direction over time. Analysts classify these trends as ''secular'' for long time-frames, ''primary'' for medium time-frames, and ''secondary'' for short time-frames. Traders attempt to identify market trends using technical analysis, a framework which characterizes market trends as predictable price tendencies within the market when price reaches support and resistance levels, varying over time. A market trend can only be determined in hindsight, since at any time prices in the future are not known. Market terminology The terms "bull market" and "bear market" describe upward and downward market trends, respectively, and can be used to describe either the market as a whole or specific sectors and securities. The terms come from London's Exchange Alley in the early 18th century, where traders who engaged in naked short selling were called "bear-skin jobbers" because they sold a bear's skin (the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Cat Bounce
In finance, a dead cat bounce is a small, brief recovery in the price of a declining stock. Derived from the idea that "even a dead cat will bounce if it falls from a great height", the phrase, which originated on Wall Street, is also popularly applied to any case where a subject experiences a brief resurgence during or following a severe decline. This may also be known as a "sucker rally". History The earliest citation of the phrase in the news media dates to December 1985 when the Singaporean and Malaysian stock markets bounced back after a hard fall during the recession of that year. Journalists Chris Sherwell and Wong Sulong of the ''Financial Times'' were quoted as saying the market rise was "what we call a dead cat bounce". Both the Singaporean and Malaysian economies continued to fall after the quote, although both economies recovered in the following years. The phrase was used again the following year about falling oil prices. In the San Jose Mercury News, Raymond F. DeVo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral Finance
Behavioral economics studies the effects of psychological, cognitive, emotional, cultural and social factors on the decisions of individuals or institutions, such as how those decisions vary from those implied by classical economic theory. Behavioral economics is primarily concerned with the bounds of rationality of economic agents. Behavioral models typically integrate insights from psychology, neuroscience and microeconomic theory. The study of behavioral economics includes how market decisions are made and the mechanisms that drive public opinion. The concepts used in behavioral economics today can be traced back to 18th-century economists, such as Adam Smith, who deliberated how the economic behavior of individuals could be influenced by their desires. The status of behavioral economics as a subfield of economics is a fairly recent development; the breakthroughs that laid the foundation for it were published through the last three decades of the 20th century. Behavior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)