|
Buddhabrot Zoom
The Buddhabrot is the probability distribution over the trajectories of points that escape the Mandelbrot fractal. Its name reflects its pareidolic resemblance to classical depictions of Gautama Buddha, seated in a meditation pose with a forehead mark ('' tikka''), a traditional topknot (''ushnisha'') and ringlet hair. Discovery The ''Buddhabrot'' rendering technique was discovered by Melinda Green, who later described it in a 1993 Usenet post to sci.fractals. Previous researchers had come very close to finding the precise Buddhabrot technique. In 1988, Linas Vepstas relayed similar images to Cliff Pickover for inclusion in Pickover's then-forthcoming book ''Computers, Pattern, Chaos, and Beauty''. This led directly to the discovery of Pickover stalks. Noel Griffin also implemented this idea in the 1993 "Mandelcloud" option in the Fractint renderer. However, these researchers did not filter out non-escaping trajectories required to produce the ghostly forms reminiscent of Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhabrot 20000
The Buddhabrot is the probability distribution over the trajectories of points that escape the Mandelbrot fractal. Its name reflects its pareidolic resemblance to classical depictions of Gautama Buddha, seated in a meditation pose with a forehead mark ('' tikka''), a traditional topknot (''ushnisha'') and ringlet hair. Discovery The ''Buddhabrot'' rendering technique was discovered by Melinda Green, who later described it in a 1993 Usenet post to sci.fractals. Previous researchers had come very close to finding the precise Buddhabrot technique. In 1988, Linas Vepstas relayed similar images to Cliff Pickover for inclusion in Pickover's then-forthcoming book ''Computers, Pattern, Chaos, and Beauty''. This led directly to the discovery of Pickover stalks. Noel Griffin also implemented this idea in the 1993 "Mandelcloud" option in the Fractint renderer. However, these researchers did not filter out non-escaping trajectories required to produce the ghostly forms reminiscent of Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is called the ''length'' of the sequence. Unlike a set, the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in a sequence, and unlike a set, the order does matter. Formally, a sequence can be defined as a function from natural numbers (the positions of elements in the sequence) to the elements at each position. The notion of a sequence can be generalized to an indexed family, defined as a function from an ''arbitrary'' index set. For example, (M, A, R, Y) is a sequence of letters with the letter 'M' first and 'Y' last. This sequence differs from (A, R, M, Y). Also, the sequence (1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8), which contains the number 1 at two different positions, is a valid sequence. Sequences can be ''finite'', as in these examples, or ''infi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
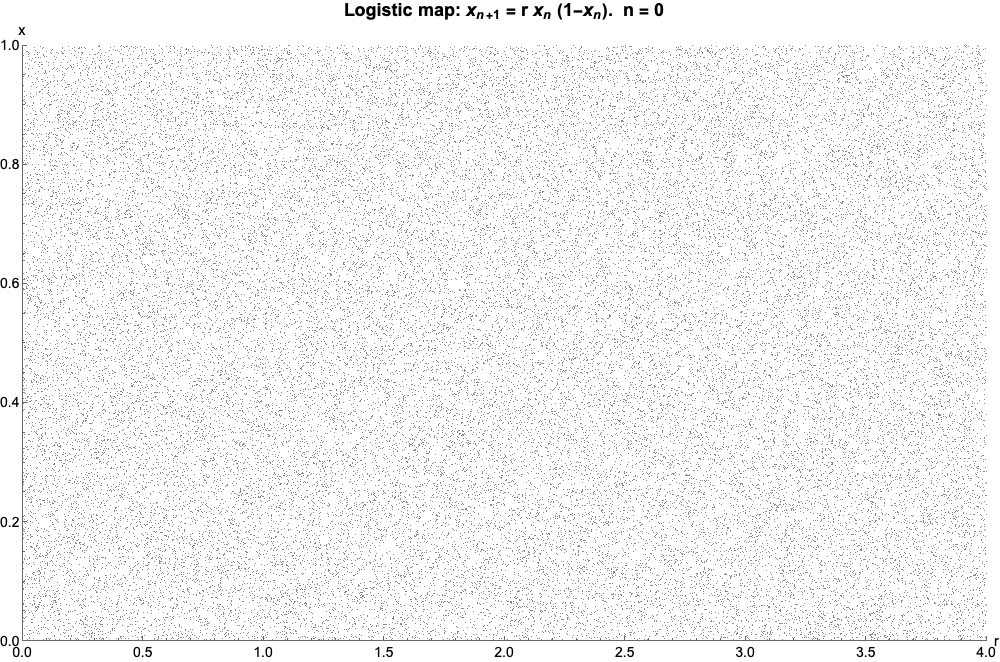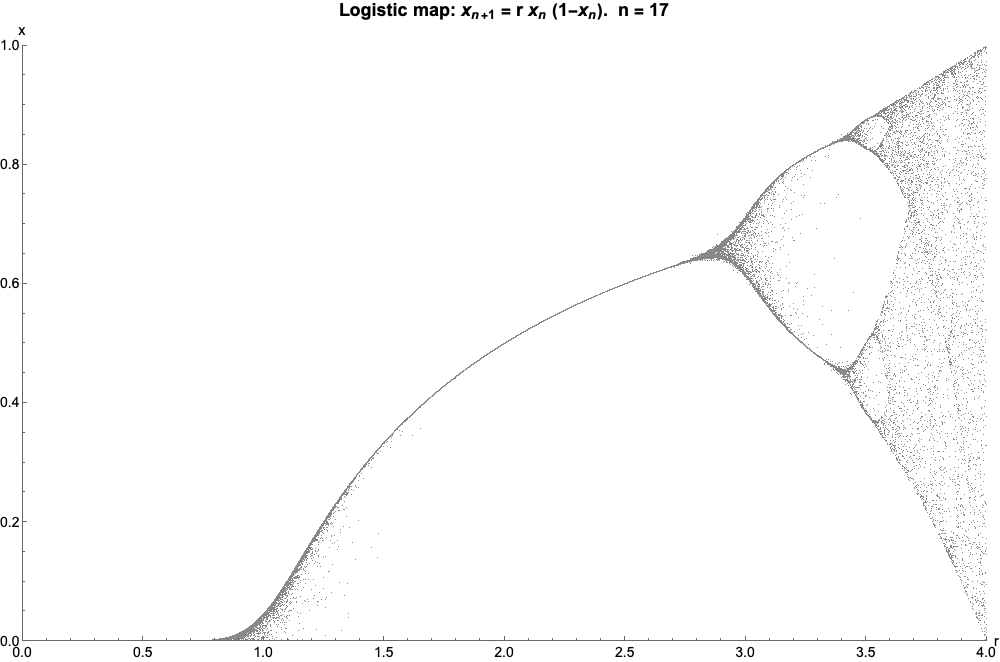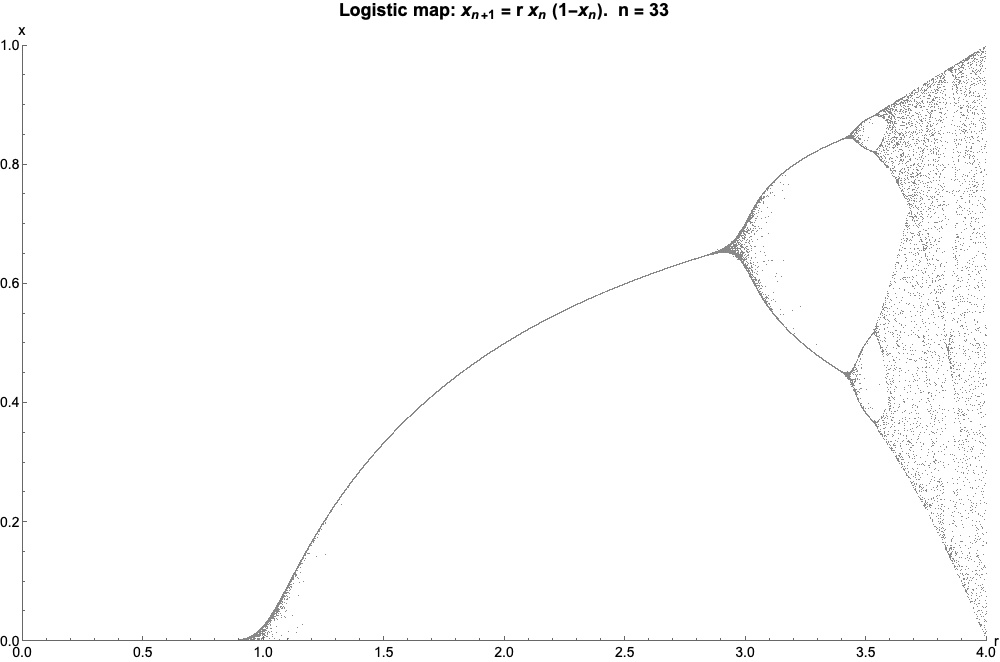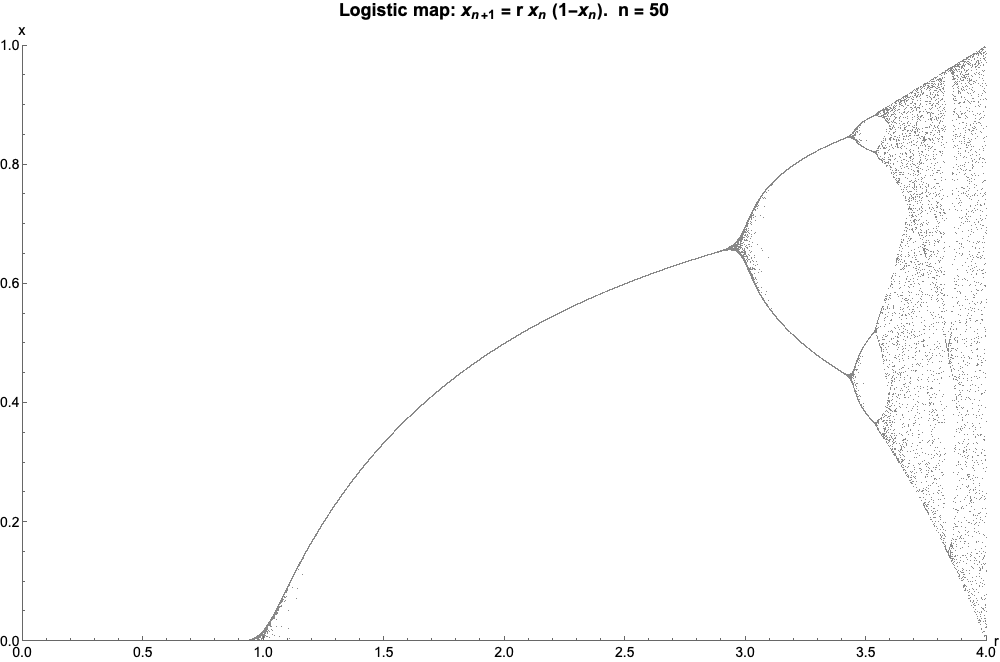
Logistic Map
The logistic map is a polynomial mapping (equivalently, recurrence relation) of degree 2, often referred to as an archetypal example of how complex, chaotic behaviour can arise from very simple non-linear dynamical equations. The map was popularized in a 1976 paper by the biologist Robert May, in part as a discrete-time demographic model analogous to the logistic equation written down by Pierre François Verhulst. Mathematically, the logistic map is written where is a number between zero and one, that represents the ratio of existing population to the maximum possible population. This nonlinear difference equation is intended to capture two effects: * ''reproduction'' where the population will increase at a rate proportional to the current population when the population size is small. * ''starvation'' (density-dependent mortality) where the growth rate will decrease at a rate proportional to the value obtained by taking the theoretical "carrying capacity" of the environment l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhabrot Logistic Map Animation Tn
The Buddhabrot is the probability distribution over the trajectories of points that escape the Mandelbrot fractal. Its name reflects its pareidolic resemblance to classical depictions of Gautama Buddha, seated in a meditation pose with a forehead mark ('' tikka''), a traditional topknot (''ushnisha'') and ringlet hair. Discovery The ''Buddhabrot'' rendering technique was discovered by Melinda Green, who later described it in a 1993 Usenet post to sci.fractals. Previous researchers had come very close to finding the precise Buddhabrot technique. In 1988, Linas Vepstas relayed similar images to Cliff Pickover for inclusion in Pickover's then-forthcoming book ''Computers, Pattern, Chaos, and Beauty''. This led directly to the discovery of Pickover stalks. Noel Griffin also implemented this idea in the 1993 "Mandelcloud" option in the Fractint renderer. However, these researchers did not filter out non-escaping trajectories required to produce the ghostly forms reminiscent of Hindu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhabrot Logistic Map
The Buddhabrot is the probability distribution over the trajectories of points that escape the Mandelbrot fractal. Its name reflects its pareidolic resemblance to classical depictions of Gautama Buddha, seated in a meditation pose with a forehead mark ('' tikka''), a traditional topknot (''ushnisha'') and ringlet hair. Discovery The ''Buddhabrot'' rendering technique was discovered by Melinda Green, who later described it in a 1993 Usenet post to sci.fractals. Previous researchers had come very close to finding the precise Buddhabrot technique. In 1988, Linas Vepstas relayed similar images to Cliff Pickover for inclusion in Pickover's then-forthcoming book ''Computers, Pattern, Chaos, and Beauty''. This led directly to the discovery of Pickover stalks. Noel Griffin also implemented this idea in the 1993 "Mandelcloud" option in the Fractint renderer. However, these researchers did not filter out non-escaping trajectories required to produce the ghostly forms reminiscent of Hindu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RGB Color Space
An RGB color space is any additive color space based on the RGB color model. An RGB color space is defined by chromaticity coordinates of the red, green, and blue additive primaries, the white point which is usually a standard illuminant, and the transfer function which is also known as the tone response curve (TRC) or gamma. Applying Grassmann's law of light additivity, a colorspace so defined can produce colors which are enclosed within the 2D triangle on the chromaticity diagram defined by those primary coordinates. The TRC and white point further define the possible colors, creating a volume in a 3D shape that never exceeds the triangular bounds. The primary colors are often specified in terms of their xyY chromaticity coordinates, though the uʹ,vʹ coordinates from the UCS chromaticity diagram may be used. Both xyY and uʹ,vʹ are derived from the CIE 1931 color space, a device independent space also known as XYZ which uses the 2° standard observer, an averaging of expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Color
False color (or pseudo color) refers to a group of color rendering methods used to display images in color which were recorded in the visible or non-visible parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. A false-color image is an image that depicts an object in colors that differ from those a photograph (a true-color image) would show. In this image, colors have been assigned to three different wavelengths that our eyes cannot normally see. In addition, variants of ''false color'' such as pseudocolor, density slicing, and choropleths are used for information visualization of either data gathered by a single grayscale channel or data not depicting parts of the electromagnetic spectrum (e.g. elevation in relief maps or tissue types in magnetic resonance imaging). Types of color renderings True color The concept behind true color can help in understanding false color. An image is called a ''true-color'' image when it offers a natural color rendition, or when it comes close to it. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grayscale
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a grayscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an ''amount'' of light; that is, it carries only intensity information. Grayscale images, a kind of black-and-white or gray monochrome, are composed exclusively of shades of gray. The contrast ranges from black at the weakest intensity to white at the strongest. Grayscale images are distinct from one-bit bi-tonal black-and-white images, which, in the context of computer imaging, are images with only two colors: black and white (also called ''bilevel'' or '' binary images''). Grayscale images have many shades of gray in between. Grayscale images can be the result of measuring the intensity of light at each pixel according to a particular weighted combination of frequencies (or wavelengths), and in such cases they are monochromatic proper when only a single frequency (in practice, a narrow band of frequencies) is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray Scale
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a grayscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an ''amount'' of light; that is, it carries only intensity information. Grayscale images, a kind of black-and-white or gray monochrome, are composed exclusively of shades of gray. The contrast ranges from black at the weakest intensity to white at the strongest. Grayscale images are distinct from one-bit bi-tonal black-and-white images, which, in the context of computer imaging, are images with only two colors: black and white (also called ''bilevel'' or ''binary images''). Grayscale images have many shades of gray in between. Grayscale images can be the result of measuring the intensity of light at each pixel according to a particular weighted combination of frequencies (or wavelengths), and in such cases they are monochromatic proper when only a single frequency (in practice, a narrow band of frequencies) is captu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Array Data Structure
In computer science, an array is a data structure consisting of a collection of ''elements'' (values or variables), each identified by at least one ''array index'' or ''key''. An array is stored such that the position of each element can be computed from its index tuple by a mathematical formula. The simplest type of data structure is a linear array, also called one-dimensional array. For example, an array of ten 32-bit (4-byte) integer variables, with indices 0 through 9, may be stored as ten words at memory addresses 2000, 2004, 2008, ..., 2036, (in hexadecimal: 0x7D0, 0x7D4, 0x7D8, ..., 0x7F4) so that the element with index ''i'' has the address 2000 + (''i'' × 4). The memory address of the first element of an array is called first address, foundation address, or base address. Because the mathematical concept of a matrix can be represented as a two-dimensional grid, two-dimensional arrays are also sometimes called "matrices". In some cases the term "vector" is used in comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)