|
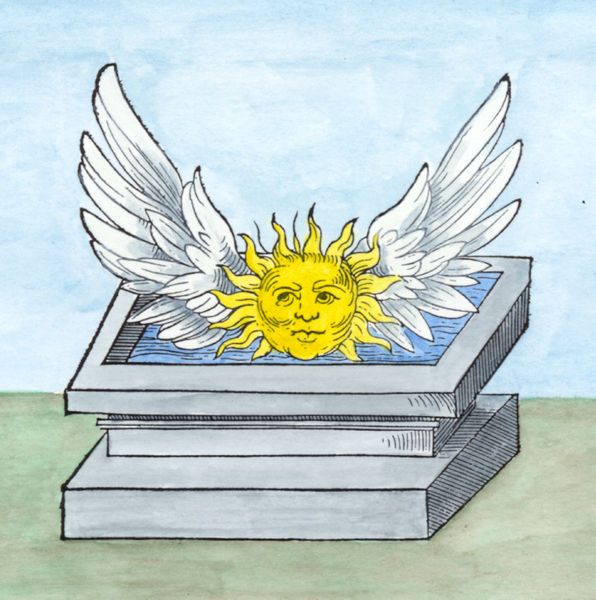
Buch Der Heiligen Dreifaltigkeit
The ''Buch der heiligen Dreifaltigkeit'' ("Book of the Holy Trinity") is an early 15th-century alchemical treatise, attributed to Frater Ulmannus (latinization of the German given name ''Ulmann'', from OHG '' uodal-man''), a German Franciscan. The text survives in at least four 15th-century manuscripts, the archetype Cod. 78 A 11 (Berlin), dated to between 1410–1419, and three copies,: Heidelberg Cpg 843 Fasc. 3 (15th century); Munich, Staatsbibl., Cgm 598 (late 15th century, after 1467) and St. Gallen, Kantonsbibl., VadSlg Ms. 428 (dated 1488). The treatise describes the alchemical process in terms of Christian mythology. The theme of the book is the analogy of the passion, death and resurrection of the Christ with the alchemical process leading to the '' lapis philosophorum''. The text is one of the most important alchemical works of late medieval Germany. It is not atypically a combination of alchemy and Christian mysticism. Ganzenmüller (1956) speculated that the book may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemical
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD.Principe, Lawrence M. The secrets of alchemy'. University of Chicago Press, 2012, pp. 9–14. Alchemists attempted to purify, mature, and perfect certain materials. Common aims were chrysopoeia, the transmutation of "base metals" (e.g., lead) into "noble metals" (particularly gold); the creation of an elixir of immortality; and the creation of panaceas able to cure any disease. The perfection of the human body and soul was thought to result from the alchemical ''magnum opus'' ("Great Work"). The concept of creating the philosophers' stone was variously connected with all of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosarium Philosophorum
''The Rosary of the Philosophers'' (''Rosarium philosophorum sive pretiosissimum donum Dei'') is a 16th-century alchemical treatise. It was published in 1550 as part II of ''De Alchimia Opuscula complura veterum philosophorum'' (Frankfurt). The term ''rosary'' in the title is unrelated to the Catholic prayer beads; it refers to a "rose garden", metaphoric of an anthology or collection of wise sayings. The 1550 print includes a series of 20 woodcuts with German-language captions, plus a title page showing a group of philosophers disputing about the production of the '' lapis philosophorum''. Some of the woodcut images have precedents in earlier (15th-century) German alchemical literature, especially in the '' Buch der heiligen Dreifaltigkeit'' (ca. 1410) which has the direct precedents of woodcuts 10, 17 and 19, allegorical of the complete ''hieros gamos'', nrs. 10 and 17 in the form of the "Hermetic androgyne" and nr. 19 in terms of Christian iconography, showing Mary flanked by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellcome Library
The Wellcome Library is founded on the collection formed by Sir Henry Wellcome (1853–1936), whose personal wealth allowed him to create one of the most ambitious collections of the 20th century. Henry Wellcome's interest was the history of medicine in a broad sense and included subjects such as alchemy or witchcraft, but also anthropology and ethnography. Since Henry Wellcome's death in 1936, the Wellcome Trust has been responsible for maintaining the Library's collection and funding its acquisitions. The library is free and open to the public. History Henry Wellcome began collecting books seriously in the late 1890s, using a succession of agents and dealers, and by travelling around the world to gather whatever could be found. Wellcome's first major entry into the market took place at the auction of William Morris's library in 1898, where he was the biggest single purchaser, taking away about a third of the lots. His interests were truly international and the broad coverage of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Rylands Research Institute And Library
The John Rylands Research Institute and Library is a late-Victorian neo-Gothic building on Deansgate in Manchester, England. It is part of the University of Manchester. The library, which opened to the public in 1900, was founded by Enriqueta Augustina Rylands in memory of her husband, John Rylands. It became part of the university in 1972, and now houses the majority of the Special Collections of The University of Manchester Library, the third largest academic library in the United Kingdom. Special collections built up by both libraries were progressively concentrated in the Deansgate building. The special collections, believed to be among the largest in the United Kingdom, include medieval illuminated manuscripts and examples of early European printing, including a Gutenberg Bible, the second largest collection of printing by William Caxton, and the most extensive collection of the editions of the Aldine Press of Venice. The Rylands Library Papyrus P52 has a claim to be t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick I, Elector Of Brandenburg
Frederick (Middle High German: ''Friderich'''','' Standard German: ''Friedrich''; 21 September 1371 – 20 September 1440) was the last Burgrave of Nuremberg from 1397 to 1427 (as Frederick VI), Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach from 1398, Margrave of Brandenburg-Kulmbach from 1420, and Elector of Brandenburg (as Frederick I) from 1415 until his death. He became the first member of the House of Hohenzollern to rule the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Biography Frederick was born in Nuremberg, the second-born son of Burgrave Frederick V (1333–1398) and the Wettin princess Elisabeth of Meissen. He entered early into the service of his brother-in-law, the Habsburg duke Albert III of Austria. After Albert's death in 1395, he fought on the side of the Luxembourg king Sigismund of Hungary against invading Ottoman forces. He and his elder brother John, husband of Sigismund's sister Margaret of Bohemia, fought in the 1396 Battle of Nicopolis where they suffered a disastrous defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John, Margrave Of Brandenburg-Kulmbach
John, nicknamed the Alchemist (german: Johann der Alchimist; 1406 – 16 November 1464) was a Margrave of Brandenburg-Kulmbach and served as the peace-loving Margrave of Brandenburg after the abdication of his father, Frederick I, the first member of the House of Hohenzollern to rule Brandenburg. Biography John was the eldest son of Frederick I, Margrave of Brandenburg (1371–1440), and Elisabeth of Bavaria-Landshut (1383–1442), daughter of Frederick, Duke of Bavaria, and his second wife Maddalena Visconti. After marrying Barbara of Saxe-Wittenberg (1405–1465), daughter of Rudolf III, Duke of Saxe-Wittenberg, John hoped to eventually succeed to Saxe-Wittenberg once its line of Ascanian dukes died out. When this happened in November 1422, however, Emperor Sigismund was on poorer terms with the Hohenzollerns and was only willing to compensate John with a monetary payment. John began participating in governmental affairs in Brandenburg in 1424. Frustrated by disputes with the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Magic
Renaissance magic was a resurgence in Hermeticism and Neo-Platonic varieties of the Magic (supernatural), magical arts which arose along with Renaissance humanism in the 15th and 16th centuries CE. These magical arts (called ''#Artes magicae, artes magicae'') were divided into seven types. There was great uncertainty in distinguishing practices of superstition, occultism, and perfectly sound scholarly knowledge or pious ritual. The intellectual and spiritual tensions erupted in the Early Modern witch-hunt, witch craze, further reinforced by the turmoil of the Protestant Reformation, especially in Germany, England, and Scotland. Artes magicae The seven ''artes magicae'' or ''artes prohibitae'', arts prohibited by canon law, as expounded by Johannes Hartlieb in 1456, their sevenfold partition reflecting that of the artes liberales and artes mechanicae, were: #nigromancy ('black magic', demonolatry) #geomancy #hydromancy #aeromancy #pyromancy #chiromancy #scapulimancy The divisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Renaissance
The German Renaissance, part of the Northern Renaissance, was a cultural and artistic movement that spread among Germany, German thinkers in the 15th and 16th centuries, which developed from the Italian Renaissance. Many areas of the arts and sciences were influenced, notably by the Renaissance humanism in Northern Europe, spread of Renaissance humanism to the various German states and principalities. There were many advances made in the fields of architecture, the arts, and the sciences. Germany produced two developments that were to dominate the 16th century all over Europe: Printing press, printing and the Protestant Reformation. One of the most important German humanists was Conrad Celtes, Konrad Celtis (1459–1508). Celtis studied at Cologne and Heidelberg, and later travelled throughout Italy collecting Latin and Greek manuscripts. Heavily influenced by Tacitus, he used the ''Germania (book), Germania'' to introduce German history and geography. Eventually he devoted h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakob Böhme
Jakob Böhme (; ; 24 April 1575 – 17 November 1624) was a German philosopher, Christian mystic, and Lutheran Protestant theologian. He was considered an original thinker by many of his contemporaries within the Lutheran tradition, and his first book, commonly known as ''Aurora'', caused a great scandal. In contemporary English, his name may be spelled Jacob Boehme (retaining the older German spelling); in seventeenth-century England it was also spelled Behmen, approximating the contemporary English pronunciation of the German ''Böhme''. Böhme had a profound influence on later philosophical movements such as German idealism and German Romanticism. Hegel described Böhme as "the first German philosopher". Biography Böhme was born on 24 April 1575 at Alt Seidenberg (now Stary Zawidów, Poland), a village near Görlitz in Upper Lusatia, a territory of the Kingdom of Bohemia. His father, George Wissen, was Lutheran, reasonably wealthy, but a peasant nonetheless. Böhme was the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uodal
{{Disambiguation ...
Odal (''oþal'', Anglo-Saxon ''éðel'', German ''uodal-'', ''adel'') is a Germanic word which relates to property, heritability or nobility. It can refer to the following: * Odal (rune), a Germanic rune **after the rune, the Œ ligature *''Ethel-'', ''Aethel-'', ''Uodal-'' as an element in Germanic names, see Ethel *Allodium: ** Odelsrett, a traditional Scandinavian law ** Udal law, the Scottish derivative of the Odelsrett * Odal, Norway, a traditional district in Norway See also * Aetheling * Auður (other) ''Auður'' (Modern Icelandic spelling) or ''Auðr'' (Old Icelandic spelling) is an Old Norse-Icelandic language, Icelandic female personal name. It also has the variant forms ''Unnr'' (Old Icelandic) and ''Unnur'' (Modern Icelandic). It is sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Mysticism
Christian mysticism is the tradition of mystical practices and mystical theology within Christianity which "concerns the preparation f the personfor, the consciousness of, and the effect of ..a direct and transformative presence of God" or Divine ''love''. Until the sixth century the practice of what is now called mysticism was referred to by the term ''contemplatio'', c.q. ''theoria'', from '' contemplatio'' (Latin; Greek θεωρία, ''theoria''), "looking at", "gazing at", "being aware of" God or the Divine.William Johnson, ''The Inner Eye of Love: Mysticism and Religion'' (HarperCollins 1997 ), p. 24 Christianity took up the use of both the Greek (''theoria'') and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapis Philosophorum
The philosopher's stone or more properly philosophers' stone (Arabic: حجر الفلاسفة, , la, lapis philosophorum), is a mythic alchemical substance capable of turning base metals such as mercury into gold (, from the Greek , "gold", and , "to make") or silver. It is also called the elixir of life, useful for rejuvenation and for achieving immortality; for many centuries, it was the most sought-after goal in alchemy. The philosopher's stone was the central symbol of the mystical terminology of alchemy, symbolizing perfection at its finest, enlightenment, and heavenly bliss. Efforts to discover the philosopher's stone were known as the Magnum Opus ("Great Work"). History Antiquity The earliest known written mention of the philosopher's stone is in the ''Cheirokmeta'' by Zosimos of Panopolis (c. 300 AD). Alchemical writers assign a longer history. Elias Ashmole and the anonymous author of ''Gloria Mundi'' (1620) claim that its history goes back to Adam, who acquired th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |