|
Bubble Column Reactor
A bubble column reactor is an apparatus used to generate and control gas-liquid chemical reactions. It consists of a vertically-arranged cylindrical column filled with liquid, at the bottom of which gas is inserted. Principle The introduction of gas takes place at the bottom of the column and causes a turbulent stream to enable an optimum gas exchange. Numerous forms of construction exist. The mixing is done by the gas sparging and it requires less energy than mechanical stirring. The liquid can be in parallel flow or counter-current. Bubble column reactors are characterized by a high liquid content and a moderate phase boundary surface. The bubble column is particularly useful in reactions where the gas-liquid reaction is slow in relation to the absorption rate. This is the case for gas-liquid reactions with a Hatta number Ha <0.3. Bubble column reactors are used in various types of chemical reactions like |
Bubble Column
Bubble, Bubbles or The Bubble may refer to: Common uses * Bubble (physics), a globule of one substance in another, usually gas in a liquid ** Soap bubble * Economic bubble, a situation where asset prices are much higher than underlying fundamentals Arts, entertainment and media Fictional characters * Bubble, a character in ''Absolutely Fabulous'' * Bubbles, an oriole from the ''Angry Birds'' franchise * Bubble, in the video game ''Clu Clu Land'' * Bubbles (''The Wire'') * Bubbles (''Trailer Park Boys'') * Bubbles, a yellow tang fish in the ''Finding Nemo'' franchise * Bubbles, in ''Jabberjaw'' * Bubbles Utonium, in ''The Powerpuff Girls'' ** Bubbles (Miyako Gotokuji), in ''Powerpuff Girls Z'' * Bubbles (''The Adventures of Little Carp'') * Bubbles, in ''The Adventures of Timmy the Tooth'' * Bubbles the Clown, a doll used in the BBC's Test Card F * Cobra Bubbles, in ''Lilo & Stitch'' * Bubbles DeVere, in ''Little Britain'' * Bubbles Yablonsky, the protagonist in a series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between those layers. Turbulence is commonly observed in everyday phenomena such as surf, fast flowing rivers, billowing storm clouds, or smoke from a chimney, and most fluid flows occurring in nature or created in engineering applications are turbulent. Turbulence is caused by excessive kinetic energy in parts of a fluid flow, which overcomes the damping effect of the fluid's viscosity. For this reason turbulence is commonly realized in low viscosity fluids. In general terms, in turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear of many sizes which interact with each other, consequently drag due to friction effects increases. This increases the energy needed to pump fluid through a pipe. The onset of turbulence can be predicted by the dimensionless Rey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparging (chemistry)
In chemistry, sparging, also known as gas flushing in metallurgy, is a technique in which a gas is bubbled through a liquid in order to remove ''other'' dissolved gas(es) and/or dissolved volatile liquid(s) from that liquid. It is a method of degassing. According to Henry's law, the concentration of each gas in a liquid is proportional to the partial pressure of that gas (in the gaseous state) in contact with the liquid. Sparging introduces a gas that has little or no partial pressure of the gas(es) to be removed, and increases the area of the gas-liquid interface, which encourages some of the dissolved gas(es) to diffuse into the sparging gas before the sparging gas escapes from the liquid. Many sparging processes, such as solvent removal, use air as the sparging gas. To remove oxygen, or for sensitive solutions or reactive molten metals, a chemically inert gas such as nitrogen, argon, or helium is used. Liquid chromatography Solvents used in high-performance liquid chromatogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption (chemistry)
In chemistry, absorption is a physical or chemical phenomenon or a process in which atoms, molecules or ions enter some bulk phase – liquid or solid material. This is a different process from adsorption, since molecules undergoing absorption are taken up by the volume, not by the surface (as in the case for adsorption). A more common definition is that "Absorption is a chemical or physical phenomenon in which the molecules, atoms and ions of the substance getting absorbed enters into the bulk phase (gas, liquid or solid) of the material in which it is taken up." A more general term is ''sorption'', which covers absorption, adsorption, and ion exchange. Absorption is a condition in which something takes in another substance. In many processes important in technology, the chemical absorption is used in place of the physical process, e.g., absorption of carbon dioxide by sodium hydroxide – such acid-base processes do not follow the Nernst partition law (see: solubility). For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatta Number
The Hatta number (Ha) was developed by Shirôji Hatta, who taught at Tohoku University. It is a dimensionless parameter that compares the rate of reaction in a liquid film to the rate of diffusion through the film. R.B. Bird, W.E. Stewart, E.N. Lightfoot, Transport Phenomena, 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons, 2002 For a second order reaction (), the maximum rate of reaction assumes that the liquid film is saturated with gas at the interfacial concentration ; thus, the maximum rate of reaction is . Ha^2 = = = For a reaction order in and order in : Ha = It is an important parameter used in Chemical Reaction Engineering. References See also * Dimensionless quantity *Dimensional analysis In engineering and science, dimensional analysis is the analysis of the relationships between different physical quantities by identifying their base quantities (such as length, mass, time, and electric current) and units of measure (such as mi ... Catalysis Dimensionless numbers o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wet Oxidation
Wet oxidation is a form of hydrothermal treatment. It is the oxidation of dissolved or suspended components in water using oxygen as the oxidizer. It is referred to as "Wet Air Oxidation" (WAO) when air is used. The oxidation reactions occur in superheated water at a temperature above the normal boiling point of water (100 °C), but below the critical point (374 °C). The system must be maintained under pressure to avoid excessive evaporation of water. This is done to control energy consumption due to the latent heat of vaporization. It is also done because liquid water is necessary for most of the oxidation reactions to occur. Compounds oxidize under wet oxidation conditions that would not oxidize under dry conditions at the same temperature and pressure. Wet oxidation has been used commercially for around 60 years. It is used predominantly for treating wastewater. It is often referred to as Zimpro (from ZIMmerman PROcess), after Fred J. Zimmermann who commercia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
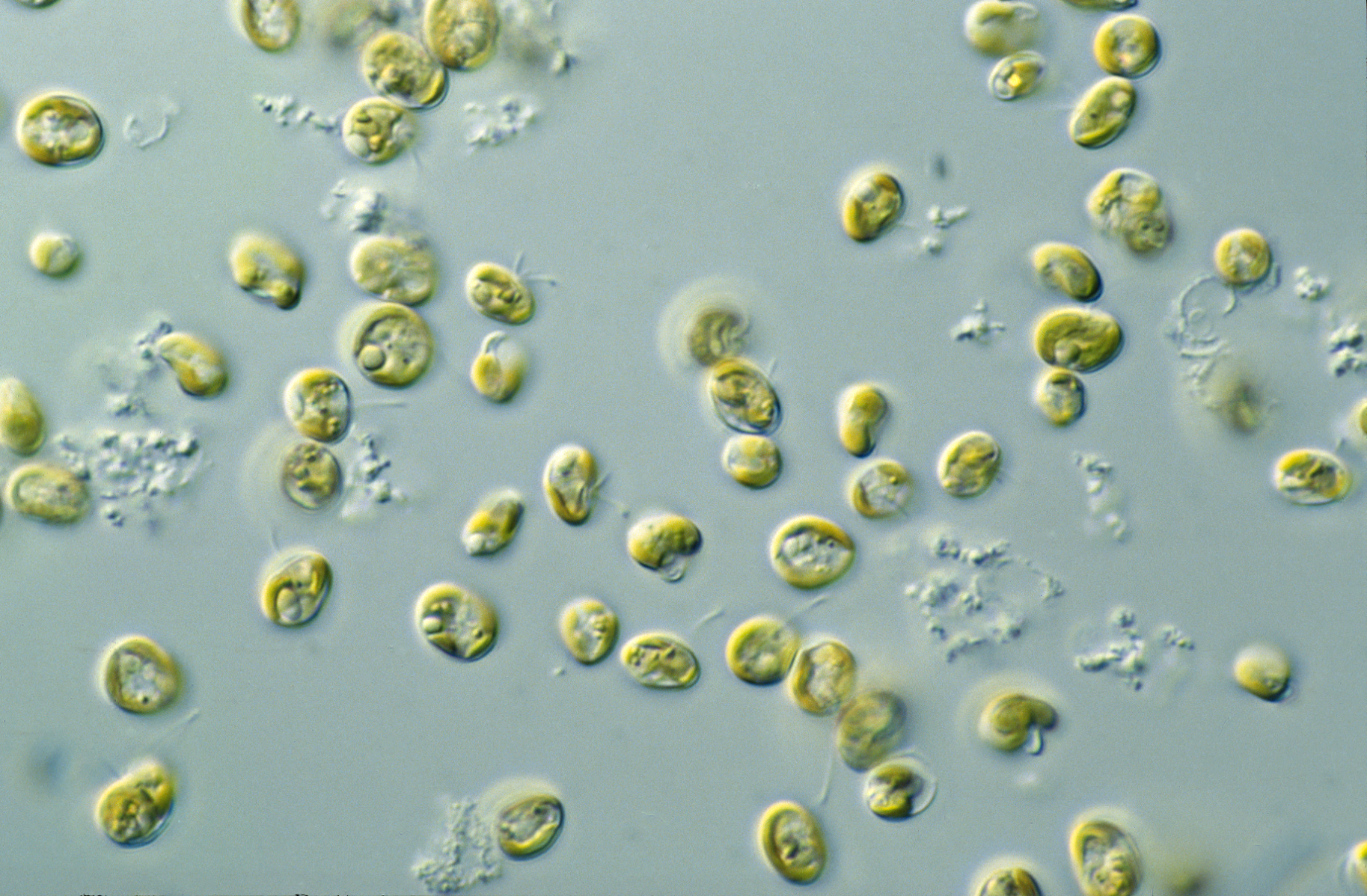
Algae Bioreactor
An algae bioreactor is used for cultivating micro or macro algae. Algae may be cultivated for the purposes of biomass production (as in a seaweed cultivator), wastewater treatment, CO2 fixation, or aquarium/pond filtration in the form of an algae scrubber. Algae bioreactors vary widely in design, falling broadly into two categories: open reactors and enclosed reactors. Open reactors are exposed to the atmosphere while enclosed reactors, also commonly called photobioreactors, are isolated to varying extents from the atmosphere. Specifically, algae bioreactors can be used to produce fuels such as biodiesel and bioethanol, to generate animal feed, or to reduce pollutants such as NOx and CO2 in flue gases of power plants. Fundamentally, this kind of bioreactor is based on the photosynthetic reaction, which is performed by the chlorophyll-containing algae itself using dissolved carbon dioxide and sunlight energy. The carbon dioxide is dispersed into the reactor fluid to make it a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |