|
Brugg–Hendschiken Railway Line
The Brugg–Hendschiken railway line is a standard gauge railway line located in the canton of Aargau, in Switzerland. It runs from to . The line runs north-south and interchanges with several other lines, including the Rupperswil–Immensee, Heitersberg / Zofingen–Wettingen railway line, Zofingen–Wettingen, Baden–Aarau railway line, Baden–Aarau, and Bözberg Line, Bözberg. The Aargau Southern Railway opened the line in 1882 and it has belonged to Swiss Federal Railways since 1902. History The Aargau Southern Railway completed the line on 1 June 1882. It was the final line built by that company. The line passed to Swiss Federal Railways in 1902 after the Aargau Southern Railway, along with its corporate parents the Swiss Central Railway and Swiss Northeastern Railway, were nationalized. SBB electrified the line at in 1927, completing the work on 5 May. Double-tracking came in stages: in the area around Brugg (1969), between and (1975), and finally between Othmarsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aargau
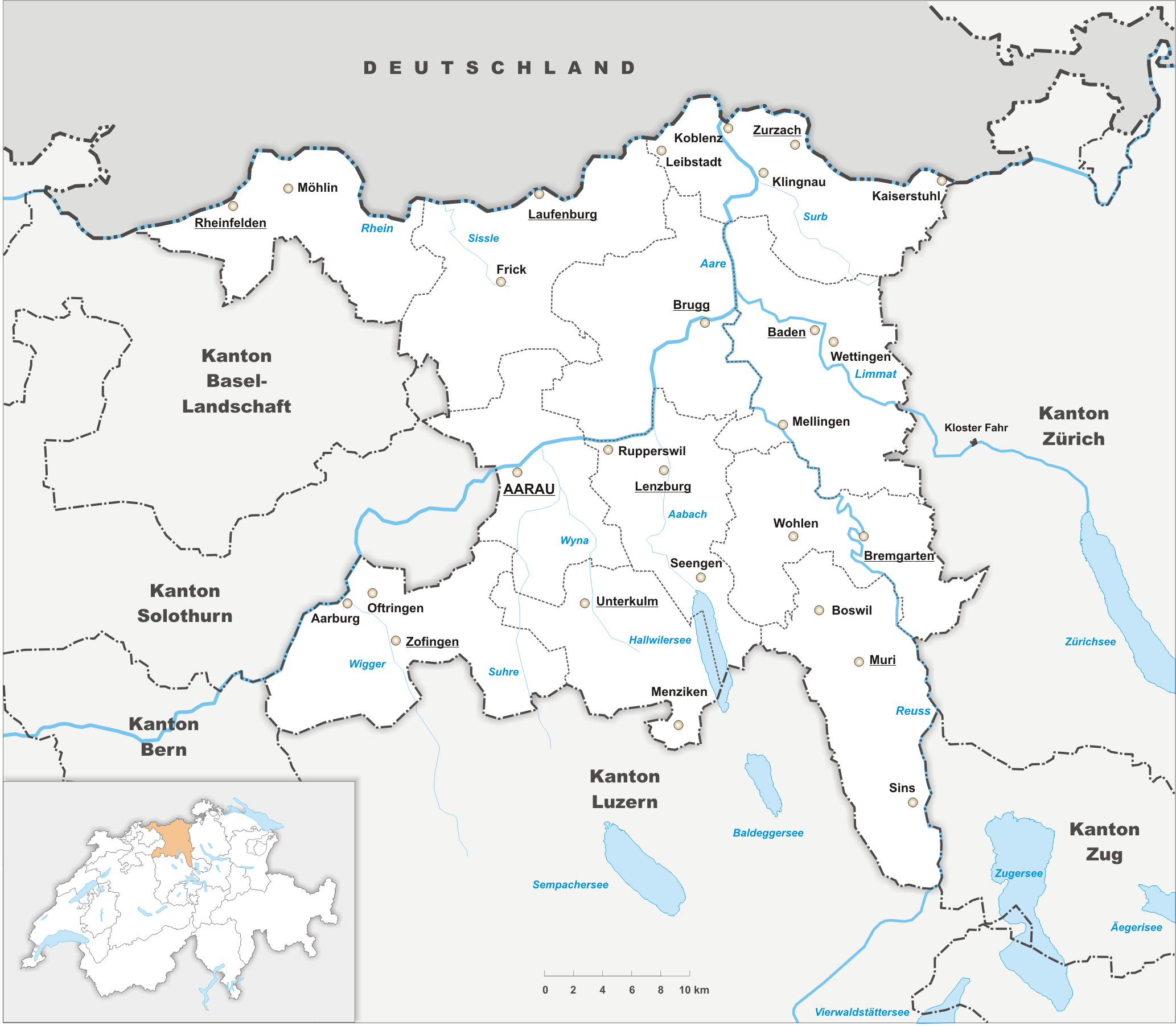
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau (german: Kanton Aargau; rm, Chantun Argovia; french: Canton d'Argovie; it, Canton Argovia), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau. Aargau is one of the most northerly cantons of Switzerland. It is situated by the lower course of the Aare River, which is why the canton is called ''Aar- gau'' (meaning "Aare province"). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland. History Early history The area of Aargau and the surrounding areas were controlled by the Helvetians, a member of the Celts, as far back as 200 BC. It was eventually occupied by the Romans and then by the 6th century, the Franks. The Romans built a major settlement called Vindonissa, near the present location of Brugg. Medieval Aargau The reconstructed Old High German name of Aargau is ''Argowe'', first unambiguously attested (in the spelling ''Argue'') in 795. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aargau S-Bahn
The Aargau S-Bahn (german: S-Bahn Aargau or german: S-Bahnen Aargau) is an S-Bahn-style regional rail network serving the canton of Aargau, Switzerland. History Upon the timetable change on 14 December 2008, an S-Bahn numbering system was introduced for regional rail services in Aargau. The new S-Bahn network was designed to complement the existing adjacent S-Bahn networks in Central Switzerland, Zurich and Basel. With that in mind, the line numbers selected for the new network were in the 20s (except the S14 Menziken–Aarau–Schöftland), so that there would be no conflict with the other networks. The new network was essentially a redesignation of its existing lines. No new stops were built for it, and no new rolling stock was purchased. In some cases, however, certain services in the 2007/2008 timetable were modified (e.g. the Langenthal–Baden through connection), and to a limited extent the frequency of services was increased. On 15 December 2019 the S29 was extended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Federal Railways
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usually referred to by the initials of its German, French, and Italian names, either as SBB CFF FFS, or used separately. The Romansh version of its name, ''Viafiers federalas svizras'', is not officially used. The official English abbreviation is "SBB", instead of the English acronym such as "SFR", which stands for ''Swiss Federal Railways'' itself. The company, founded in 1902, is headquartered in Bern. It used to be a government institution, but since 1999 it has been a special stock corporation whose shares are held by the Swiss Confederation and the Swiss cantons. It is currently the largest rail and transport company of Switzerland, and operates on most standard gauge lines of the Swiss network. It also heavily collaborates with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rupperswil–Immensee Railway Line
The Rupperswil–Immensee railway line is a railway line in the cantons of Aargau and Zug, in Switzerland. It runs from to . The line runs north-south and interchanges with several other lines, including the Baden–Aarau, Heitersberg, Zofingen–Wettingen, Seetal, Brugg–Hendschiken, Bremgarten–Dietikon, Zug–Lucerne, and finally the Lucerne–Immensee and Gotthard at Immensee. The Aargau Southern Railway opened the line in stages between 1874 and 1882 and it has belonged to Swiss Federal Railways since 1902. History The Aargau Southern Railway opened the first section of the line, between and , on 23 June 1874. The line was extended south from Wohlen to a year later, on 1 June 1875. The extension from Muri to opened on 1 December 1881. The final extension, from Rotkreuz to , was completed on 1 June 1882. This latter extension was built in cooperation with the Gotthard Railway building north from to Immensee. The line passed to Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heitersberg Railway Line
The Heitersberg railway line (''Heitersbergstrecke'') is a Swiss railway line between the stations of Killwangen-Spreitenbach and Aarau on the east-west main line between Zürich and Bern. The main structure of the line is the 4,929 metre-long Heitersberg Tunnel, which has its west portal near Mellingen and its east portal near Killwangen. The line was built in the 1970s as part of the planned '' New Main Transversal'' (''Neue Haupttransversale'', NHT) project. It was opened on 1 June 1975 and handed over for scheduled operations on 22 May 1975. Route The Heitersberg route branches off from the Zürich– Baden–Aarau–Olten–Bern main line after Killwangen and runs through an almost five kilometre-long tunnel to Heitersberg (west portal at , east portal at ), connecting in Mellingen with the line from Wettingen built by the Swiss National Railway (''Schweizerische Nationalbahn'') and in Othmarsingen with the Brugg–Hendschiken railway line from Brugg AG to Rotkreuz. Ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zofingen–Wettingen Railway Line
The Zofingen–Wettingen railway line is a standard-gauge line in Switzerland. It was opened on 6 September 1877 between Zofingen and Baden Oberstadt together with the Aarau–Suhr railway by the Swiss National Railway (''Schweizerische Nationalbahn''; SNB). The opening of the adjacent Baden Oberstadt–Wettingen section together with the Wettingen–Effretikon railway, which represented its continuation to the east, was delayed until 15 October 1877 due to construction delays at the Limmat bridge. The SNB went bankrupt in 1878, after which the line was acquired by the Swiss Northeastern Railway (''Schweizerische Nordostbahn''; NOB) from the bankrupt estate. The NOB became part of the Swiss Federal Railways with the nationalisation of the company in 1902. History The line was built by the SNB with one track and was intended to compete with the Baden–Aarau railway of the NOB. The SNB wanted the line from Lake Constance (''Bodensee'') to western Switzerland to be as short as po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baden–Aarau Railway Line
The Baden–Aarau railway line is a railway line in the north of Switzerland. It runs from Baden via Turgi, Brugg AG and Wildegg to Aarau. Route The line runs from Baden station on the west bank of the Limmat to Turgi station, crosses the Reuss on a stone bridge (the Windisch–Gebenstorf bridge, the second oldestThe oldest railway bridge still in operation is also on the SBB line 710 between Zurich and Brugg. It is the original bridge opened in 1847 on the Swiss Northern Railway's line from Zurich to Baden over the Schäflibach in Dietikon. The small structure is now covered by the much larger structure built during the construction of the double track. railway bridge in Switzerland still in use) and continues for about 2 kilometres to the west along the Aare and then reaches Brugg AG railway station. The line then largely follows the course of the Aare to Aarau station. There are no large engineering structures apart from the Reuss Bridge. In Turgi, a line branches o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bözberg Line
Bözberg is a municipality in the district of Brugg in canton of Aargau in Switzerland. It ceased to exist in 1873, when it was split into the two new municipalities Oberbözberg and Unterbözberg. On 1 January 2013 the former municipalities of Gallenkirch, Linn, Oberbözberg and Unterbözberg merged to form the new municipality of Bözberg.Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz published by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office accessed 2 January 2013 History Gallenkirch Gallenkirch is first mentioned in 1338 as ''Gallenkilch''. During the , Gallenkirch was part of the district of |
Aargau Southern Railway
Aargau Southern Railway (german: Aargauische Südbahn) is a former railway company in Switzerland. Between 1873 and 1882, the Schweizerische Centralbahn (SCB) and the Schweizerische Nordostbahn (NOB) jointly built a connecting line to the Gotthardbahn. The line was operated by the SCB and ran from Rupperswil to Immensee. Branch lines ran from Wohlen to Bremgarten and from Hendschiken to Brugg. History The routes were opened in this order: * 23 June 1874: Rupperswil - Lenzburg - Hendschiken Hendschiken is a municipality in the district of Lenzburg in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. History Hendschiken is first mentioned in 1160 as ''Hentschikon''. During the Middle Ages, the major landowners in Hendschiken included Muri Ab ... - Wohlen * 1 June 1875: Wohlen - Muri * 1 September 1876: Wohlen - Bremgarten West * 1 December 1881: Muri - Immensee * 1 June 1882: Hendschiken - Brugg In 1902, the Aargauische Südbahn (together with the SCB and NOB) became part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Central Railway
The Swiss Central Railway (''Schweizerische Centralbahn''; SCB or S.C.B.) was one of the five major private railway companies of Switzerland. The SCB with a track length of 332 kilometres was integrated into the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) in 1902. History The SCB based in Basel was founded on 4 February 1853 by Johann Jakob Speiser, Achilles Bischoff and Karl Geigy. The shares were mainly owned by Parisian banks. But Basel banks and the cantons of Basel-Stadt and Basel-Landschaft were also involved. The issue of shares worth Swiss Francs (CHF) 36 million and bonds worth CHF 12 million were planned. Speculation on the Paris stock exchange, however, led to a sharp fall in prices. Thus, the value of the SCB shares fell from CHF 500 to 200 and the share capital finally amounted to only CHF 14.5 million. The cantons of Luzern and Bern and Bernese municipalities rescued the company by buying shares and subsidies totaling CHF 6 million. The main goal of the SCB was the cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Northeastern Railway
The Swiss Northeastern Railway (''Schweizerische Nordostbahn''; NOB) was an early railway company in Switzerland. It also operated shipping on Lake Constance (''Bodensee'') and Lake Zürich. Until the merger of the Western Swiss Railways into the Jura–Simplon Railway (JS) in 1890/91, it was the largest Swiss railway company. History The Swiss Northeast Railway was created on 1 July 1853 by the merger of the Swiss Northern Railway (''Schweizerische Nordbahn''—SNB— informally known as the ''Spanisch Brötli, Spanisch-Brötli-Bahn''), and the Zürich-Lake Constance Railway (''Zürich-Bodenseebahn''). The originally planned continuation of the Northern Railway from Baden, Switzerland, Baden to Basel initially failed due to the different interests of the cantons of Canton of Zürich, Zürich, Canton of Aargau, Aargau and Canton of Basel, Basel. The main initiator of the merger was the Zürich-based businessman Alfred Escher, who previously headed the Zürich-Lake Constance R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zürich S-Bahn
The Zürich S-Bahn (german: S-Bahn Zürich) system is a network of rail lines that has been incrementally expanded to cover the ZVV area, which comprises the entire canton of Zürich and portions of neighbouring cantons (Aargau, Glarus, Schaffhausen, Schwyz, St. Gallen, Thurgau and Zug), with a few lines extending into or crossing the territory of southern Germany. The network is one of many commuter rail operations in German speaking countries to be described as an S-Bahn. The entire ZVV S-Bahn network went into operation in May 1990, although many of the lines were already in operation. Unusual among rapid transit services, the Zürich S-Bahn provides first class commuter travel; about a quarter of seats on each train are first class. History Before the construction of the Zürich S-Bahn, most trains to Zürich terminated at Zürich Hauptbahnhof (literally ''Zürich Main Station''), apart from the Sihltal Zürich Uetliberg Bahn lines which terminated at Zürich Sel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |