|
Brothers (ship)
Several vessels have been named ''Brothers'': * was launched in 1782 at Liverpool as a Guineaman. She made seven complete voyages as a slave ship in the triangular trade in enslaved people. A French privateer captured her in 1795, on her eighth voyage after she had embarked her captives. In a highly unusual move, the privateer sold ''Brothers'' and her slaves to the master of a Spanish vessel that the privateer had captured. The purchaser then took ''Brothers'' into Havana. * was the name ship of a two-vessel class of "brick- avisos" (advice brigs), built to a design by Raymond-Antoine Haran and launched in 1787. She served the French Navy for several years carrying dispatches until in 1793 and captured her off Jérémie. The Royal Navy took her into service briefly as ''Goelan'' and sold her in 1794. As the merchant brig ''Brothers'' she appears to have sailed as a whaling ship in the British southern whale fishery until 1808 or so, and then traded between London and the . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guineaman
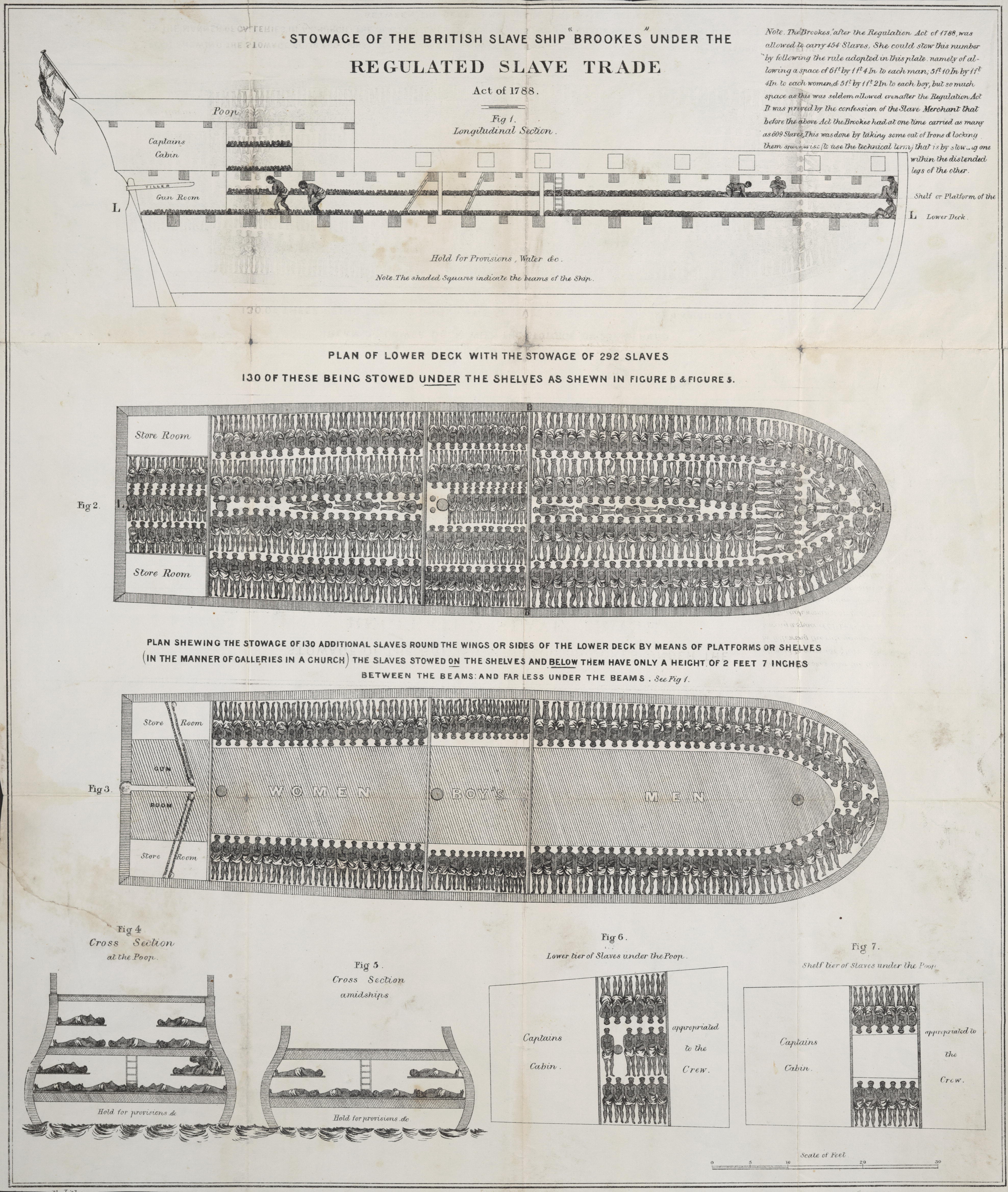
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast in West Africa. Atlantic slave trade In the early 1600s, more than a century after the arrival of Europeans to the Americas, demand for unpaid labor to work plantations made slave-trading a profitable business. The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the last two decades of the 18th century, during and following the Kongo Civil War. To ensure profitability, the owners of the ships divided their hulls into holds with little headroom, so they could transport as many slaves as possible. Unhygienic conditions, dehydration, dysentery and scurvy led to a high mortality rate, on average 15% and up to a third of captives. Often the ships carried hundreds of slaves, who were chained tightly to plank beds. For example, the slave ship ''Henrietta Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Slave Trade
upStatue of slave trader toppled_in_2020_.html" ;"title="The Centre, Bristol">The Centre, Bristol, erected in 1895, Statue of Edward Colston#Toppling and removal">toppled in 2020 ">The Centre, Bristol">The Centre, Bristol, erected in 1895, Statue of Edward Colston#Toppling and removal">toppled in 2020 Bristol, a port city in south-west England, was involved in the transatlantic slave trade. Bristol's part in the trade was prominent in the 17th and 18th centuries as the city's merchants used their position to gain involvement. It is estimated that over 500,000 enslaved African people were traded by Bristol merchants. Background Located on the banks of the River Avon in the South West of England, the city of Bristol has been an important location for maritime trade for centuries. In the Anglo-Saxon period slaves were exported from a number of ports, but after the Norman Conquest churchmen called for its abolition. Bristol was the main centre and slaves were brought there from al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penal Transportation
Penal transportation or transportation was the relocation of convicted criminals, or other persons regarded as undesirable, to a distant place, often a colony, for a specified term; later, specifically established penal colonies became their destination. While the prisoners may have been released once the sentences were served, they generally did not have the resources to return home. Origin and implementation Banishment or forced exile from a polity or society has been used as a punishment since at least the 5th century BC in Ancient Greece. The practice of penal transportation reached its height in the British Empire during the 18th and 19th centuries. Transportation removed the offender from society, mostly permanently, but was seen as more merciful than capital punishment. This method was used for criminals, debtors, military prisoners, and political prisoners. Penal transportation was also used as a method of colonization. For example, from the earliest days of English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world. The EIC had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three Presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time. The operations of the company had a profound effect on the global balance of trade, almost single-handedly reversing the trend of eastward drain of Western bullion, seen since Roman times. Originally chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies", the company rose to account for half of the world's trade duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitby
Whitby is a seaside town, port and civil parish in the Scarborough borough of North Yorkshire, England. Situated on the east coast of Yorkshire at the mouth of the River Esk, Whitby has a maritime, mineral and tourist heritage. Its East Cliff is home to the ruins of Whitby Abbey, where Cædmon, the earliest recognised English poet, lived. The fishing port emerged during the Middle Ages, supporting important herring and whaling fleets, and was where Captain Cook learned seamanship and, coincidentally, where his vessel to explore the southern ocean, ''The Endeavour'' was built.Hough 1994, p. 55 Tourism started in Whitby during the Georgian period and developed with the arrival of the railway in 1839. Its attraction as a tourist destination is enhanced by the proximity of the high ground of the North York Moors national park and the heritage coastline and by association with the horror novel '' Dracula''. Jet and alum were mined locally, and Whitby jet, which was mined by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nantucket
Nantucket () is an island about south from Cape Cod. Together with the small islands of Tuckernuck and Muskeget, it constitutes the Town and County of Nantucket, a combined county/town government that is part of the U.S. state of Massachusetts. It is the only such consolidated town-county in Massachusetts. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,255, making it the least populated county in Massachusetts. Part of the town is designated the Nantucket CDP, or census-designated place. The region of Surfside on Nantucket is the southernmost settlement in Massachusetts. The name "Nantucket" is adapted from similar Algonquian names for the island, but is very similar to the endonym of the native Nehantucket tribe that occupied the region at the time of European settlement. Nantucket is a tourist destination and summer colony. Due to tourists and seasonal residents, the population of the island increases to at least 50,000 during the summer months. The average sale price f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hired Armed Vessel
During the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries the Royal Navy made use of a considerable number of hired armed vessels. These were generally smaller vessels, often cutters and luggers, that the Navy used for duties ranging from carrying and passengers to convoy escort, particularly in British coastal waters, and reconnaissance.Winfield (2008), p.387. Doctrine The Navy Board usually hired the vessel complete with master and crew rather than bareboat. Contracts were for a specified time or on an open-ended monthly hire basis. During periods of peace, such as the period between the Treaty of Amiens and the commencement of the Napoleonic Wars, the Admiralty returned the vessels to their owners, only to rehire many on the outbreak of war. The Admiralty provided a regular naval officer, usually a lieutenant for the small vessels, to be the commander. The civilian master then served as the sailing master. For purposes of prize money or salvage, hired armed vessels received the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Builder's Old Measurement
Builder's Old Measurement (BOM, bm, OM, and o.m.) is the method used in England from approximately 1650 to 1849 for calculating the cargo capacity of a ship. It is a volumetric measurement of cubic capacity. It estimated the tonnage of a ship based on length and maximum beam (nautical), beam. It is expressed in "tons burden" ( en-em , burthen , enm , byrthen ), and abbreviated "tons bm". The formula is: : \text = \frac where: * ''Length'' is the length, in foot (length), feet, from the stem (ship), stem to the sternpost; * ''Beam (nautical), Beam'' is the maximum beam, in feet. The Builder's Old Measurement formula remained in effect until the advent of steam propulsion. Steamships required a different method of estimating tonnage, because the ratio of length to beam was larger and a significant volume of internal space was used for boilers and machinery. In 1849, the Moorsom System was created in the United Kingdom. The Moorsom system calculates the cargo-carrying capaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Passage
The Middle Passage was the stage of the Atlantic slave trade in which millions of enslaved Africans were transported to the Americas as part of the triangular slave trade. Ships departed Europe for African markets with manufactured goods (first side of the triangle), which were then traded for slaves with rulers of African states and other African slave traders. Slave ships (also known as Guineamen) transported the slaves across the Atlantic (second side of the triangle). The proceeds from selling slaves was then used to buy products such as hides, tobacco, sugar, rum, and raw materials, which would be transported back to northern Europe (third side of the triangle) to complete the triangle. The First Passage was the forced march of African slaves from their inland homes, where they had often been captured by other tribes or by other members of their own tribe, to African ports where they were imprisoned until they were sold and loaded onto a ship. The Final Passage was the journ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centuries, they began fighting the American Revolutionary War in April 1775 and formed the United States of America by United States Declaration of Independence, declaring full independence in July 1776. Just prior to declaring independence, the Thirteen Colonies in their traditional groupings were: New England (Province of New Hampshire, New Hampshire; Province of Massachusetts Bay, Massachusetts; Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Rhode Island; Connecticut Colony, Connecticut); Middle (Province of New York, New York; Province of New Jersey, New Jersey; Province of Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania; Delaware Colony, Delaware); Southern (Province of Maryland, Maryland; Colony of Virginia, Virginia; Provin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slave Ship
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast in West Africa. Atlantic slave trade In the early 1600s, more than a century after the arrival of Europeans to the Americas, demand for unpaid labor to work plantations made slave-trading a profitable business. The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the last two decades of the 18th century, during and following the Kongo Civil War. To ensure profitability, the owners of the ships divided their hulls into holds with little headroom, so they could transport as many slaves as possible. Unhygienic conditions, dehydration, dysentery and scurvy led to a high mortality rate, on average 15% and up to a third of captives. Often the ships carried hundreds of slaves, who were chained tightly to plank beds. For example, the slave ship ''Henrietta Marie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
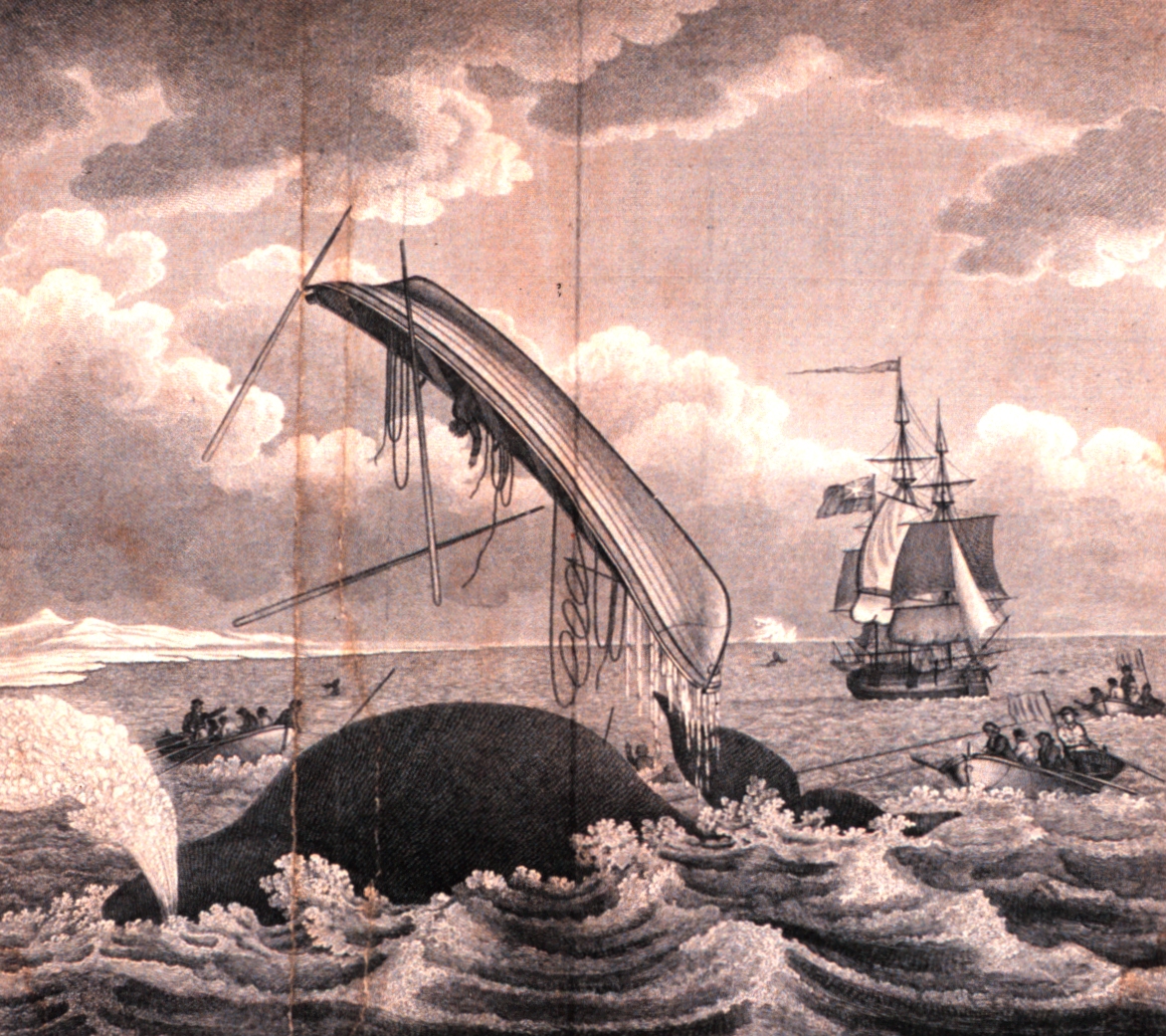
Whaling In The United Kingdom
Commercial whaling in Britain began late in the 16th century and continued after the 1801 formation of the United Kingdom and intermittently until the middle of the 20th century. The trade was broadly divided into two branches. The northern fishery involved hunting the bowhead whale off the coast of Greenland and adjacent islands. The southern fishery was activity anywhere else, including in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans and off the Antarctic. The Sperm whale, the Southern right whale and Humpback whale were the main target species in South Sea whaling. The industry went on to become a profitable national enterprise and a source of skilled mariners for the Royal Navy in times of war. Modern whaling, using factory ships and catchers fitted with bow-mounted cannons that fired explosive harpoons, continued into the 20th century and was mainly focused on the Antarctic and nearby islands where shore stations had been established. The collapse of whale stocks in the 1960s, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)








