|
Bronze Age Literature
Ancient literature comprises religious and scientific documents, tales, poetry and plays, royal edicts and declarations, and other forms of writing that were recorded on a variety of media, including stone, stone tablets, papyri, palm leaves, and metal. Before the spread of writing, oral literature did not always survive well, but some texts and fragments have persisted. One can conclude that an unknown number of written works too have likely not survived the ravages of time and are therefore lost. Incomplete list of ancient texts Bronze Age Early Bronze Age: 3rd millennium BC (approximate dates shown). The earliest written literature dates from about 2600 BC (classical Sumerian). The earliest literary author known by name is Enheduanna, a Sumerian priestess and public figure dating to ca. 24th century BC. Certain literary texts are difficult to date, such as the '' Egyptian Book of the Dead'', which was recorded in the '' Papyrus of Ani'' around 1240 BC, but other versions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Literature
Oral literature, orature or folk literature is a genre of literature that is spoken or sung as opposed to that which is written, though much oral literature has been transcribed. There is no standard definition, as anthropologists have used varying descriptions for oral literature or folk literature. A broad conceptualization refers to it as literature characterized by oral transmission and the absence of any fixed form. It includes the stories, legends, and history passed through generations in a spoken form. Background Pre-literate societies, by definition, have no written literature, but may possess rich and varied oral traditions—such as folk epics, folk narratives (including fairy tales and fables), folk drama, proverbs and folksongs—that effectively constitute an oral literature. Even when these are collected and published by scholars such as folklorists and paremiographers, the result is still often referred to as "oral literature". The different genres of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
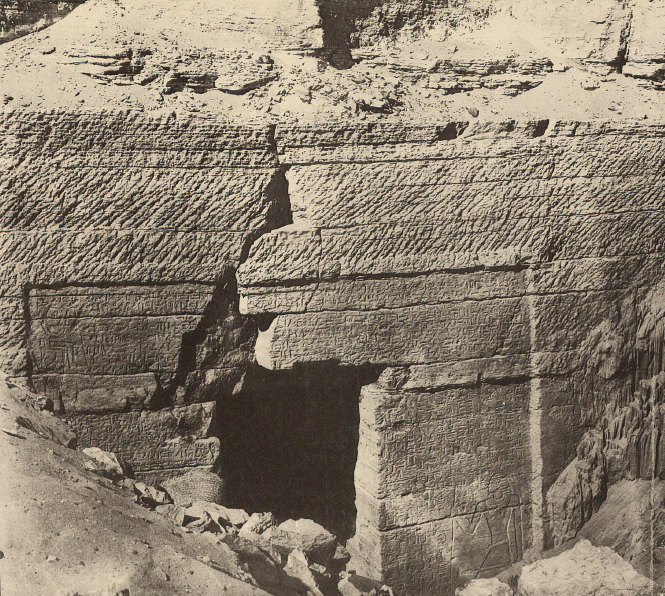
Autobiography Of Weni
The Autobiography of Weni is a tomb inscription from ancient Egypt, which is significant to Egyptology studies. Weni the Elder, or Uni, was a court official of the 6th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt. The Tomb of Weni was lost as a result of Auguste Mariette's 1880 description of Weni's tomb being unclear (" nthe high hill which gives the middle cemetery its name"). It was rediscovered in 1999 by an American archaeologist team led by Dr. Janet Richards. More recent works in the necropolis of Pepi I in Saqqara uncovered a second tomb for Weni with a near-identical copy of his biography. Biography Weni began his career under Teti, and rose through the ranks of the administration under Pepi I Meryre, for whom he was in turn a judge, a general and a vizier. Later, Weni became the governor of Upper Egypt during the reign of Merenre Nemtyemsaf I. As judge he investigated the queen who was apparently suspected of involvement in a conspiracy. While he was general, he reorganized the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
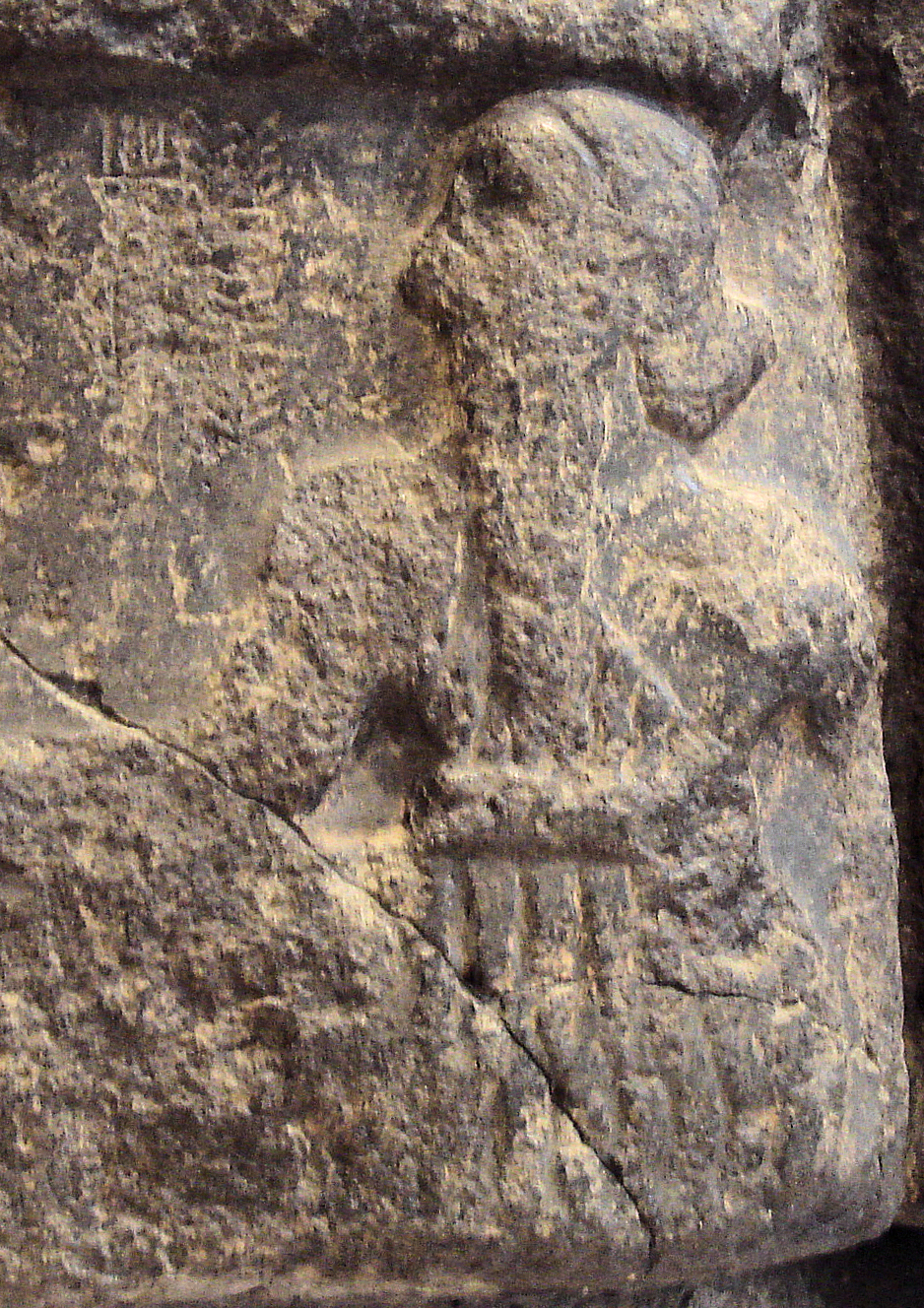
Legend Of Etana
Etana (, ''E.TA.NA'') was the probably fictional thirteenth king of the first dynasty of Kish. He is listed in the ''Sumerian King List'' as the successor of Arwium, the son of Mashda, as king of Kish. The list also calls Etana "the shepherd, who ascended to heaven and consolidated all the foreign countries", and states that he ruled 1,560 years (some copies read 635) before being succeeded by his son Balih, said to have ruled 400 years. The kings on the early part of the ''SKL'' are usually not considered historical, except when they are mentioned in contemporary Early Dynastic documents. Etana is not one of them. Myth of Etana A Babylonian legend says that Etana was desperate to have a child, until one day he helped save an eagle from starving, who then took him up into the sky to find the plant of birth. This led to the birth of his son, Balih. In the detailed form of the legend, there is a tree with the eagle's nest at the top, and a serpent at the base. Both the serp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laws Of Eshnunna
The Laws of Eshnunna (abrv. LE) are inscribed on two cuneiform tablets discovered in Tell Abū Harmal, Baghdad, Iraq. The Iraqi Directorate of Antiquities headed by Taha Baqir unearthed two parallel sets of tablets in 1945 and 1947. The two tablets are separate copies of an older source and date back to ca. 1930 BC. An additional fragment was later found at Me-Turan. The differences between the Code of Hammurabi and the Laws of Eshnunna significantly contributed to illuminating the development of ancient and cuneiform law. Eshnunna was north of Ur on the Tigris River and became politically important after the fall of the third dynasty of Ur, founded by Ur-Nammu. In distinction from the other Mesopotamian collections of law, this one got its name after the city where it had originated – Eshnunna, located on the bank of the Diyala River, tributary to the Tigris. This collection of laws is not a real systemized codex; nearly sixty of its sections are preserved. The Laws are written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tale Of The Shipwrecked Sailor
The "Tale of the Shipwrecked Sailor" is a Middle Kingdom story of an Ancient Egyptian voyage to "the King's mines". Historical information At least one source states that the papyrus having the story written upon it is located within the Imperial Museum in St. Petersburg, but that there is no information about where it was originally discovered. Alternatively it is stated that, in fact, Vladimir Golénishcheff discovered the papyrus in 1881 (also stated as a finding originating from the Middle Kingdom). The scribe who copied it, and who claimed to be "''excellent of fingers''" (''cunning of fingers'') despite having made a few slips in the copying, is known as Amenaa, or Ameni-amenna. The signature of Amenaa was mentioned in the 1987 edition of The Guinness Book of Records as the oldest surviving signature on a papyrus. Synopsis The tale begins with a ''follower'' (sailor) announcing or stating his return from a voyage at sea. He is returning from an apparently failed exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
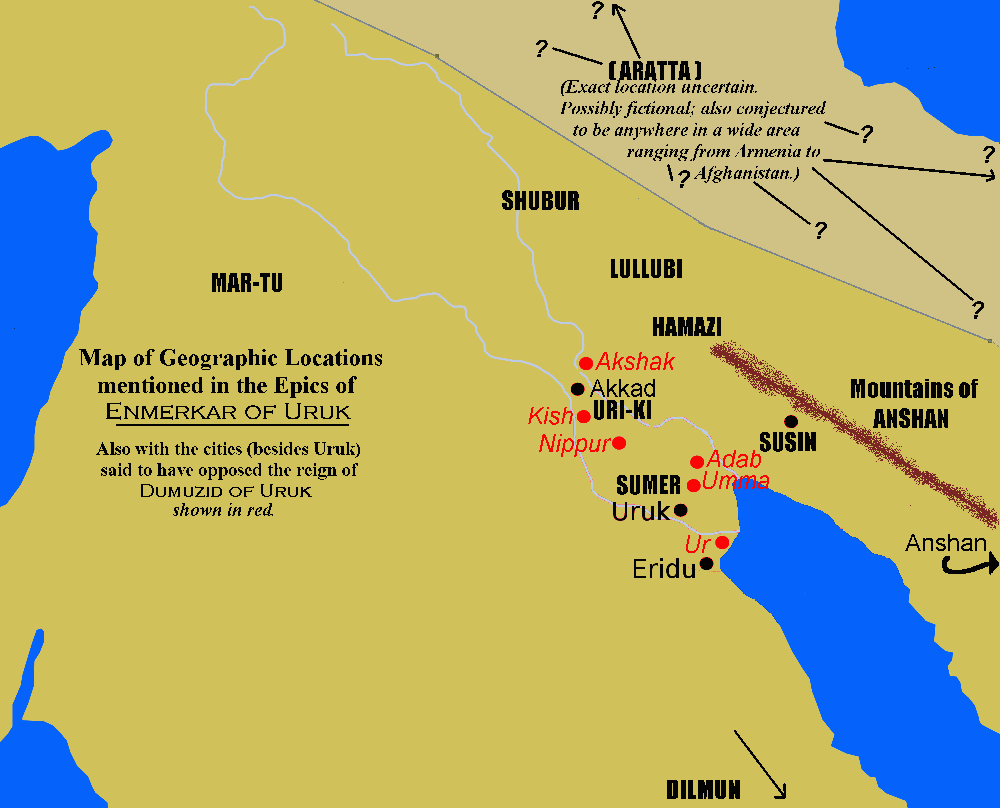
Enmerkar And The Lord Of Aratta
''Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta'' is a legendary Sumerian account, preserved in early post-Sumerian copies, composed in the Neo-Sumerian period (ca. 21st century BC). It is one of a series of accounts describing the conflicts between Enmerkar, king of Unug-Kulaba, and the unnamed king of Aratta. Because it gives a Sumerian account of the "confusion of tongues", and also involves Enmerkar constructing temples at Eridu and Uruk, it has, since the time of Samuel Kramer, been compared with the Tower of Babel narrative in the Book of Genesis. Synopsis Near the beginning of the account, the following background is provided: "In those days of yore, when the destinies were determined, the great princes allowed Unug Kulaba's ''E-ana'' to lift its head high. Plenty, and carp floods and the rain which brings forth dappled barley were then increased in Unug Kulaba. Before the land of Dilmun yet existed, the ''E-ana'' of Unug Kulaba was well founded." '' E-ana'' was a temple in Uruk bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lament For Ur
The Lament for Ur, or Lamentation over the city of Ur is a Sumerian lament composed around the time of the fall of Ur to the Elamites and the end of the city's third dynasty (c. 2000 BC). Laments It contains one of five known Mesopotamian "city laments"—dirges for ruined cities in the voice of the city's tutelary goddess. The other city laments are: *The Lament for Sumer and Ur *The Lament for Nippur *The Lament for Eridu *The Lament for Uruk The Book of Lamentations of the Old Testament, which bewails the destruction of Jerusalem by Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon in the sixth century B.C., is similar in style and theme to these earlier Mesopotamian laments. Similar laments can be found in the Book of Jeremiah, the Book of Ezekiel and the Book of Psalms, Psalm 137 (). Compilation The first lines of the lament were discovered on the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology catalogue of the Babylonian section, tablet numbers 2204, 2270, 2302 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffin Texts
The Coffin Texts are a collection of ancient Egyptian funerary spells written on coffins beginning in the First Intermediate Period. They are partially derived from the earlier Pyramid Texts, reserved for royal use only, but contain substantial new material related to everyday desires, indicating a new target audience of common people. Coffin texts are dated back to 2100 BCE. Ordinary Egyptians who could afford a coffin had access to these funerary spells and the pharaoh no longer had exclusive rights to an afterlife. As the modern name of this collection of some 1,185 spells implies, they were mostly inscribed on Middle Kingdom coffins. They were also sometimes written on tomb walls, stelae, canopic chests, papyri and mummy masks. Due to the limited writing surfaces of some of these objects, the spells were often abbreviated, giving rise to long and short versions, some of which were later copied in the Book of the Dead. Content In contrast to the Pyramid Texts which focus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code Of Ur-Nammu
The Code of Ur-Nammu is the oldest known law code surviving today. It is from Mesopotamia and is written on tablets, in the Sumerian language c. 2100–2050 BCE. Discovery The first copy of the code, in two fragments found at Nippur, in what is now Iraq, was translated by Samuel Kramer in 1952. These fragments are held at the Istanbul Archaeological Museums. Owing to its partial preservation, only the prologue and five of the laws were discernible.Kramer, ''History begins at Sumer'', pp. 52–55. Kramer noted that luck was involved in the discovery: Further tablets were found in Ur and translated in 1965, allowing some 30 of the 57 laws to be reconstructed. Another copy found in Sippar contains slight variants. Background The preface directly credits the laws to king Ur-Nammu of Ur (2112–2095 BCE). The author who had the laws written onto cuneiform tablets is still somewhat under dispute. Some scholars have attributed it to Ur-Nammu's son Shulgi. Although it is known tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debate Between Bird And Fish
The "Debate between bird and fish" is an essay written in the Sumerian language on clay tablets, dating back to the mid to late 3rd millennium BC. Seven ''"debate"'' topics are known from Sumerian literature, falling in the category of 'disputations'; some examples are: The Debate between Winter and Summer; Debate between sheep and grain; the Tree and the Reed; bird and fish; and ''The Dispute between Silver and Mighty Copper'', etc. These appeared some centuries after writing was established in Sumerian Mesopotamia. The debates are philosophical and address humanity's place in the world. Some of the debates may be from 2100 BC. The bird and fish debate is a 190-line text of cuneiform script. It begins with a discussion of the gods having given Mesopotamia and dwelling places for humans; for water for the fields, the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, and the marshes, marshland, grazing lands for humans, and the birds of the marshes, and fish are all given. The debate then begins st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia after the long-lived civilization of Sumer. It was centered in the city of Akkad (city), Akkad () and its surrounding region. The empire united Akkadian language, Akkadian and Sumerian language, Sumerian speakers under one rule. The Akkadian Empire exercised influence across Mesopotamia, the Levant, and Anatolia, sending military expeditions as far south as Dilmun and Magan (civilization), Magan (modern Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, and Oman) in the Arabian Peninsula.Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. "Akkad" ''Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary''. ninth ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster 1985. ). The Akkadian Empire reached its political peak between the 24th and 22nd centuries BC, following the conquests by its founder Sargon of Akkad. Under Sargon and his successors, the Akkadian language was briefly imposed on neighboring conquered states such as Elam and Gutian people, Gutium. Akkad is sometimes regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autobiography Of Harkhuf
The Autobiography of Harkhuf is a private tomb inscription from ancient Egypt. It is significant in Egyptology as one of the two most important, and the most famous, autobiographical inscriptions of Old Kingdom officials. His name sometimes spelled as Herkhuf, Horkhuf, or Hirkhuf, all that is known of his life comes from the inscriptions in his tomb at Qubbet el-Hawa on the west bank of the Nile at Aswan, near the First Cataract of the Nile. He was a native of Elephantine. Harkhuf served under kings Merenre I, fourth king of the 6th Dynasty (ca. 2255–2246 B.C.), and Pepi II, the last powerful king of the 6th Dynasty (ca. 2246–2152 B.C.). He was appointed governor of Upper Egypt. His primary business was trade with Nubia, forging political bonds with local leaders, and preparing the ground for an Egyptian expansion into Nubia. He led four major expeditions to Nubia. His written account of these expeditions is the most important source for Egypt's relations with Nubia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |