|
Brontok
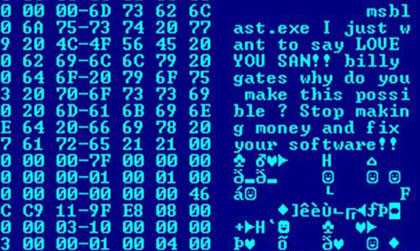
Brontok is a computer worm running on Microsoft Windows. It is able to disperse by e-mail. Variants include: * Brontok.A * Brontok.D * Brontok.F * Brontok.G * Brontok.H * Brontok.I * Brontok.K * Brontok.Q * Brontok.U * Brontok.BH The most affected countried were Russia, Vietnam and Brazil, followed by Spain, Mexico, Iran, Azerbaijan, India and the Philippines. Other names Other names for this worm include: W32/Rontokbro.gen@MM, W32.Rontokbro@mm, BackDoor.Generic.1138, W32/Korbo-B, Worm/Brontok.a, Win32.Brontok.A@mm, Worm.Mytob.GH, W32/Brontok.C.worm, Win32/Brontok.E, Win32/Brontok.X@mm, and W32.Rontokbro.D@mm. Origin Brontok originated in Indonesia. It was first discovered in 2005. The name refers to ''elang brontok'', a bird species native to South & Southeast Asia. It arrives as an attachment of e-mail named kangen.exe (''kangen'' itself means "to miss someone/thing"). The virus/email itself contains a message in Indonesian (and some English). When translated, this read ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaskus
Kaskus is an Indonesian Internet forum that describes itself as "the largest Indonesian community". Registration is required for new users to participate in the community, and every registered member has access to more than twenty regional and subject-related sub-forums. The community initially used the vBulletin forum but switched to a new engine they developed called "New Kaskus" in mid-2012. History Kaskus was created on November 6, 1999 by Indonesian students Andrew Darwis, Ronald Stephanus, Ken Dean Lawadinata and Budi Dharmawan. Kaskus was originally intended as an informal forum for abroad Indonesian students. The name Kaskus itself is an abbreviation of the word ''"Kasak-Kusuk"'' which translates to 'gibberish' or 'whispers'. ''PC Magazine Indonesia'' named Kaskus in August 2005 as being the best site and largest online community and in 2006, as the choice of readers in 2006. On May 23, 2006, the management was forced to change their .com domain to .us, due to the outbrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daprosy Worm
Daprosy worm was a malicious computer program that spreads via local area network (LAN) connections, spammed e-mails and USB mass storage devices. Infection comes from a single read1st.exe file where several dozen clones are created at once bearing the names of compromised folders. The most obvious symptom of Daprosy infection is the presence of ''Classified.exe'' or ''Do not open - secrets!.exe'' files from infected folders. Although first observed in early May 2009, the worm was first announced to the public as Daprosy trojan worm by Symantec in July 2009 and was later identified as Autorun-AMS, Autorun-AMW and Autorun-APL by Sophos. It acquired additional aliases from antivirus companies and others tag it as an incarnation or variation of the Autorun.H. The worm belongs to the “slow” mass mailer category where copies of which are attached and sent to addresses intercepted from the keyboard. The e-mail consists of a promotion of and installation instruction for an im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Email Worms
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic (digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" meant only physical mail (hence '' e- + mail''). Email later became a ubiquitous (very widely used) communication medium, to the point that in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries. ''Email'' is the medium, and each message sent therewith is also called an ''email.'' The term is a mass noun. Email operates across computer networks, primarily the Internet, and also local area networks. Today's email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver, and store messages. Neither the users nor their computers are required to be online simultane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software (abbreviated to AV software), also known as anti-malware, is a computer program used to prevent, detect, and remove malware. Antivirus software was originally developed to detect and remove computer viruses, hence the name. However, with the proliferation of other malware, antivirus software started to protect from other computer threats. In particular, modern antivirus software can protect users from malicious browser helper objects (BHOs), browser hijackers, ransomware, keyloggers, backdoors, rootkits, trojan horses, worms, malicious LSPs, dialers, fraud tools, adware, and spyware. Some products also include protection from other computer threats, such as infected and malicious URLs, spam, scam and phishing attacks, online identity (privacy), online banking attacks, social engineering techniques, advanced persistent threat (APT), and botnet DDoS attacks. History 1949–1980 period (pre-antivirus days) Although the roots of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, which was released five years before, at the time being the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows desktop operating systems. Development was completed on November 8, 2006, and over the following three months, it was released in stages to computer hardware and software manufacturers, business customers and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; it is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform. New features of Windows Vista include an updated graphical user interface and visual style dubbed Aero, a new search component called Windows Search, redesigned networking, audio, print and display sub-systems, and new multimedia tools such as Windows DVD Maker. Vist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript. Web browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and render the documents into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page semantically and originally included cues for the appearance of the document. HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages. With HTML constructs, images and other objects such as interactive forms may be embedded into the rendered page. HTML provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, links, quotes, and other items. HTML elements are delineated by ''tags'', written using angle brackets. Tags such as and directly introduce content into the page. Other tags such as sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Command Prompt
Command Prompt, also known as cmd.exe or cmd, is the default command-line interpreter for the OS/2, eComStation, ArcaOS, Microsoft Windows ( Windows NT family and Windows CE family), and ReactOS operating systems. On Windows CE .NET 4.2, Windows CE 5.0 and Windows Embedded CE 6.0 it is referred to as the Command Processor Shell. Its implementations differ between operating systems, but the behavior and basic set of commands are consistent. is the counterpart of in DOS and Windows 9x systems, and analogous to the Unix shells used on Unix-like systems. The initial version of for Windows NT was developed by Therese Stowell. Windows CE 2.11 was the first embedded Windows release to support a console and a Windows CE version of . The ReactOS implementation of is derived from FreeCOM, the FreeDOS command line interpreter. Operation interacts with the user through a command-line interface. On Windows, this interface is implemented through the Win32 console. may take ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Explorer
File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is a file manager application that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface for accessing the file systems. It is also the component of the operating system that presents many user interface items on the screen such as the taskbar and desktop. Controlling the computer is possible without Windows Explorer running (for example, the command in Task Manager on NT-derived versions of Windows will function without it, as will commands typed in a command prompt window). Overview Windows Explorer was first included with Windows 95 as a replacement for File Manager, which came with all versions of Windows 3.x operating systems. Explorer could be accessed by double-clicking the new My Computer desktop icon or launched from the new Start Menu that replaced the earlier Program Manager. There is also a shortcut key combination: . Successive version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regedit
The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores low-level settings for the Microsoft Windows operating system and for applications that opt to use the registry. The kernel, device drivers, services, Security Accounts Manager, and user interfaces can all use the registry. The registry also allows access to counters for profiling system performance. In other words, the registry or Windows Registry contains information, settings, options, and other values for programs and hardware installed on all versions of Microsoft Windows operating systems. For example, when a program is installed, a new subkey containing settings such as a program's location, its version, and how to start the program, are all added to the Windows Registry. When introduced with Windows 3.1, the Windows Registry primarily stored configuration information for COM-based components. Windows 95 and Windows NT extended its use to rationalize and centralize the information in the profusion of INI files, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Registry
The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores low-level settings for the Microsoft Windows operating system and for applications that opt to use the registry. The kernel, device drivers, services, Security Accounts Manager, and user interfaces can all use the registry. The registry also allows access to counters for profiling system performance. In other words, the registry or Windows Registry contains information, settings, options, and other values for programs and hardware installed on all versions of Microsoft Windows operating systems. For example, when a program is installed, a new subkey containing settings such as a program's location, its version, and how to start the program, are all added to the Windows Registry. When introduced with Windows 3.1, the Windows Registry primarily stored configuration information for COM-based components. Windows 95 and Windows NT extended its use to rationalize and centralize the information in the profusion of INI fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Worm
A computer worm is a standalone malware computer program that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers. It often uses a computer network to spread itself, relying on security failures on the target computer to access it. It will use this machine as a host to scan and infect other computers. When these new worm-invaded computers are controlled, the worm will continue to scan and infect other computers using these computers as hosts, and this behaviour will continue. Computer worms use recursive methods to copy themselves without host programs and distribute themselves based on the law of exponential growth, thus controlling and infecting more and more computers in a short time. Worms almost always cause at least some harm to the network, even if only by consuming bandwidth, whereas viruses almost always corrupt or modify files on a targeted computer. Many worms are designed only to spread, and do not attempt to change the systems they pass through. However, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |