|
Bromus Aleutensis
''Bromus aleutensis'', commonly known as the Aleutian brome, is a perennial grass found in North America. ''B. aleutensis'' has a diploid number of 56. Taxonomy It has been suggested that ''Bromus aleutensis'' may be a modified version of the similar '' Bromus sitchensis'' in which reproduction occurs at an earlier developmental state as a response to the climate of the Aleutian Islands. In addition, while ''B. aleutensis'' is mostly self-fertilizing and ''B. sitchensis'' is mostly outcrossing, anther lengths close to in some individuals of ''B. aleutensis'' suggests outcrossing. Description ''B aleutensis'' is a perennial grass that is loosely cespitose. The decumbent culms are tall and thick. The striate and pilose leaf sheaths have dense hairs. Auricles are rarely present. The glabrous ligules are long. The somewhat pilose leaf blades are long and wide. The open panicles are long. Lower branches of the inflorescence are long and number one to two per node, with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Bernhard Von Trinius
Carl Bernhard von Trinius (6 March 1778, Eisleben – 12 March 1844, St. Petersburg) was a German-born botanist and physician. He studied medicine at several universities, earning his medical doctorate at the University of Göttingen in 1802. In 1808, after time spent as a physician in Hasenpoth, he served as a personal physician to Antoinette, Duchess of Württemberg (née Princess of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld) for the next 16 years. During this time period, he traveled extensively throughout Germany and Russia. In St. Petersburg, he became good friends to author Ernst Moritz Arndt. After the death of the duchess in 1824, he remained in St. Petersburg as an imperial physician, and along with a medical practice, he dealt with botanical concerns at the Academy of Sciences.biography @ |
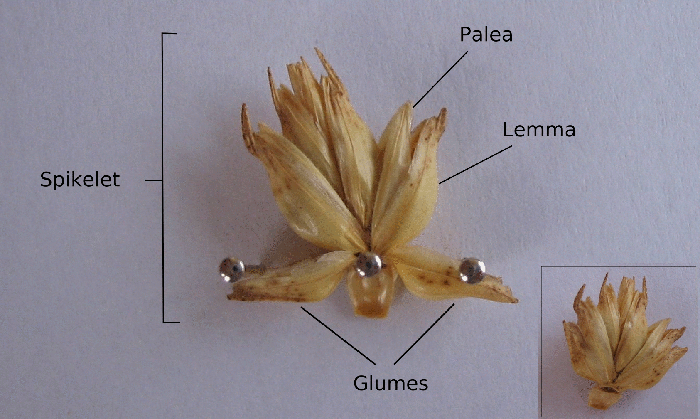
Glume
In botany, a glume is a bract (leaf-like structure) below a spikelet in the inflorescence (flower cluster) of grasses (Poaceae) or the flowers of sedges (Cyperaceae). There are two other types of bracts in the spikelets of grasses: the lemma and palea. In grasses, two bracts known as "glumes" form the lowermost organs of a spikelet (there are usually two but one is sometimes reduced; or rarely, both are absent). Glumes may be similar in form to the lemmas, the bracts at the base of each floret This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary o .... In sedges, by contrast, a glume is a scale at the base of each flower in a spikelet. References {{reflist Plant morphology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grasses Of The United States
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromus
''Bromus'' is a large genus of grasses, classified in its own tribe Bromeae. They are commonly known as bromes, brome grasses, cheat grasses or chess grasses. Estimates in the scientific literature of the number of species have ranged from 100 to 400, but plant taxonomists currently recognize around 160–170 species. ''Bromus'' is part of the cool-season grass lineage (subfamily Pooideae), which includes about 3300 species. Within Pooideae, ''Bromus'' is classified in tribe Bromeae (it is the only genus in the tribe). ''Bromus'' is closely related to the wheat-grass lineage (tribe Triticeae) that includes such economically important genera as ''Triticum'' (wheat), ''Hordeum'' (barley) and '' Secale'' (rye). Etymology The generic name ''Bromus'' is derived from the Latin ''bromos'', a borrowed word from the Ancient Greek (). and mean ''oats'', but seems to have referred specifically to ''Avena sativa'' (Hippocrates ''On Regimen in Acute Diseases'' 2.43, Dioscorides Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusarium Patch
Fusarium patch is a disease in turf grass settings also called pink snow mold or Microdochium patch. In many cool season grass species in North America, it is caused by the fungus ''Microdochium nivale'' . The white-pink mycelium on infected leaf blades is a distinguishing characteristic of the ''Microdochium nivale'' pathogen. Fusarium patch is considered economically important in the turf grass industry because of its tendency to cause significant injury to golf greens, thereby decreasing putting surface quality. Dissimilar from other snow molds, such as gray snow mold, ''Microdochium nivale'' does not need snow cover to cause widespread infection. Hosts and symptoms ''M. nivale'' can infect all cool-season turf grass species. Annual bluegrass (''Poa annua''), perennial ryegrass (''Lolium perenne'') and creeping bentgrass (''Agrostis stolonifera'') are more susceptible. In the fall, ''M.nivale'' infection begins as small, orange to red-brown spots, circular and only a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing 180th meridian, longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude (Amatignak Island) and the easternmost by longitude ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemma (botany)
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the flowers of grasses, sedges and some other Monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external—the lemma—and one internal—the palea. The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic—maize being an important exception—and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It is the lowermost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spikelets
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the flowers of grasses, sedges and some other Monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external—the lemma—and one internal—the palea. The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic—maize being an important exception—and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It is the lowermost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Heinrich Rudolf Grisebach
August Heinrich Rudolf Grisebach () was a German botanist and phytogeographer. He was born in Hannover on 17 April 1814 and died in Göttingen on 9 May 1879. Biography Grisebach studied at the Lyceum in Hanover, the cloister-school at Ilfeld, and the University of Göttingen. He graduated in medicine from the University of Berlin in 1836. He undertook expeditions to Provence, Turkey, the Balkans, and Norway. In 1837 he became associate professor and in 1847 full professor at the medical faculty in Göttingen and was named director of the botanical garden there in 1875. While his main fields of interest were phytogeography and systematics, especially the Gentianaceae and Malpighiaceae, he considered his ''Flora of the British West Indian Islands'' his most important work. Much of his collection, especially the types of species described by him, are housed at the Göttingen University Herbarium. His taxonomic classification is set out in his ''Grundriss der systematischen Botani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panicle
A panicle is a much-branched inflorescence. (softcover ). Some authors distinguish it from a compound spike inflorescence, by requiring that the flowers (and fruit) be pedicellate (having a single stem per flower). The branches of a panicle are often racemes. A panicle may have determinate or indeterminate growth. This type of inflorescence is largely characteristic of grasses such as oat and crabgrass, as well as other plants such as pistachio and mamoncillo. Botanists use the term paniculate in two ways: "having a true panicle inflorescence" as well as "having an inflorescence with the form but not necessarily the structure of a panicle". Corymb A corymb may have a paniculate branching structure, with the lower flowers having longer pedicels than the upper, thus giving a flattish top superficially resembling an umbel. Many species in the subfamily Amygdaloideae, such as hawthorns and rowans, produce their flowers in corymbs. up'' Sorbus glabrescens'' corymb with fruit See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligule
A ligule (from "strap", variant of ''lingula'', from ''lingua'' "tongue") is a thin outgrowth at the junction of leaf and leafstalk of many grasses (Poaceae) and sedges. A ligule is also a strap-shaped extension of the corolla, such as that of a ray floret in plants in the daisy family Asteraceae. Poaceae and Cyperaceae The ligule is part of the leaf that is found at the junction of the blade and sheath of the leaf. It may take several forms, but it is commonly some form of translucent membrane or a fringe of hairs. The membranous ligule can be very short 1–2 mm (Kentucky bluegrass, ''Poa pratensis'') to very long 10–20 mm (Johnson grass, ''Sorghum halepense''), it can also be smooth on the edge or very ragged. Some grasses do not have a ligule, for example barnyardgrass (''Echinochloa crus-galli''). A ligule can also be defined as a membrane-like tissue or row of delicate hairs typically found in grasses at the junction of the leaf sheath and blade. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |