|
Broad-spectrum Antibiotic
A broad-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that acts on the two major bacterial groups, Gram-positive and Gram-negative, or any antibiotic that acts against a wide range of disease-causing bacteria. These medications are used when a bacterial infection is suspected but the group of bacteria is unknown (also called empiric therapy) or when infection with multiple groups of bacteria is suspected. This is in contrast to a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, which is effective against only a specific group of bacteria. Although powerful, broad-spectrum antibiotics pose specific risks, particularly the disruption of native, normal bacteria and the development of antimicrobial resistance. An example of a commonly used broad-spectrum antibiotic is ampicillin. Bacterial targets Antibiotics are often grouped by their ability to act on different bacterial groups. Although bacteria are biologically classified using taxonomy, disease-causing bacteria have historically been classified by their micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
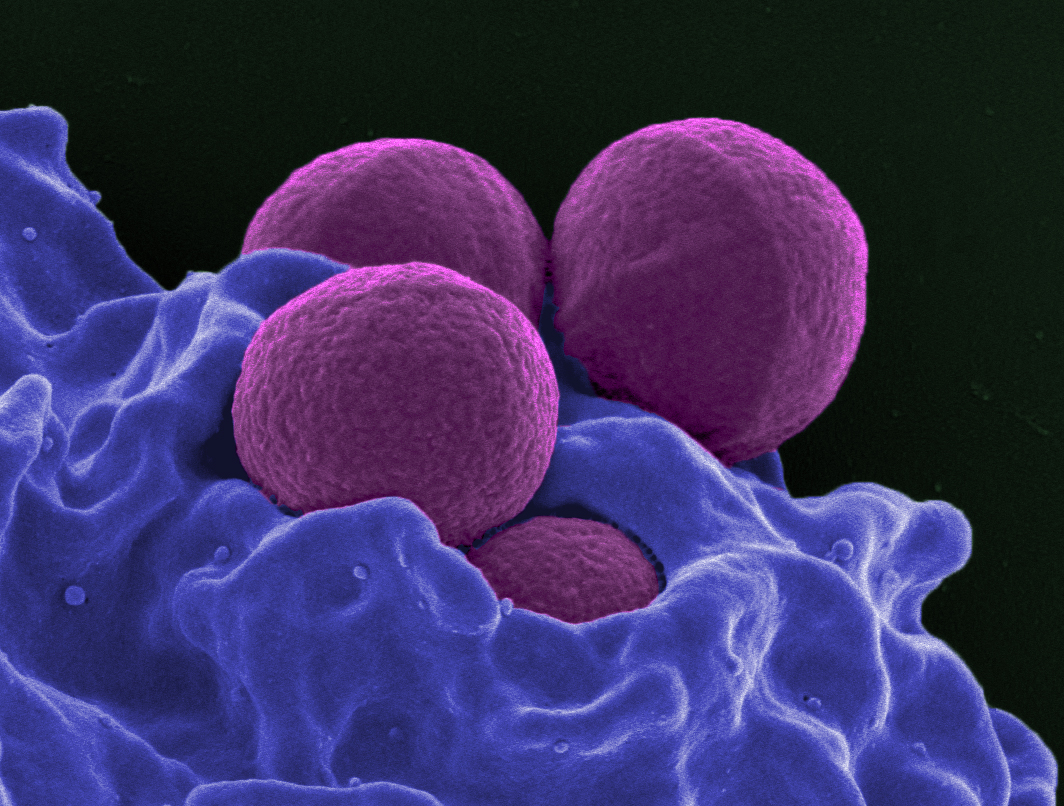
Neutrophil MRSA II
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in different animals. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiated into subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin ( H&E) histological or cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells stain dark blue and eosinophilic white blood cells stain bright red, neutrophils stain a neutral pink. Normally, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Medium
A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss ''Physcomitrella patens''. Different types of media are used for growing different types of cells. The two major types of growth media are those used for cell culture, which use specific cell types derived from plants or animals, and those used for microbiological culture, which are used for growing microorganisms such as bacteria or fungi. The most common growth media for microorganisms are nutrient broths and agar plates; specialized media are sometimes required for microorganism and cell culture growth. Some organisms, termed fastidious organisms, require specialized environments due to complex nutritional requirements. Viruses, for example, are obligate intracellular parasites and require a growth medium containing living cells. Types The most common growth media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomycin
Streptomycin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, endocarditis, brucellosis, ''Burkholderia'' infection, plague, tularemia, and rat bite fever. For active tuberculosis it is often given together with isoniazid, rifampicin, and pyrazinamide. It is administered by injection into a vein or muscle. Common side effects include vertigo, vomiting, numbness of the face, fever, and rash. Use during pregnancy may result in permanent deafness in the developing baby. Use appears to be safe while breastfeeding. It is not recommended in people with myasthenia gravis or other neuromuscular disorders. Streptomycin is an aminoglycoside. It works by blocking the ability of 30S ribosomal subunits to make proteins, which results in bacterial death. Albert Schatz first isolated streptomycin in 1943 from ''Streptomyces griseus''. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoglycosides
Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial medications that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside (sugar). The term can also refer more generally to any organic molecule that contains amino sugar substructures. Aminoglycoside antibiotics display bactericidal activity against Gram-negative aerobes and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen but generally not against Gram-positive and anaerobic Gram-negative bacteria.ME Levison, MD, 2012, Aminoglycosides, The Merck Manua accessed 22 February 2014. Streptomycin is the first-in-class aminoglycoside antibiotic. It is derived from ''Streptomyces griseus'' and is the earliest modern agent used against tuberculosis. Streptomycin lacks the common 2-deoxystreptamine moiety (image right, below) present in most other members of this class. Other examples of aminoglycosides include the deoxystreptamine-containin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minocycline
Minocycline, sold under the brand name Minocin among others, is a tetracycline antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections such as pneumonia. It is generally less preferred than the tetracycline doxycycline. It is also used for the treatment of acne and rheumatoid arthritis. It is taken by mouth or applied to the skin. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, allergic reactions, and kidney problems. Serious side effects may include anaphylaxis, a lupus-like syndrome, and easy sunburning. Use in the later part of pregnancy may harm the baby and safety during breastfeeding is unclear. It works by decreasing a bacterium's ability to make protein thus stopping its growth. Minocycline was patented in 1961 and came into commercial use in 1971. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 236th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescriptions. Medical uses Acne Minocycline and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doxycycline
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus, and syphilis. It is also used to prevent malaria in combination with quinine. Doxycycline may be taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and an increased risk of sunburn. Use during pregnancy is not recommended. Like other agents of the tetracycline class, it either slows or kills bacteria by inhibiting protein production. It kills malaria by targeting a plastid organelle, the apicoplast. Doxycycline was patented in 1957 and came into commercial use in 1967. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Doxycycline is available as a generic medicine. In 2020, it was the 79th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minocycline
Minocycline, sold under the brand name Minocin among others, is a tetracycline antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections such as pneumonia. It is generally less preferred than the tetracycline doxycycline. It is also used for the treatment of acne and rheumatoid arthritis. It is taken by mouth or applied to the skin. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, allergic reactions, and kidney problems. Serious side effects may include anaphylaxis, a lupus-like syndrome, and easy sunburning. Use in the later part of pregnancy may harm the baby and safety during breastfeeding is unclear. It works by decreasing a bacterium's ability to make protein thus stopping its growth. Minocycline was patented in 1961 and came into commercial use in 1971. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 236th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescriptions. Medical uses Acne Minocycline and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crohn's Disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer. While the precise causes of Crohn's disease (CD) are unknown, it is believed to be caused by a combination of environmental, immune, and bacterial factors in genetically susceptible individuals. It results in a chronic inflammatory disorder, in which the body's immune system defends the gastrointestinal tract, possibly targeting microbial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
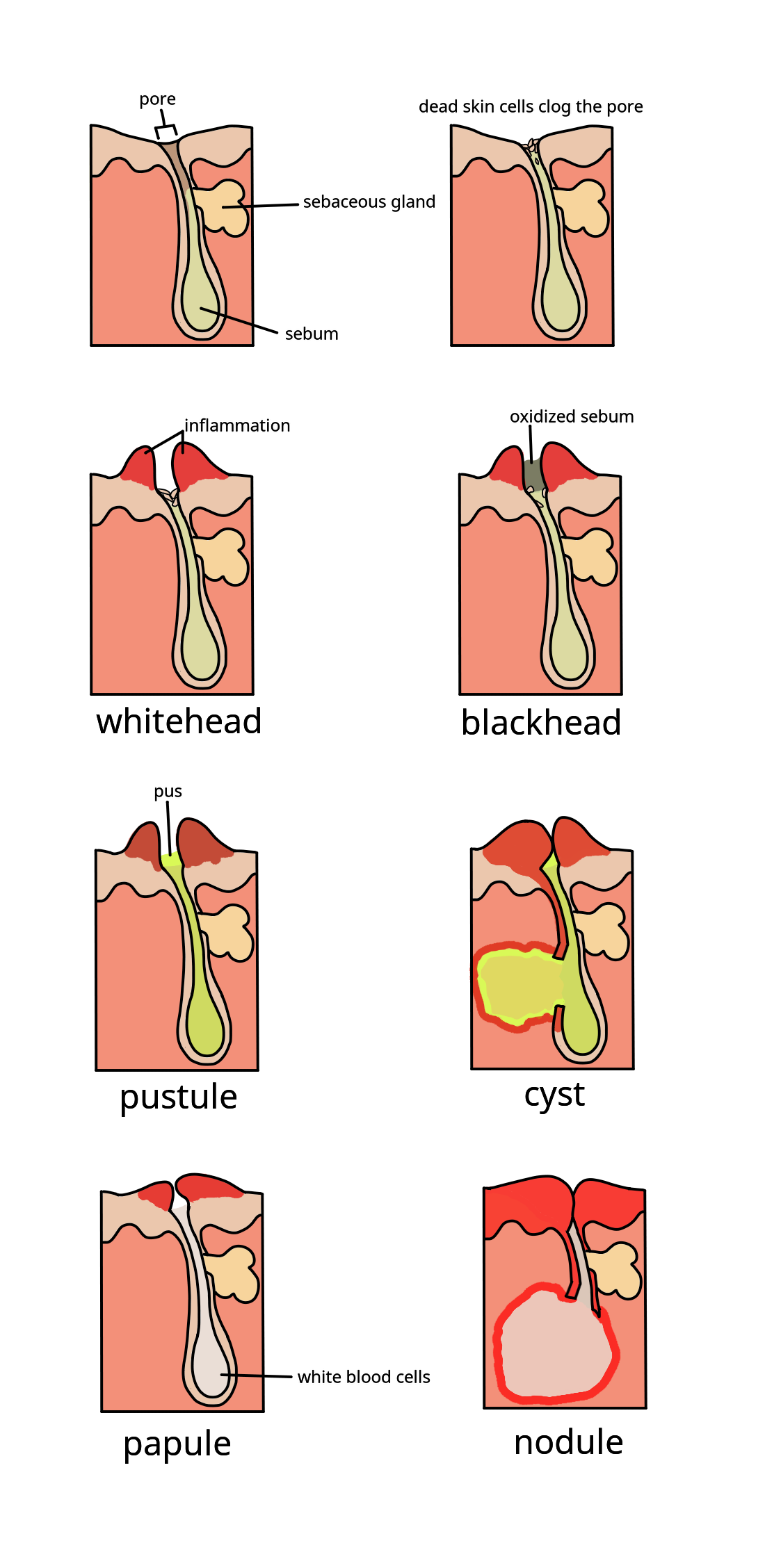
Acne Vulgaris
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight appear to play a part. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production of sebum. Another common factor is the excessive growth of the bacterium ''Cutibacterium acnes'', which is present on the skin. Treatments for acne are ava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doxycycline
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus, and syphilis. It is also used to prevent malaria in combination with quinine. Doxycycline may be taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and an increased risk of sunburn. Use during pregnancy is not recommended. Like other agents of the tetracycline class, it either slows or kills bacteria by inhibiting protein production. It kills malaria by targeting a plastid organelle, the apicoplast. Doxycycline was patented in 1957 and came into commercial use in 1967. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Doxycycline is available as a generic medicine. In 2020, it was the 79th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
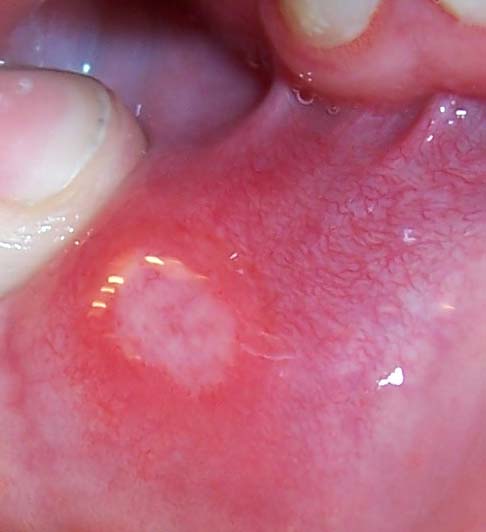
Candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of '' Candida'' (a type of yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it may be referred to as a yeast infection or thrush. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Yeast infections of the penis are less common and typically present with an itchy rash. Very rarely, yeast infections may become invasive, spreading to other parts of the body. This may result in fevers along with other symptoms depending on the parts involved. More than 20 types of ''Candida'' can cause infection with ''Candida albicans'' being the most common. Infections of the mouth are most common among children less than one month old, the elderly, and those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |