|
British South American Airways
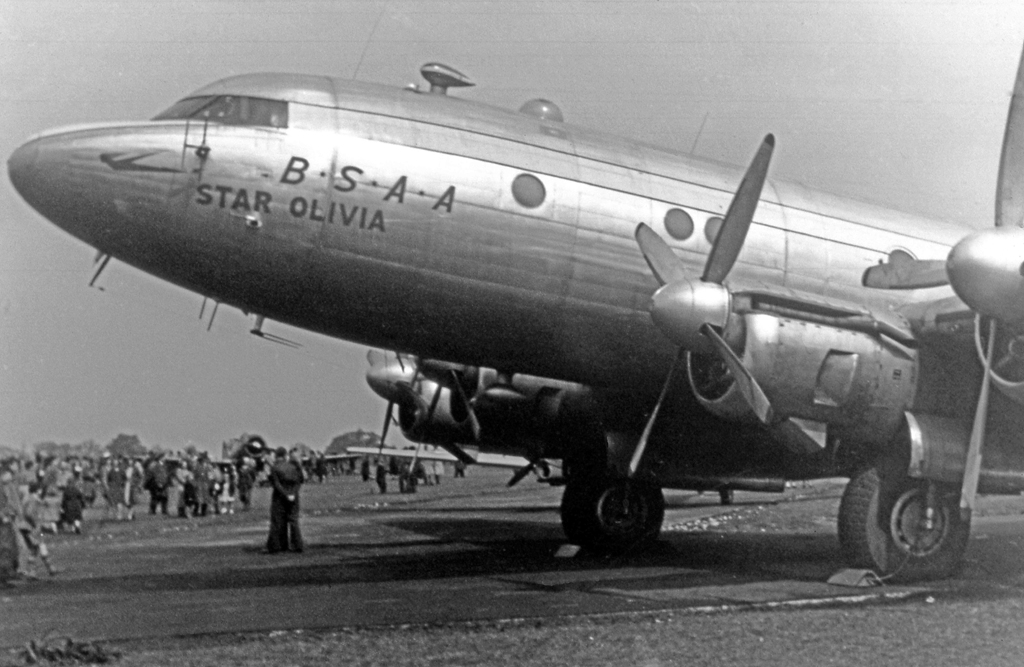
British South American Airways (BSAA) was a state-run airline of the United Kingdom in the mid-late 1940s responsible for services to the Caribbean and South America. Originally named British Latin American Air Lines it was renamed before services started in 1946. BSAA operated mostly Avro aircraft: Yorks, Lancastrians and Tudors and flew to Bermuda, the West Indies, Mexico and the western coast of South America. After two high-profile aircraft disappearances it was merged into the British Overseas Airways Corporation at the end of 1949. Most of BSAA's aircraft were given individual aircraft names beginning with "Star", which have long been used in long-range celestial navigation. History British Latin American Air Lines (BLAIR) was formed on 25 January 1944 by shipping interests (Royal Mail Lines, Pacific Steam Navigation Company, Lamport & Holt Line, Booth Steamship Company and Blue Star Line) to complement the shipping services to South America, at the end of 1945 the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langley Airfield
Langley, also known as Langley Marish, is a suburb of Slough in Berkshire, South East England. It is east of the town centre of Slough, and west of Charing Cross in Central London. It was a separate civil parish until the 1930s, when the built up part of Langley was incorporated into Slough. Langley was in the historic county of Buckinghamshire, being transferred to the administrative county of Berkshire in 1974. Etymology The place-name Langley derives from two Middle English words: ''lang'' meaning long and ''leah'', a wood or clearing. Langley was formed of a number of clearings: George Green, Horsemoor Green, Middle Green, Sawyers Green and Shreding Green. They became the sites for housing which merged into one village centred on the parish church in St Mary's Road. The clearings are remembered in the names of streets or smaller green fields. ''Marish'' or ''Maries'' commemorates Christiana de Marecis who held the manor for a short time in the reign of Edward I. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Overseas Airways Corporation
British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC) was the British state-owned airline created in 1939 by the merger of Imperial Airways and British Airways Ltd. It continued operating overseas services throughout World War II. After the passing of the Civil Aviation Act 1946, European and South American services passed to two further state-owned airlines, British European Airways (BEA) and British South American Airways (BSAA). BOAC absorbed BSAA in 1949, but BEA continued to operate British domestic and European routes for the next quarter century. A 1971 Act of Parliament merged BOAC and BEA, effective 31 March 1974, forming today's British Airways. For most of its history its main rival was Pan Am. History War years On 24 November 1939, BOAC was created by Act of Parliament to become the British state airline, formed from the merger of Imperial Airways and British Airways Ltd. The companies had been operating together since war was declared on 3 September 1939, when their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gee (navigation)
Gee, sometimes written GEE, was a radio navigation system used by the Royal Air Force during World War II. It measured the time delay between two radio signals to produce a fix, with accuracy on the order of a few hundred metres at ranges up to about . It was the first hyperbolic navigation system to be used operationally, entering service with RAF Bomber Command in 1942. Gee was devised by Robert Dippy as a short-range blind landing system to improve safety during night operations. During development by the Telecommunications Research Establishment (TRE) at Swanage, the range was found to be far better than expected. It then developed into a long-range, general navigation system. For large, fixed targets, such as the cities that were attacked at night, Gee offered enough accuracy to be used as an aiming reference without the need to use a bombsight or other external references. Jamming reduced its usefulness as a bombing aid, but it remained in use as a navigational aid in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BSAA Star Dust Accident
On 2 August 1947, ''Star Dust'', a British South American Airways (BSAA) Avro Lancastrian airliner on a flight from Buenos Aires, Argentina, to Santiago, Chile, crashed into Mount Tupungato in the Argentine Andes. An extensive search operation failed to locate the wreckage, despite covering the area of the crash site. The fate of the aircraft and its occupants remained unknown for over fifty years, giving rise to various conspiracy theories about its disappearance. In the late 1990s, pieces of wreckage from the missing aircraft began to emerge from the glacial ice. It is now believed that the crew became confused as to their exact location while flying at high altitudes through the (then poorly understood) jet stream. Mistakenly believing they had already cleared the mountain tops, they started their descent when they were in fact still behind cloud-covered peaks. ''Star Dust'' crashed into Mount Tupungato, killing all aboard and burying itself in snow and ice. The last wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Refueling
Aerial refueling, also referred to as air refueling, in-flight refueling (IFR), air-to-air refueling (AAR), and tanking, is the process of transferring aviation fuel from one aircraft (the tanker) to another (the receiver) while both aircraft are in flight. The two main refueling systems are ''probe-and-drogue'', which is simpler to adapt to existing aircraft, and the ''flying boom'', which offers faster fuel transfer, but requires a dedicated boom operator station. The procedure allows the receiving aircraft to remain airborne longer, extending its range or loiter time. A series of air refuelings can give range limited only by crew fatigue/physical needs and engineering factors such as engine oil consumption. As the receiver aircraft can be topped up with extra fuel in the air, air refueling can allow a takeoff with a greater payload which could be weapons, cargo, or personnel: the maximum takeoff weight is maintained by carrying less fuel and topping up once airborne. Aerial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Aviation Act 1946
Civil may refer to: * Civic virtue, or civility *Civil action, or lawsuit * Civil affairs *Civil and political rights * Civil disobedience *Civil engineering * Civil (journalism), a platform for independent journalism *Civilian, someone not a member of armed forces * Civil law (other), multiple meanings * Civil liberties * Civil religion * Civil service *Civil society *Civil war A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ... * Civil (surname) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathfinder (RAF)
The Pathfinders were target-marking squadrons in RAF Bomber Command during World War II. They located and marked targets with flares, which a main bomber force could aim at, increasing the accuracy of their bombing. The Pathfinders were normally the first to receive new blind-bombing aids like Gee, Oboe and the H2S radar. The early Pathfinder Force (PFF) squadrons was expanded to become a group, No. 8 (Pathfinder Force) Group in January 1943. The initial Pathfinder Force was five squadrons, while No. 8 Group ultimately grew to a strength of 19 squadrons. While the majority of Pathfinder squadrons and personnel were from the Royal Air Force, the group also included many from the air forces of other Commonwealth countries. History Background At the start of the war in September 1939, RAF Bomber Command's doctrine was based on tight formations of heavily armed bombers attacking during daylight and fending off attacks by fighters with their defensive guns. In early missions ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avro Lancaster
The Avro Lancaster is a British Second World War heavy bomber. It was designed and manufactured by Avro as a contemporary of the Handley Page Halifax, both bombers having been developed to the same specification, as well as the Short Stirling, all three aircraft being four-engined heavy bombers adopted by the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the same wartime era. The Lancaster has its origins in the twin-engine Avro Manchester which had been developed during the late 1930s in response to the Air Ministry Specification P.13/36 for a medium bomber for "world-wide use" which could carry a torpedo internally, and make shallow dive-bombing attacks. Originally developed as an evolution of the Manchester (which had proved troublesome in service and was retired in 1942), the Lancaster was designed by Roy Chadwick and powered by four Rolls-Royce Merlins and in one of the versions, Bristol Hercules engines. It first saw service with RAF Bomber Command in 1942 and as the strategic bom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Star Line
The Blue Star Line was a Merchant Navy (United Kingdom), British passenger and cargo shipping company formed in 1911, being in operation until 1998. Formation Blue Star Line was formed as an initiative by the Vestey Brothers, a Liverpool-based butchers company, who had founded the Union Cold Storage Company to take advantage of refrigeration practices. They developed a large importation business, shipping frozen meat from South America to Britain, initially from Argentina on ships of the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company, and other shipping lines that called at South American ports. The high prices charged for transport by these companies led the Vestey brothers to start to operate their own ships. They chartered their first ships from 1904, and began to buy their own ships from 1909 onwards. The Blue Star Line was officially inaugurated on 28 July 1911, initially using second-hand ships. They ordered their first new ship in 1914, and by the outbreak of the First World War were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
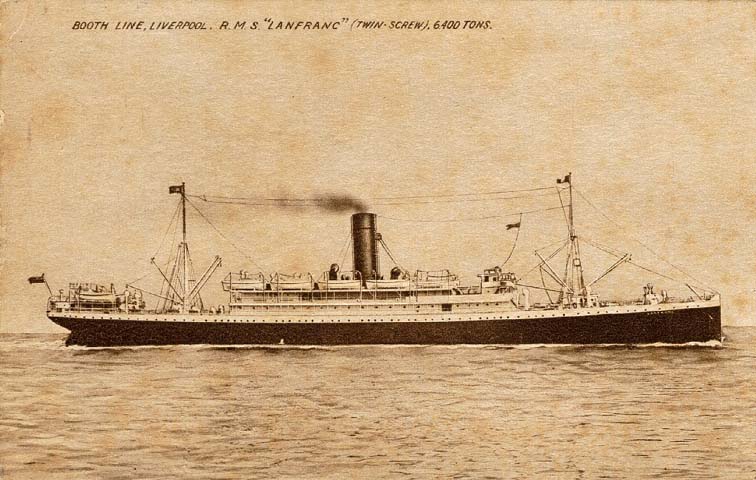
Booth Steamship Company
Alfred Booth and Company was a British trading and shipping company that was founded in 1866 and traded for more than a century. It was founded in Liverpool, England, by two brothers, Alfred and Charles Booth. It grew into a significant merchant shipping company with its head office in Liverpool and interests in the United States and South America. The group was broken up in 1964 and the last Booth company from the group was sold in 1986. History Alfred and Charles Booth were cousins of William James Lamport, co-founder of the Liverpool shipping company Lamport and Holt Line, and worked in the company's office. In 1851 Lamport transferred minority shareholdings in a cargo steamship, the ''Nile'', to several associates including Charles Booth and George Holt. In 1854 Lamport, Holt, Booth and Holt's father, also called George Holt, all took minority shares in a new ship, the ''Orontes''. At the time it was common for a merchant ship to be in 64 shares held by a number of ow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamport And Holt
Lamport and Holt was a UK merchant shipping line. It was founded as a partnership in 1845, reconstituted as a limited company in 1911 and ceased trading in 1991. From 1845 until 1975 Lamport and Holt was headquartered in Liverpool. The founders of Booth Line and Blue Funnel Line had family links with the original partners in Lamport and Holt, and worked for them before founding their own steamship lines in the 1860s. Lamport and Holt was an independent partnership until 1911, when it became a limited company and the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company (RMSP) took it over. RMSP collapsed as a result of the Royal Mail Case in 1931 but was reconstituted as Royal Mail Lines in 1932. Vestey Group bought Lamport and Holt in 1944 and absorbed it into its Blue Star Line subsidiary in 1991. For much of its history Lamport and Holt traded with the east coast of South America, operating liner services there to and from New York, Britain and mainland Europe. from 1902 to 1928 it operated a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Steam Navigation Company
The Pacific Steam Navigation Company ( es, Compañía de Vapores del Pacífico, links=no) was a British commercial shipping company that operated along the Pacific coast of South America, and was the first to use steam ships for commercial traffic in the Pacific Ocean. History The company was founded by William Wheelwright in London in 1838 and began operations in 1840 when two steam ships ''Chile'' and ''Peru'' were commissioned to carry mail. Early ports of call were Valparaíso, Coquimbo, Huasco, Copiapó, Cobija, Iquique, Arica, Islay Province, Islay, Pisco, Peru, Pisco and Callao. In 1846 the company expanded its routes to include Huanchaco, Lambayeque, Peru, Lambayeque, Paita, Guayaquil, Buenaventura, Valle del Cauca, Buenaventura and Panama City. In 1852 the company gained a contract for British Government mail to posts in western South America. Two direct routes were also established - Liverpool to Callao in 1868 and London to Sydney in 1877. In common with its contempor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)