|
British Rail Class 305
The British Rail Class 305 was an alternating current (AC) electric multiple unit (EMU). Under the pre-1973 British Rail numbering system, the class was known as AM5. When TOPS was introduced, the class became Class 305. Subclasses Class 305 had three subclasses: *305/1 3-car units, standard class accommodation only, 52 units built in 1960 *305/2 4-car units, first and standard class accommodation, 19 units built in 1959 *305/3 4-car units, first and standard class accommodation, 8 units converted from 305/1 in 1988 by adding a TC from units *305/9 3-car unit, non-passenger departmental conversion, converted 1984 Operations 305/1 units were generally deployed on inner suburban services on the Lea Valley lines out of London Liverpool Street to Chingford, Enfield Town and Hertford East. They mainly worked the Chingford and Enfield branches, where their average scheduled speed was . However, they were also used on the Great Eastern lines out of London Liverpool Street and occas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantograph (transport)
A pantograph (or "pan" or "panto") is an apparatus mounted on the roof of an electric train, tram or electric bus to collect power through contact with an overhead line. By contrast, battery electric buses and trains are charged at charging stations. The pantograph is a common type of current collector; typically, a single or double wire is used, with the return current running through the rails. The term stems from the resemblance of some styles to the mechanical pantographs used for copying handwriting and drawings. Invention The pantograph, with a low-friction, replaceable graphite contact strip or "shoe" to minimise lateral stress on the contact wire, first appeared in the late 19th century. Early versions include the bow collector, invented in 1889 by Walter Reichel, chief engineer at Siemens & Halske in Germany, and a flat slide-pantograph first used in 1895 by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad The familiar diamond-shaped roller pantograph was devised and patented b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
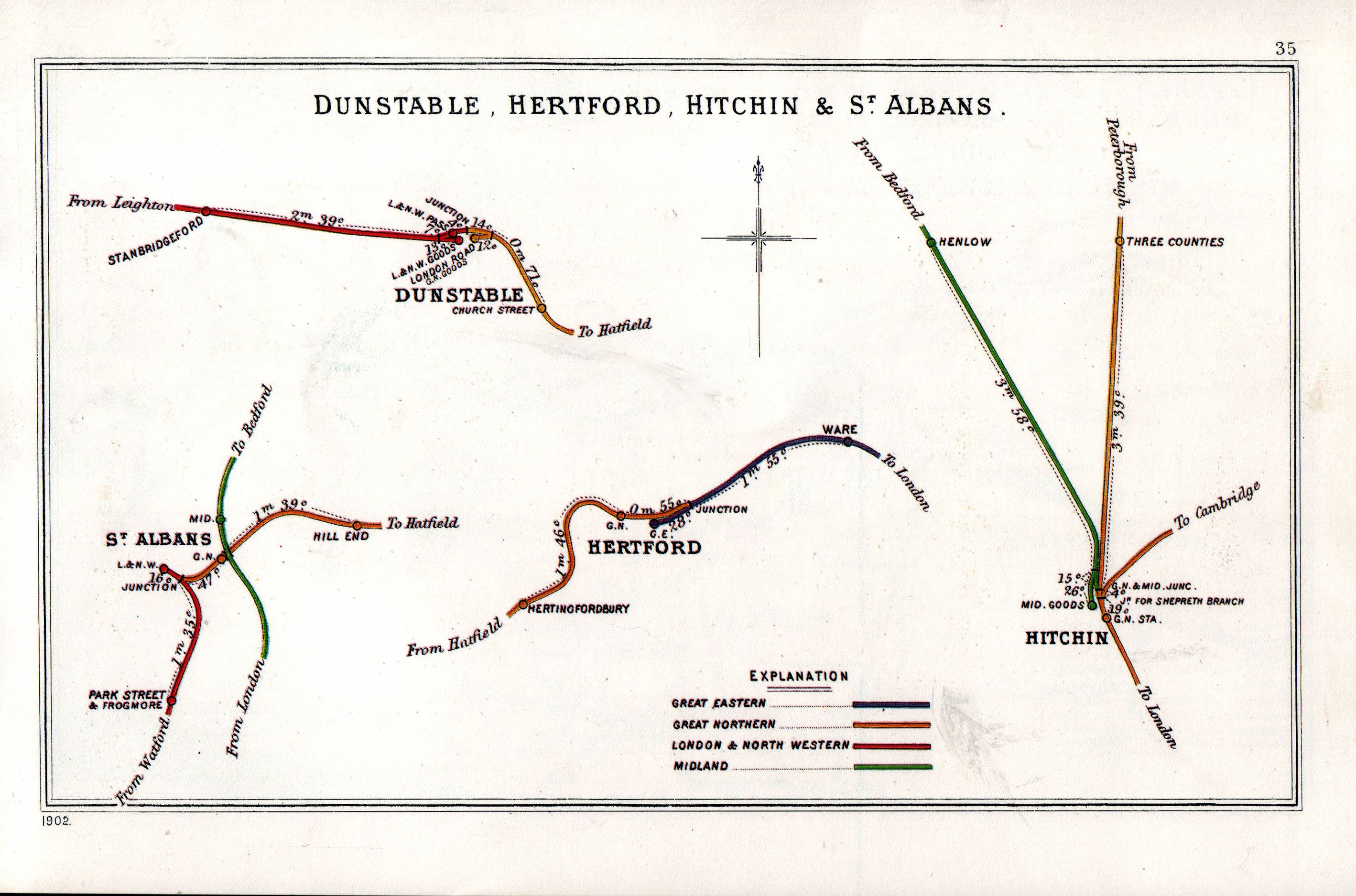
Hertford East
Hertford East railway station is the northern terminus of the Hertford East branch line off the West Anglia Main Line in the east of England, and is located in the town of Hertford in Hertfordshire. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street and is one of two stations in the town, the other being on the Hertford Loop Line. Its three-letter station code is HFE. The station and all trains calling are operated by Greater Anglia. There are two platforms, although platform number one is generally only used during peak times, during times of disruption and primarily for trains to and from Stratford station. History The first station opened on 31st October 1843 sited to the east of the present station. The current station, designed by W. N. Ashbee, was opened by the Great Eastern Railway on 27 February 1888, replacing the first station. The station was listed in 1974 as a Grade II* listed building; in 1996 the buffer stop lights on platform 1 were separately listed in their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enfield Town Railway Station
Enfield Town is one of three northern termini of the Lea Valley lines on the London Overground network in England. It is the most central of several stations in the London Borough of Enfield, north London. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street, the southern terminus. Its three-letter station code is ENF and it is in Travelcard zone 5. In 2015 the line and Enfield Town station were transferred from Abellio Greater Anglia operation to London Overground and added to the Tube map. History The station was opened on 1 March 1849 by the Eastern Counties Railways as Enfield. It was renamed Enfield Town on 1 April 1886. A house which had stood on the site since the late 17th century is said to have been the birthplace of Isaac D'Israeli, father of Benjamin Disraeli. It later became a school, at which John Keats was educated. It then became the original station-house before being demolished in 1872. The fine 17th-century brickwork facade, once attributed to Christopher Wren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chingford Railway Station
Chingford is a railway station located in Chingford in the London Borough of Waltham Forest, east London, operated by London Overground since 31 May 2015. It is one of three northern termini of the Lea Valley lines, down the line from London Liverpool Street. The station is close to Queen Elizabeth's Hunting Lodge. The station is in Travelcard Zone 5. History The Eastern Counties Railway had begun its venture into a main line railway that would head north to compete with the Great Northern. Limited funds and incessant squabbling had slowed its progress. After the merger with several other lines, the ECR became part of the Great Eastern Railway. The GER planned a network of lines to serve countryside around London by its Metropolitan Station and Railways Act of 1864. It also planned a line to High Beach, to serve Epping Forest, which reached a terminus in Bull Lane (now Kings Road) at the very end of Hale End Road (now Larkshall Road) in Chingford, in 1873. In 1878 the smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Liverpool Street
Liverpool Street station, also known as London Liverpool Street, is a central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station in the north-eastern corner of the City of London, in the ward of Bishopsgate Without. It is the terminus of the West Anglia Main Line to Cambridge, the Great Eastern Main Line to Norwich, commuter trains serving east London and destinations in the East of England, and the Stansted Express service to Stansted Airport. The station opened in 1874, as a replacement for Bishopsgate station as the Great Eastern Railway's main London terminus. By 1895, it had the most platforms of any London terminal station. During the First World War, an air raid on the station killed 16 on site, and 146 others in nearby areas. In the build-up to the Second World War, the station served as the entry point for thousands of child refugees arriving in London as part of the ''Kindertransport'' rescue mission. The station was damaged by the 1993 Bishopsgate bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lea Valley Lines
The Lea Valley lines are two commuter lines and two branches in north-east London, so named because they run along the Lower Lea Valley of the River Lea. They were part of the Great Eastern Railway, now part of the ''Anglia Route'' of Network Rail. On 31 May 2015, services between London Liverpool Street to Chingford, Cheshunt and Enfield Town were transferred to London Overground; services from London Liverpool Street and Stratford via Tottenham Hale to Hertford East and Bishops Stortford remain with Greater Anglia. History The first section was opened by the Eastern Counties Railway (ECR) on 20 June 1839 from the London end at Devonshire Street to Romford, extended on 1 July 1840 to Bishopsgate (London end) and Brentwood. The Northern and Eastern Railway (N&ER) opened its first section from that line at Stratford to Broxbourne on 15 September 1840, and to Harlow in 1841; though it remained a separate entity, its line was leased to the ECR from 1 January 1844. A branch f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Allan Publishing
Ian Allan Publishing was an English publisher, established in 1942, which specialised in transport books. It was founded by Ian Allan. In 1942 Ian Allan, then working in the public relations department for the Southern Railway at Waterloo station, decided he could deal with many of the requests he received about rolling stock by collecting the information into a book. The result was his first book, ''ABC of Southern Locomotives''. This proved to be a success, contributing to the emergence of trainspotting as a popular hobby in the UK, and leading to the formation of the company.Ian Allan…the man who launched a million locospotters ''The Railway Magazine'' issue 1174 February 1999 pages 20-27 The company grew from a small producer of books for train enthusiasts and spotters to a large transport publisher. Each year it published books covering subjects such as military and civil aviation, naval and maritime topics, buses, trams, trolleybuses and steam railways, including hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TOPS
Total Operations Processing System (TOPS) is a computer system for managing railway locomotives and rolling stock, known for many years of use in the United Kingdom. TOPS was originally developed between the Southern Pacific Railroad (SP), Stanford University and IBM as a replacement for paper-based systems for managing rail logistics. A jointly-owned consultancy company, ''TOPS On-Line Inc.'', was established in 1960 with the goal of implementing TOPS, as well as selling it to third parties. Development was protracted, requiring around 660 man-years of effort to produce a releasable build. During mid-1968, the first phase of the system was introduced on the SP, and quickly proved its advantages over the traditional methods practiced prior to its availability. In addition to SP, TOPS was widely adopted throughout North America and beyond. While it was at one point in widespread use across many of the United States railroads, the system has been perhaps most prominently used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Multiple Unit
An electric multiple unit or EMU is a multiple-unit train consisting of self-propelled carriages using electricity as the motive power. An EMU requires no separate locomotive, as electric traction motors are incorporated within one or a number of the carriages. An EMU is usually formed of two or more semi-permanently coupled carriages, but electrically powered single-unit railcars are also generally classed as EMUs. The great majority of EMUs are passenger trains, but versions also exist for carrying mail. EMUs are popular on commuter and suburban rail networks around the world due to their fast acceleration and pollution-free operation. Being quieter than diesel multiple units (DMUs) and locomotive-hauled trains, EMUs can operate later at night and more frequently without disturbing nearby residents. In addition, tunnel design for EMU trains is simpler as no provision is needed for exhausting fumes, although retrofitting existing limited-clearance tunnels to accommodate the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current and vice versa. In certain applications, like guitar amplifiers, different waveforms are used, such as triangular waves or square waves. Audio a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janney Coupler
Janney couplers are a semi-automatic form of railway coupling that allow rail cars and locomotives to be securely linked together without rail workers having to get between the vehicles. They are also known as American, AAR, APT, ARA, MCB, knuckle, Buckeye, tightlock (in the UK), Henricot (in Belgium) or Centre Buffer Couplers. Background Janney couplers were first patented in 1873 by Eli H. Janney (). Andrew Jackson Beard was amongst various inventors that made a multitude of improvements to the knuckle coupler; Beard's patents were granted 23 November 1897, which then sold for approximately $50,000, and granted 16 May 1899. In the UK, several versions of Janney couplers are fitted to a limited number of coaches, multiple units, wagons and locomotives. Janney Type E, Type F Interlock, and Type H tightlock couplings are compatible subtypes, each intended for specific rail car types. Prior to the formation of the Association of American Railroads (AAR) these were known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

_p139_-_Liverpool_Street_and_Broad_Street_stations_(plan).jpg)



