|
British Computer
Computers designed or built in Britain include: *Acorn Computers ** Acorn Eurocard systems **Acorn System 1 **Acorn Atom **BBC Micro **Acorn Electron **BBC Master **Acorn Archimedes **RiscPC **Acorn Network Computer *Amstrad **Amstrad CPC **Amstrad PCW **Amstrad NC100 **PC1512 ** PPC 512 and 640 ** Amstrad PC2286 **Amstrad Mega PC *Apricot Computers **Apricot PC **Apricot Portable ** Apricot Picobook Pro *Bear Microcomputer Systems ** Newbear 77-68 *Bywood Electronics **SCRUMPI 2 **SCRUMPI 3 *Cambridge Computer **Cambridge Z88 *CAP computer *Compukit UK101 *Dragon 32/64 *Enterprise (computer) *Ferranti MRT *Flex machine *Gemini Computers **Gemini Galaxy ** Gemini Challenger * GEC ** GEC 2050 **GEC 4000 series ** GEC Series 63 *Grundy NewBrain * ICL **ICL 2900 Series **ICL Series 39 **One Per Desk *Jupiter Ace *Nascom **Nascom 1 **Nascom 2 *Plessey System 250 *Raspberry Pi *Research Machines **Research Machines 380Z ** LINK 480Z **RM Nimbus *SAM Coupé * Science of Cambridge ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
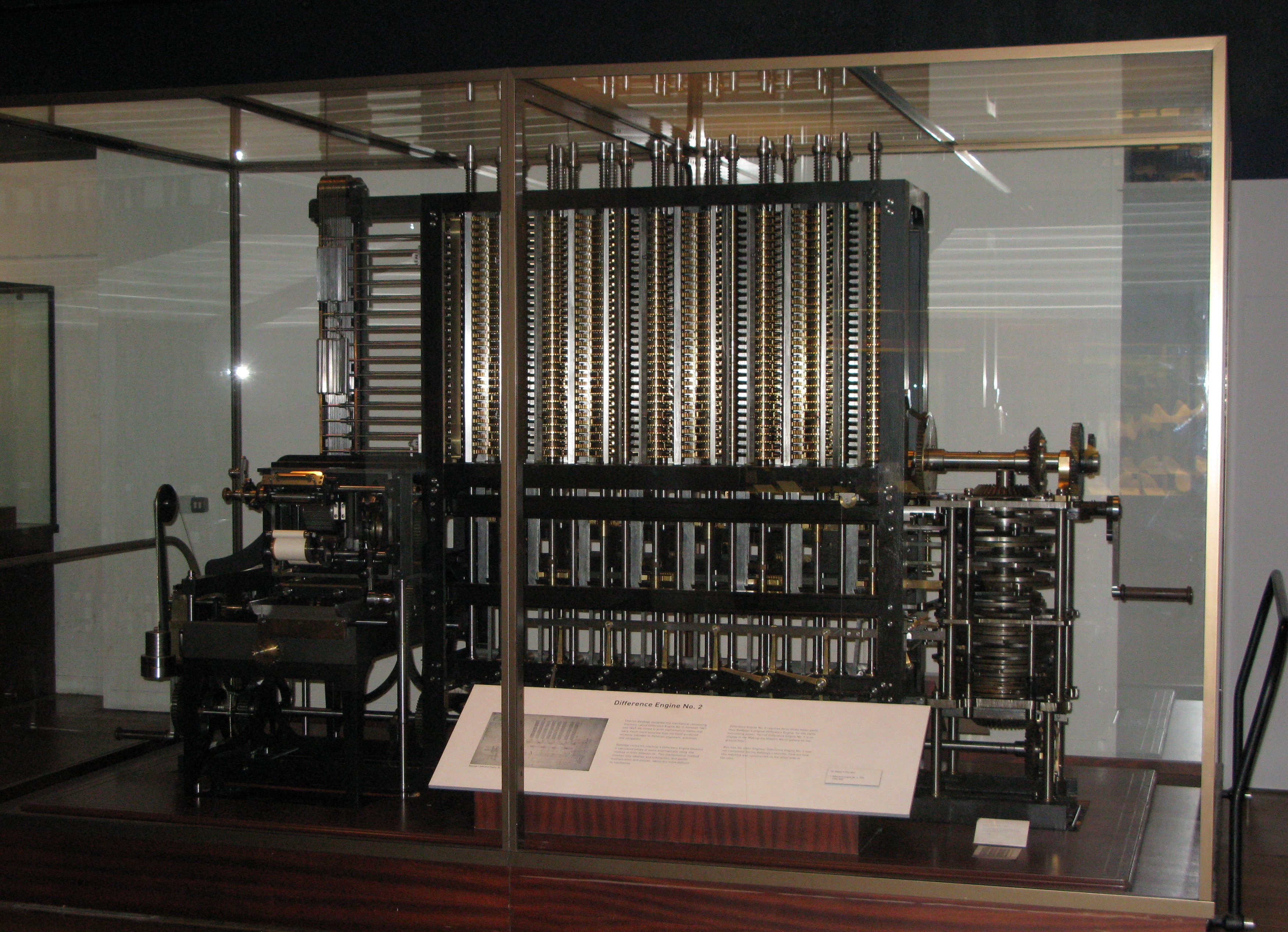
Babbage Difference Engine
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer. Babbage is considered by some to be " father of the computer". Babbage is credited with inventing the first mechanical computer, the Difference Engine, that eventually led to more complex electronic designs, though all the essential ideas of modern computers are to be found in Babbage's Analytical Engine, programmed using a principle openly borrowed from the Jacquard loom. Babbage had a broad range of interests in addition to his work on computers covered in his book ''Economy of Manufactures and Machinery''. His varied work in other fields has led him to be described as "pre-eminent" among the many polymaths of his century. Babbage, who died before the complete successful engineering of many of his designs, including his Difference Engine and Analytical Engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amstrad PPC 512
The Amstrad PPC512 and Amstrad PPC640 were the first portable IBM PC compatible computers made by Amstrad. Released in 1987, they were a development of the desktop PC-1512 and PC-1640 models. As Portable computer, portable computers, they contained all the elements necessary to perform computing on the move. They had a keyboard and a monochrome Liquid-crystal display, LCD display built in and also had space for disposable batteries to power the PC where a suitable alternative power source (i.e. mains or 12 volt vehicle power) was not available. The PCs came with either one or two double density double side Floppy disk, floppy disc drives and the PPC640 model also featured a modem. Both models were supplied with ''PPC Organiser'' software and the PPC640 was additionally supplied with the ''Mirror II'' communications software. Hardware The two computers had very similar specifications. The PPC512 had an NEC V30 processor running at 8 MHz, 512 Kibibyte, KiB of memory, a ful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise (computer)
The Enterprise is a Zilog Z80-based home computer announced in 1983, but through a series of delays, not commercially available until 1985. The specification as released was powerful and one of the higher end in its class (though not by the margin envisaged in 1983). This was due to the use of ASICs for graphics and sound which took workload away from the CPU, an extensive implementation of ANSI BASIC and a bank switching system to allow for larger amounts of RAM than the Z80 natively supported. It also featured a distinctive and colourful case design, and promise of multiple expansion options. Ultimately it was not commercially successful, after multiple renames, delays and a changing market place. Its manufacturer calling in the receivers in 1986 with significant debt. It was developed by British company Intelligent Software and marketed by Enterprise Computers. Its two variants are the Enterprise 64, with 64 kilobytes of Random Access Memory (RAM), and the Enterprise 128, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon 32/64
The Dragon 32 and Dragon 64 are home computers that were built in the 1980s. The Dragons are very similar to the TRS-80 Color Computer, and were produced for the European market by Dragon Data, Ltd., initially in Swansea, Wales before moving to Port Talbot, Wales (until 1984) and by Eurohard S.A. in Casar de Cáceres, Spain (from 1984 to 1987), and for the US market by Tano of New Orleans, Louisiana. The model numbers reflect the primary difference between the two machines, which have 32 and 64 kilobytes of RAM, respectively. Product history Dragon Data entered the market in August 1982 with the Dragon 32. The Dragon 64 followed a year later. The computers sold well initially and attracted the interest of independent software developers including Microdeal. A companion magazine, ''Dragon User'', began publication shortly after the microcomputer's launch. Despite this initial success, there were two technical impediments to the Dragon's acceptance. The graphics capabilitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compukit UK101
The Compukit UK101 microcomputer (1979) is a kit clone of the Ohio Scientific Superboard II single-board computer, with a few enhancements for the UK market - notably replacing the 24×24 (add guardband kit to give 32×32) screen display with a more useful 48×16 layout working at UK video frequencies. The video output is black and white with 256 characters generated by a two kilobyte ROM. It has no bit-mapped graphics capability. The video is output through a UHF modulator, designed to connect to a TV set. History The UK101 design was published in Practical Electronics, a popular hobbyists magazine at the time. The August, September, October and November 1979 issues carried the four parts of the article, credited to "Dr A. A. Berk". Later issues of the magazine contained information on modifications and additions to the machine, including a series of articles on building an expansion unit. Kits of parts for building the machine were available from CompShop Ltd of 14 Stati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAP Computer
The Cambridge CAP computer was the first successful experimental computer that demonstrated the use of security capabilities, both in hardware and software.Levy, p.96 It was developed at the University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory in the 1970s. Unlike most research machines of the time, it was also a useful service machine. The sign currently on the front of the machine reads: The CAP project on memory protection ran from 1970 to 1977. It was based on capabilities implemented in hardware, under M. Wilkes and R. Needham with D. Wheeler responsible for the implementation. R. Needham was awarded a BCS Technical Award in 1978 for the ''CAP (Capability Protection) Project''. Design The CAP was designed such that any access to a memory segment or hardware required that the current process held the necessary capabilities. The 32-bit processor featured microprogramming control, two 256-entry caches, a 32-entry write buffer and the capability unit itself, which had 64 regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge Z88
The Cambridge Computer Z88 is a Zilog Z80-based portable computer released in 1987 by Cambridge Computer, the company formed for such purpose by Clive Sinclair. It was approximately A4 paper sized and lightweight at , running on four AA batteries for 20 hours of use. It was packaged with a built-in combined word processing/spreadsheet/database application called ''PipeDream'' (functionally equivalent to a 1987 BBC Micro ROM called Acornsoft View Professional), along with several other applications and utilities, such as a Z80-version of the BBC BASIC programming language. History The Z88 evolved from Sir Clive Sinclair's ''Pandora'' portable computer project which had been under development at Sinclair Research during the mid-1980s. Following the sale of Sinclair Research to Amstrad, Sinclair released the Z88 through his Cambridge Computer mail-order company. The machine was launched at the ''Which Computer?'' Show on 17 February 1987. Early models were contract-manufactured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge Computer
Sinclair Research Ltd is a British consumer electronics company founded by Clive Sinclair in Cambridge. It was originally incorporated in 1973 as Westminster Mail Order Ltd, renamed Sinclair Instrument Ltd, then Science of Cambridge Ltd, then Sinclair Computers Ltd, and finally Sinclair Research Ltd. It remained dormant until 1976, when it was activated with the intention of continuing Sinclair's commercial work from his earlier company Sinclair Radionics, and adopted the name Sinclair Research in 1981. In 1980, Clive Sinclair entered the home computer market with the ZX80 at £99.95, at that time the cheapest personal computer for sale in the United Kingdom. In 1982 the ZX Spectrum was released, becoming the UK's best selling computer, and competing aggressively against Commodore and Amstrad. At the height of its success, and largely inspired by the Japanese Fifth Generation Computer program, the company established the "MetaLab" research centre at Milton Hall near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newbear 77-68
The Newbear 77-68 was a kit of parts from which a purchaser could construct a first generation home computer based around a Motorola 6800 microprocessor. Because it was designed to be assembled by its owner at home, it was also a homebuilt computer. The 77-68 was designed by Tim Moore and was offered for sale by Bear Microcomputer Systems of Newbury, Berkshire, England from June 1977. It was among the first, if not ''the'' first, of British home computers and was featured in the launch edition of ''Personal Computer World'' magazine in February 1978. The Newbear 77-68 was both a home computer and a homebuilt computer, since it was designed to not only be used at home (hence a home computer), but also be assembled at home by its owner (hence a homebuilt computer). Description The basic 77-68 comprised an 8-inch square printed circuit board accommodating the microprocessor, Static RAM of 256 8 bit words and the bare essentials in terms of input/output and timing logic to make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apricot Picobook Pro
The Apricot Picobook Pro is the first product of the reformed Apricot Computers. It is a netbook based on the VIA NanoBook, first shown to the press on October 15 2008. Specifications *CPU: VIA C7-M ULV at 1.2 GHz. * Chipset: VIA VX800 System Media Processor ( Northbridge and Southbridge integrated). * Monitor: TFT 8.9 inch, 1024x600 pixels. Support to internal/external/dual monitor, or TV. *Graphics: 3D/2D S3 Graphics Chrome9 HC3 chipset integrated, shared VRAM to a max of 64 MB; DirectX 9.0. and HD video support. * RAM: 1 GB of SO-DIMM DDR2 RAM at 667 MHz. *Dimensions: 230 x 171 x 38.7 mm *Weight: 0.98 kg (2.16 lb). *Ports: On the left, VGA DE-15 and one USB 2.0 port. On the right, a second USB port, Kensington Security Slot, 8P8C and power supply. In the front, two minijack (mic/ear) and 4 in 1 Card-reader. Open, integrated Webcam of 1.3 megapixels over the TFT, keyboard and touchpad at bottom. *Keyboard: QWERTY, 80 keys *Hard disk 60&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apricot Portable
The Apricot Portable was a personal computer manufactured by ACT Ltd., and was released to the public in November 1984. It was ACT's first attempt at manufacturing a portable computer, which were gaining popularity at the time. Compared to other portable computers of its time like the Compaq Portable and the Commodore SX-64, the Apricot Portable was the first system to have an 80-column and 25-line LCD screen and the first with a speech recognition system. The Apricot Portable was designed to be easily carried in its case, but was powered by mains electricity only. It consisted of a central unit containing the motherboard, monochrome display and a floppy disk drive. It also came with a wireless keyboard and bundled software. Design The Apricot Portable was contained inside a hard charcoal gray carrying case and consisted of two main parts: the central unit (with built-in monitor) and the keyboard. An optional mouse-like track board was also available. It was used by either poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apricot PC
The Apricot PC (originally called the ''ACT Apricot'') is a personal computer produced by Apricot Computers, then still known as Applied Computer Techniques or ACT. Released in late 1983, it was ACT's first independently developed microcomputer, following on from the company's role of marketing and selling the ACT Sirius 1, and was described as "the first 16-bit system to be Sirius-compatible, rather than IBM-compatible", indicating the influence that the Sirius 1 had in the United Kingdom at the time. It achieved success in the United Kingdom, with reviewers noting the system's high resolution display (for its time) and its trackball cable (later models used IR). It used an Intel 8086 processor running at . A 8087 math co-processor was optional. The amount of memory was , expandable to . It came with a CRT green-screen 9" with text mode or graphics and was equipped with two floppy discs and a keyboard with an integrated LCD display. The ''Apricot Xi'' was a similar computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_School_-_Charles_Babbage_(1792–1871)_-_814168_-_National_Trust.jpg)



