|
British Bombay
The Bombay Presidency or Bombay Province, also called Bombay and Sind (1843–1936), was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India, with its capital in the city that came up over the seven islands of Bombay. The first mainland territory was acquired in the Konkan region with the Treaty of Bassein (1802). Mahabaleswar was the summer capital. The Bombay province has its beginnings in the city of Bombay that was leased in fee tail to the East India Company, via the Royal Charter of 27 March 1668 by King Charles II of England, who had in turn acquired Bombay on 11 May 1661, through the royal dowry of Catherine Braganza by way of his marriage treaty with the Portuguese princess, daughter of John IV of Portugal. The English East India Company transferred its Western India headquarters from Surat in the Gulf of Cambay after it was sacked, to the relatively safe Bombay Harbour in 1687. The province was brought under Direct rule along with other parts of British I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Presidency
Surat is a city in the western Indian States and territories of India, state of Gujarat. The word Surat literally means ''face'' in Gujarati language, Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of the river Tapti near its confluence with the Arabian Sea, it used to be a large seaport. It is now the commercial and economic center in South Gujarat, and one of the largest urban areas of western India. It has well-established diamond and textile industry, and is a major supply centre for apparels and accessories. About 90% of the world's diamonds supply are cut and polished in the city. It is the second largest city in Gujarat after Ahmedabad and the List of most populous cities in India, eighth largest city by population and List of million-plus urban agglomerations in India, ninth largest urban agglomeration in India. It is the administrative capital of the Surat district. The city is located south of the state capital, Gandhinagar; south of Ahmedabad; and north of Mumbai. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainland
Mainland is defined as "relating to or forming the main part of a country or continent, not including the islands around it egardless of status under territorial jurisdiction by an entity" The term is often politically, economically and/or demographically more significant than politically associated remote territories, such as exclaves or oceanic islands situated outside the continental shelf. In geography, "mainland" can denote the continental (i.e. non-insular) part of any polity or the main island within an island nation. In geopolitics, "mainland" is sometimes used interchangeably with terms like metropole as an antonym to overseas territories. In the sense of "heartland", mainland is the opposite of periphery. In some language a separate concept of "mainland" is missing and is replaced with a "continental portion". The term is relative: in Tasmania, continental Australia is the mainland, while to residents of Flinders Island, the main island of Tasmania is also "th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombay Harbour
Mumbai Harbour (also English; Bombay Harbour or Front Bay, Marathi''Mumba'ī bandar''), is a natural deep-water harbour in the southern portion of the Ulhas River estuary. The narrower, northern part of the estuary is called Thana Creek. The harbour opens to the Arabian Sea to the south. The historical island of Elephanta is one of the six islands that lie in the harbour. ''Front Bay'' is the official name of the harbour, so named because the city started as a tiny settlement facing the harbour. The waterbody behind the original settlement, forming an arc between the former Colaba island and Bombay island, up to the Malabar Hill promontory or peninsula, was similarly called Back Bay. Front Bay is home to the Mumbai Port, which lies in the south section of the western edge of the harbour. Jawaharlal Nehru Port and Navi Mumbai lie to the east on the Konkan mainland, and the city of Mumbai lies to the west on Salsette Island. The Gateway of India with its jetty for Elephanta i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sack Of Surat
Battle of Surat, also known as the Sack of Surat, was a land battle that took place on January 5, 1664, near the city of Surat, in present-day Gujarat, India; between Maratha ruler Shivaji and Inayat Khan, a Mughal captain. The Marathas defeated the Mughal force, and ransacked the city of Surat for six days. According to James Grant Duff, a captain in the British India Regiment, Surat was attacked by Shivaji on 5 January 1664. Surat was a wealthy port city in the Mughal Empire and was useful for the Mughals as it was used for the sea trade of the Arabian Sea. The city was well populated mostly by Hindus and a few Muslims, especially the officials in the Mughal administration of the city. The attack was so sudden that the population had no chance to flee. The plunder was continued for six days and two-thirds of the city was burnt down. The loot was then transferred to Rajgad fort. Background As Shaista Khan, the Mughal governor, was in Deccan for more than three years fighting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
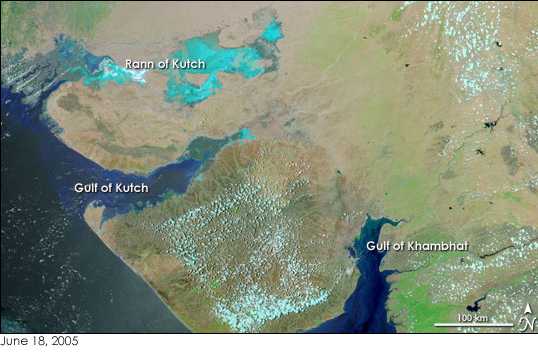
Gulf Of Cambay
The Gulf of Khambhat, historically known as the Gulf of Cambay, is a bay on the Arabian Sea coast of India, bordering the state of Gujarat just north of Mumbai and Diu Island. The Gulf of Khambhat is about long, about wide in the north and up to wide in the south. Major rivers draining Gujarat are the Narmada, Tapti, Mahi and the Sabarmati, that form estuaries in the gulf. It divides the Kathiawar Peninsula from the south-eastern part of Gujarat.Trivedi, P. and Soni, V. C. (2012)Significant bird records and local extinctions in Purna and Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuaries, Gujarat, IndiaJhala, Y. V., Qureshi, Q., Sinha, P. R. (Eds.) (2011)''Status of tigers, co-predators and prey in India, 2010.''National Tiger Conservation Authority, Government of India, New Delhi, and Wildlife Institute of India, Dehradun. TR 2011/003. There are plans to construct a dam, Kalpasar Project, across the gulf. Wildlife To the west of the Gulf, Asiatic lions inhabit the Gir Forest National Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John IV Of Portugal
John IV ( pt, João, ; 19 March 1604 – 6 November 1656), nicknamed John the Restorer ( pt, João, o Restaurador), was the King of Portugal whose reign, lasting from 1640 until his death, began the Portuguese restoration of independence from Habsburg Spanish rule. His accession established the House of Braganza on the Portuguese throne, and marked the end of the 60-year-old Iberian Union by which Portugal and Spain shared the same monarch. Before becoming king, he was John II, 8th Duke of Braganza. He was the grandson of Catherine, Duchess of Braganza, a claimant to the crown during the Portuguese succession crisis of 1580. On the eve of his death in 1656, the Portuguese Empire was at its territorial zenith, spanning the globe. Early life John IV was born at Vila Viçosa and succeeded his father Teodósio II as Duke of Braganza when the latter died insane in 1630. He married Luisa de Guzmán (1613–66), eldest daughter of Juan Manuel Pérez de Guzmán, 8th Duke of Medin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dowry Of Catherine Braganza
Catherine of Braganza ( pt, Catarina de Bragança; 25 November 1638 – 31 December 1705) was Queen of England, Scotland and Ireland during her marriage to King Charles II, which lasted from 21 May 1662 until his death on 6 February 1685. She was the daughter of King John IV of Portugal, who became the first king from the House of Braganza in 1640 after overthrowing the 60–year rule of the Spanish Habsburgs over Portugal and restoring the Portuguese throne which had first been created in 1143. Catherine served as regent of Portugal during the absence of her brother Peter II in 1701 and during 1704–1705, after her return to her homeland as a widow. Owing to her devotion to the Roman Catholic faith in which she had been raised, Catherine was unpopular in England. She was a special object of attack by the inventors of the Popish Plot. In 1678 the murder of Edmund Berry Godfrey was ascribed to her servants, and Titus Oates accused her of an intention to poison the king. Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles II Of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651, and King of England, Scotland and Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685. Charles II was the eldest surviving child of Charles I of England, Scotland and Ireland and Henrietta Maria of France. After Charles I's execution at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War, the Parliament of Scotland proclaimed Charles II king on 5 February 1649. But England entered the period known as the English Interregnum or the English Commonwealth, and the country was a de facto republic led by Oliver Cromwell. Cromwell defeated Charles II at the Battle of Worcester on 3 September 1651, and Charles fled to mainland Europe. Cromwell became virtual dictator of England, Scotland and Ireland. Charles spent the next nine years in exile in France, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Netherlands. The political crisis that followed Cromwell's death in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Charter Of 27 March 1668
{{Use Indian English, date=May 2018 The ''Royal Charter'' of 27 March 1668 was an agreement between the Kingdom of England and the English East India Company. It led to the transfer of Bombay from Charles II of England to the English East India Company for an annual rent of £10 (equivalent retail price index In the United Kingdom, the Retail Prices Index or Retail Price Index (RPI) is a measure of inflation published monthly by the Office for National Statistics. It measures the change in the cost of a representative sample of retail goods and servic ... of £1,226 in 2007). References *https://books.google.com/books?id=vXhCAAAAIAAJ&printsec=titlepage&client=firefox-a#PPA55,M1 55 History of Mumbai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world. The EIC had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three Presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time. The operations of the company had a profound effect on the global balance of trade, almost single-handedly reversing the trend of eastward drain of Western bullion, seen since Roman times. Originally chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies", the company rose to account for half of the world's trade duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fee Tail
In English common law, fee tail or entail is a form of trust established by deed or settlement which restricts the sale or inheritance of an estate in real property and prevents the property from being sold, devised by will, or otherwise alienated by the tenant-in-possession, and instead causes it to pass automatically by operation of law to an heir determined by the settlement deed. The term ''fee tail'' is from Medieval Latin , which means "cut(-short) fee" and is in contrast to "fee simple" where no such restriction exists and where the possessor has an absolute title (although subject to the allodial title of the monarch) in the property which he can bequeath or otherwise dispose of as he wishes. Equivalent legal concepts exist or formerly existed in many other European countries and elsewhere. Purpose The fee tail allowed a patriarch to perpetuate his blood-line, family-name, honour and armorials in the persons of a series of powerful and wealthy male descendants. By kee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summer Capital
A summer capital is a city used as an administrative capital during extended periods of particularly hot summer weather. The term is mostly of relevance in historical contexts of political systems with ruling classes that would migrate to a summer capital, making it less prevalent in modern times. The ubiquity of air conditioning systems also reduces the imperative to periodically relocate to summer capitals. Summer capitals around the world China Shangdu (Xanadu) was an "Upper Capital" during Kublai Khan's reign in the 13th century. In the Qing dynasty, Chengde Mountain Resort in Chengde was often being used by emperor to perform their official function during the summer months. In the era of the Republic of China, core members of Nationalist Party of China often held meetings at Kuling, Jiujiang in summer to make important internal decisions. Foreign businessmen and missionaries also like to spend summer time in Kuling during ROC government rule. In the era of the People's Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |