|
Bristoliinae
The Bristoliinae is an extinct subfamily of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with species of small to average size. Species belonging to this subfamily lived during the Botomian and Toyonian stage (''Olenellus''-zone), 522-513 million years ago, in the former continent of Laurentia, including what are today Mexico, the Appalachian Mountains and the south-western United States, and Canada (Northwest Territories). Etymology The Bristoliinae are named for the type species '' Bristolia bristolensis''. Description The headshield (or cephalon) carries spines (called genal spines) of approximately 4-8 thorax segments long (measured parallel to the midline). The genal spines are attached in front of the back of the headshield. The central raised portion of the cephalon that represents the axis in the cephalon (or glabella) touches the flattened ledge that borders the cephalon. The furrows that separate border, eye ridges, glabella and its lobes are distinct. Communalities an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biceratopsidae
Biceratopsidae is an extinct family of redlichiid trilobites, with species of small to average size. Species of belonging to this family lived during the Toyonian stage (''Olenellus''-zone), 522–513 million years ago, in the former continent of Laurentia, including what are today the south-western United States and Canada. It contains the subfamilies Biceratopsinae and Bristoliinae. Habitat The Biceratopsidae were probably marine bottom dweller, like all Olenellina. References Olenelloidea Trilobite families Cambrian trilobites Cambrian first appearances Cambrian Series 2 extinctions {{redlichiida-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristolia
''Bristolia'' is an extinct genus of trilobite, fossil marine arthropods, with eight or more small to average size species. It is common in and limited to the Lower Cambrian (Upper ''Olenellus''-zone) shelf deposits across the southwestern US, which constitutes part of the former paleocontinent of Laurentia. Taxonomy ''Bristolia'' can be separated into two distinct groups: one consisting of ''B. insolens'' and ''B. anteros'', the other comprising a gradual spectrum of morphologies including ''B. mohavensis'', ''B. harringtoni'', and ''B. bristolensis'' morphotypes. The second group reveals a dynamic morphological trend. From the oldest species ''B. mohavensis'', the lineage undergoes gradational increase in intergenal angle and advancement of the genal spines, progressing through ''B. harringtoni'', culminating in ''B. bristolensis''. Younger specimens show a trend back to more acute intergenal angles and less advanced genal spines typical of ''B. fragilis''. This development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fremontella
''Fremontella'' is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the part of the Toyonian stage. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period. ''Fremontella'' shares with the other genera of the Bristoliinae The Bristoliinae is an extinct subfamily of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with species of small to average size. Species belonging to this subfamily lived during the Botomian and Toyonian stage (''Olenellus''-zone), 522-513 million years ... subfamily, Lochmanolenellus and Bristolia conspicuous and long curved spines (called genal spines) on the headshield (or cephalon). These reach back equal to 4-5 thorax segments (measured parallel to the midline). The furrows that separate border, eye ridges, glabella and its lobes are distinct (unlike in the Biceratopsinae). The area outside of the axis (or pleural lobes) of the third segment of the thorax is enlarged, and carries large trailing spine on each side. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lochmanolenellus
''Lochmanolenellus'' is an extinct genus of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with one small species, ''L. mexicana''. It lived during the Botomian stage (''Olenellus''-zone), 522–513 million years ago, in the South-West of the former continent of Laurentia, in what are today Mexico, and the South-Western United States. Etymology ''Lochmanolenellus'' is named in honor of C. Lochman, who initially described the fossils that are assigned to this genus, and for its likeness to ''Olenellus'' a distantly related genus. The species epithet ''mexicana'' refers to Mexico, where the first specimen was found. Taxonomy ''L. mexicana'' was first described as ''Wanneria mexicana prima''. There are however so many differences, that it is highly unlikely ''L. mexicana'' is more than distantly related. Later scholars assigned the species to ''Laudonia''. Although ''Laudonia'' is much more related than ''Wanneria'', ''L. mexicana'' must be considered an early representative of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropoda
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian First Appearances
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Cambrian biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Trilobites
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Cambrian bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
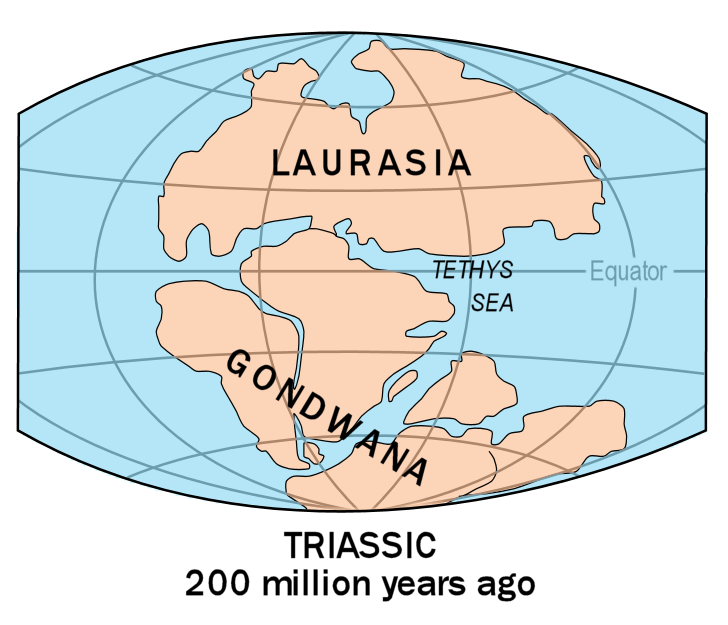
Paleocontinent
A paleocontinent or palaeocontinent is a distinct area of continental crust that existed as a major landmass in the geological past. There have been many different landmasses throughout Earth's time. They range in sizes, some are just a collection of small microcontinents while others are large conglomerates of crust. As time progresses and sea levels rise and fall more crust can be exposed making way for larger landmasses. The continents of the past shaped the evolution of organisms on Earth and contributed to the climate of the globe as well. As landmasses break apart, species are separated and those that were once the same now have evolved to their new climate. The constant movement of these landmasses greatly determines the distribution of organisms on Earth's surface. This is evident with how similar fossils are found on completely separate continents. Also, as continents move, mountain building events (orogenies) occur, causing a shift in the global climate as new rock is expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biceratopsinae
The Biceratopsinae is an extinct subfamily of redlichiid trilobites within the family Biceratopsidae, with species of small to average size. Species belonging to this subfamily lived during the Toyonian stage (Upper ''Olenellus''-zone), 516-513 million years ago, in the former continent of Laurentia, including what are today the South-Western United States and Canada. Etymology The Biceratopsinae are named for the type species '' Biceratops nevadensis''. Habitat The Biceratopsinae were probably marine bottom dweller, like all Olenellina. References Cambrian trilobites Cambrian Series 2 first appearances Cambrian Series 2 extinctions Biceratopsidae Arthropod subfamilies {{Redlichiida-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalon (arthropod Head)
The cephalon is the head section of an arthropod. It is a tagma, i.e., a specialized grouping of arthropod segments. The word cephalon derives from the Greek κεφαλή (kephalē), meaning "head". Insects In insects, ''head'' is a preferred term. The insect head consists of five segments, including three (the labial, maxillary and mandibular) necessary for food uptake, which are altogether known as the gnathocephalon and house the suboesophageal ganglion of the brain, as well as the antennal segment, and an ocular segment, as well as a non segmented fused section of the head where the archicerebrum is housed known as the acron. See also arthropod head problem. Chelicerates and crustaceans In chelicerates and crustaceans, the cephalothorax is derived from the fusion of the cephalon and the thorax, and is usually covered by a single unsegmented carapace. In relation with the arthropod head problem, phylogeny studies show that members of the Malacostraca class of cru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2016 census population of 41,790, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of 2022 is 45,605. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and only city in the territory; its population was 19,569 as of the 2016 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission. The Northwest Territories, a portion of the old North-Western Territory, entered the Canadian Confederation on July 15, 1870. Since then, the territory has been divided four times to create new provinces and territories or enlarge existing ones. Its current borders date from April 1, 1999, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |