|
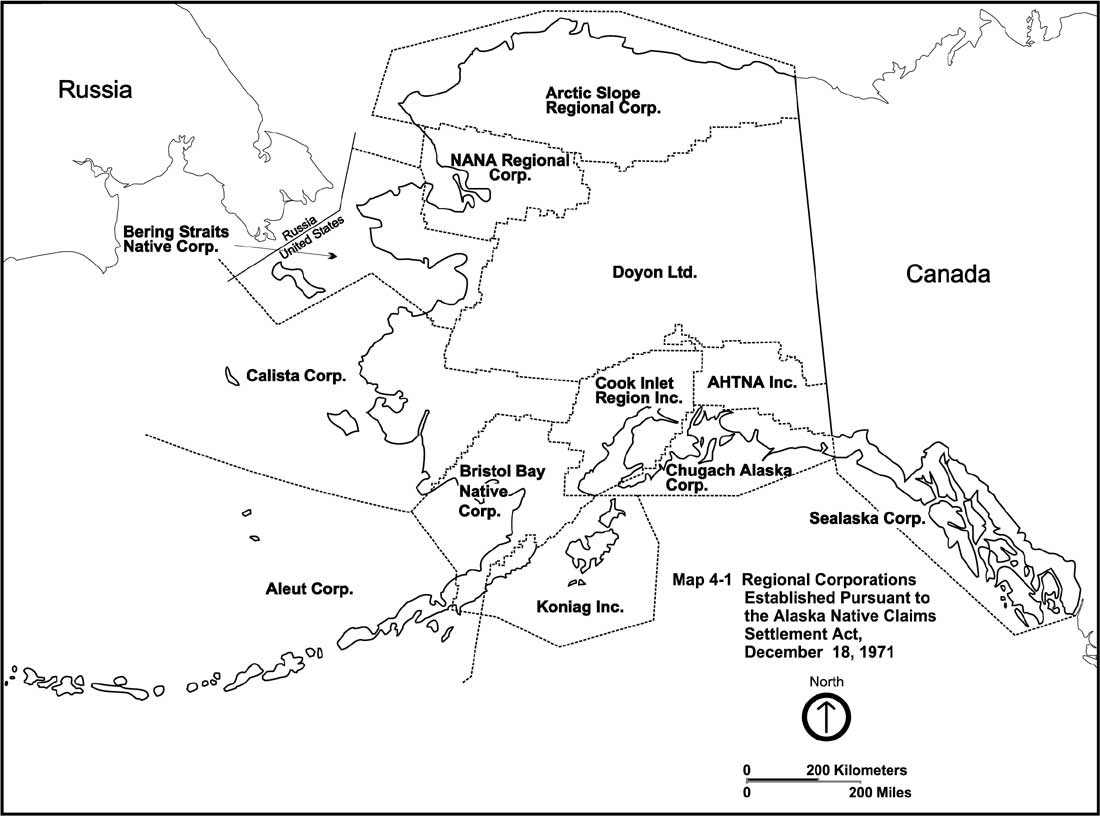
Bristol Bay Native Corporation
Bristol Bay Native Corporation, or BBNC, is one of thirteen Alaska Native Regional Corporations created under the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act of 1971 (ANCSA) in settlement of aboriginal land claims. Bristol Bay Native Corporation was incorporated in Alaska on June 13, 1972.Corporations Database Division of Corporations, Business & Professional Licensing, Alaska Department of Commerce, Community and Economic Development. Retrieved on 2015-04-16. Headquartered in Anchorage, Alaska, Anchorage, Alaska, Bristol Bay Native Corporation is a for-profit corporation with approximately 9,900 Alaska Native shareholders primarily of Eskimo, Aleut, and Indian descent. BBNC states its mission as “Enriching Our Native Way Of Life" as a corporation "that protects the past, present and future of the Natives from Bristol Bay.” BBNC's strategic goals are to build the value of BBNC's assets by increasing profitability and financial strength; to pay predictable and increasing dividends to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Native Regional Corporations
The Alaska Native Regional Corporations were established in 1971 when the United States Congress passed the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act (ANCSA) which settled land and financial claims made by the Alaska Natives and provided for the establishment of 13 regional corporations to administer those claims. Associations, regional and village corporations Under ANCSA the state was originally divided into twelve regions, each represented by a "Native association" responsible for the enrollment of past and present residents of the region. Individual Alaska Natives enrolled in these associations, and their village level equivalents, were made shareholder in the Regional and Village Corporations created by the Act. The twelve for-profit regional corporations, and a thirteenth region representing those Alaska Natives who were no longer residents of Alaska in 1971, were awarded the monetary and property compensation created by ANCSA. Village corporations and their shareholders receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act
The Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act (ANCSA) was signed into law by President Richard Nixon on December 18, 1971, constituting at the time the largest land claims settlement in United States history. ANCSA was intended to resolve long-standing issues surrounding aboriginal land claims in Alaska, as well as to stimulate economic development throughout Alaska."Recognition of aboriginal land rights in Alaska was a sharp departure from American Indian policy in other parts of the US. Observers believe this was more a result of slow economic development within Alaska than rejection of Indian policy," citing Cooley, R.A. 1983. "Evolution of Alaska land policy." in Morehouse, T. A. (editor). ''Alaskan Resources Development: Issues of the 1980s''. Boulder: Westview Press, pp. 13-49. The settlement established Alaska Native claims to the land by transferring titles to twelve Alaska Native regional corporations and over 200 local village corporations. A thirteenth regional corporation was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory to the east; it also shares a maritime border with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west, just across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. Alaska is by far the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the next three largest states (Texas, California, and Montana) combined. It represents the seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and the most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchorage, Alaska
Anchorage () is the largest city in the U.S. state of Alaska by population. With a population of 291,247 in 2020, it contains nearly 40% of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring Matanuska-Susitna Borough, had a population of 398,328 in 2020, accounting for more than half the state's population. At of land area, the city is the fourth-largest by area in the United States and larger than the smallest state, Rhode Island, which has . Anchorage is in Southcentral Alaska, at the terminus of the Cook Inlet, on a peninsula formed by the Knik Arm to the north and the Turnagain Arm to the south. In September 1975, the City of Anchorage merged with the Greater Anchorage Area Borough, creating the Municipality of Anchorage. The municipal city limits span , encompassing the urban core, a joint military base, several outlying communities, and almost all of Chugach State Park. Because of this, less than 10% of the Municipalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Natives
Alaska Natives (also known as Alaskan Natives, Native Alaskans, Indigenous Alaskans, Aboriginal Alaskans or First Alaskans) are the indigenous peoples of Alaska and include Iñupiat, Yupik, Aleut, Eyak, Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and a number of Northern Athabaskan cultures. They are often defined by their language groups. Many Alaska Natives are enrolled in federally recognized Alaska Native tribal entities, who in turn belong to 13 Alaska Native Regional Corporations, who administer land and financial claims. Ancestors of Native Alaskans or Alaska Natives migrated into the area thousands of years ago, in at least two different waves. Some are descendants of the third wave of migration, in which people settled across the northern part of North America. They never migrated to southern areas. For this reason, genetic studies show they are not closely related to native peoples in South America. Alaska Natives came from Asia. Anthropologists have stated that their journey from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eskimo
Eskimo () is an exonym used to refer to two closely related Indigenous peoples: the Inuit (including the Alaska Native Iñupiat, the Greenlandic Inuit, and the Canadian Inuit) and the Yupik peoples, Yupik (or Siberian Yupik, Yuit) of eastern Siberia and Alaska. A related third group, the Aleut, which inhabit the Aleutian Islands, are generally excluded from the definition of Eskimo. The three groups share a relatively recent common ancestor, and speak related languages belonging to the Eskaleut languages, Eskaleut language family. These circumpolar peoples have traditionally inhabited the Arctic and subarctic regions from eastern Siberia (Russia) to Alaska (United States), Northern Canada, Nunavik, Nunatsiavut, and Greenland. Many Inuit, Yupik, Aleut, and other individuals consider the term ''Eskimo'', which is of a disputed etymology, to be unacceptable and even pejorative. Eskimo continues to be used within a historical, linguistic, archaeological, and cultural context. The g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleut People
The Aleuts ( ; russian: Алеуты, Aleuty) are the indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleut people and the islands are politically divided between the US state of Alaska and the Russian administrative division of Kamchatka Krai. Etymology In the Aleut language they are known by the endonyms Unangan (eastern dialect) and Unangas (western dialect), both of which mean "people". The Russian term "Aleut" was a general term used for both the native population of the Aleutian Islands and their neighbors to the east in the Kodiak Archipelago, who were also referred to as "Pacific Eskimos". Language Aleut people speak Unangam Tunuu, the Aleut language, as well as English and Russian in the United States and Russia respectively. An estimated 150 people in the United States and five people in Russia speak Aleut. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United States are generally known by other terms). There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. As defined by the United States Census, "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives. Indigenous peoples of the United States who are not listed as American Indian or Alaska Native include Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and the Chamorro people. The US Census groups these peoples as " Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders". European colonization of the Americas, which began in 1492, resulted in a precipitous decline in Native American population because of new diseases, wars, ethni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Bay
Bristol Bay ( esu, Iilgayaq, russian: Залив Бристольский) is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km, (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow into the bay, including the Cinder, Egegik, Igushik, Kvichak, Meshik, Nushagak, Naknek, Togiak, and Ugashik. Upper reaches of Bristol Bay experience some of the highest tides in the world. One such reach, the Nushagak Bay near Dillingham and another near Naknek in Kvichak Bay have tidal extremes in excess of 10 m (30 ft), ranking them — and the area — as eighth highest in the world. Coupled with the extreme number of shoals, sandbars, and shallows, it makes navigation troublesome, especially during the area's frequently strong winds. As the shallowest part of the Bering Sea, Bristol Bay is one of the most dangerous regions for large vessels. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the north, Missouri on the northeast, Arkansas on the east, New Mexico on the west, and Colorado on the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "Sooners, The Sooner State", in reference to the settlers who staked their claims on land before the official op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncorhynchus
''Oncorhynchus'' is a genus of fish in the family Salmonidae; it contains the Pacific salmon and Pacific trout. The name of the genus is derived from the Greek ὄγκος (ónkos, “lump, bend”) + ῥύγχος (rhúnkhos, “snout”), in reference to the hooked snout (the "kype") that the males develop during mating season. Range Salmon and trout with native ranges in waters draining to the Pacific Ocean are members of the genus. Their range extends from Beringia southwards, roughly to Taiwan in the west and Mexico to the east. In North America, some subspecies of '' O. clarkii'' are native in the Rocky Mountains and Great Basin, while others are native to the Rio Grande and western tributaries of the Mississippi River Basin which drain to the Gulf of Mexico, rather than to the Pacific. Several species of ''Oncorhynchus'' have been introduced into non-native waters around the globe, establishing self-sustaining wild populations. The six Pacific salmons of ''Oncorhync ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race
The Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race, more commonly known as The Iditarod, is an annual long-distance sled dog race run in early March. It travels from Anchorage to Nome, entirely within the US state of Alaska. Mushers and a team of between 12 and 14 dogs, of which at least 5 must be on the towline at the finish line, cover the distance in 8–15 days or more. The Iditarod began in 1973 as an event to test the best sled dog mushers and teams but evolved into today's highly competitive race. Teams often race through blizzards causing whiteout conditions, sub-zero temperatures and gale-force winds which can cause the wind chill to reach . A ceremonial start occurs in the city of Anchorage and is followed by the official restart in Willow, a city north of Anchorage. The restart was originally in Wasilla through to 2007, but due to too little snow, the restart has been at Willow since 2008. The trail runs from Willow up the Rainy Pass of the Alaska Range into the sparsely pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)




.jpg)