|
Brimsdown Railway Station
Brimsdown railway station is on the Lea Valley line that forms part of the West Anglia Main Line, serving the neighbourhood of Brimsdown in the London Borough of Enfield, north London. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street and is situated between and . Its three-letter station code is BMD and it is in Travelcard zone 5. The station and all trains serving it are operated by Greater Anglia. Brimsdown station was used in 1951 as a location for part of the Alexander Mackendrick film ''The Man in the White Suit'', starring Alec Guinness, as the station where Sidney Stratton tries to buy a ticket near the end of the film. History The railway line from Stratford to was opened by the Northern & Eastern Railway on 15 September 1840. The station itself (which at one time was to be named Green Street) was financed by a local landowner and developer, and built by builder W Bangs & Co. The station opened on 1 October 1884, and services were operated by the Great Eastern R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Anglia (train Operating Company)
Greater Anglia (legal name Abellio East Anglia Limited) is a train operating company in Great Britain owned as a joint venture by Abellio, the international arm of the state-owned Dutch national rail operator Nederlandse Spoorwegen, and the Japanese trading company Mitsui & Co. It operates the East Anglia franchise, providing the commuter and intercity services from its Central London terminus at London Liverpool Street to Essex, Suffolk, Norfolk and parts of Hertfordshire and Cambridgeshire as well as many regional services throughout the East of England. Abellio began operating the franchise, then known as the Greater Anglia franchise, in February 2012. Initially, it traded under the same name until it rebranded as Abellio Greater Anglia in December 2013. Shortly after taking over operations, the company initiated a series of projects to improve service levels, including the procurement of new trains and the launch of the 'Norwich in 90' programme to reduce travel times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 (c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an Act of Parliament enacted by the British government and intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four large companies dubbed the "Big Four". This was intended to move the railways away from internal competition, and retain some of the benefits which the country had derived from a government-controlled railway during and after the Great War of 1914–1918. The provisions of the Act took effect from the start of 1923. History The British railway system had been built up by more than a hundred railway companies, large and small, and often, particularly locally, in competition with each other. The parallel railways of the East Midlands and the rivalry between the South Eastern Railway and the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway at Hastings were two examples of such local competition. During the First World War the railways were under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
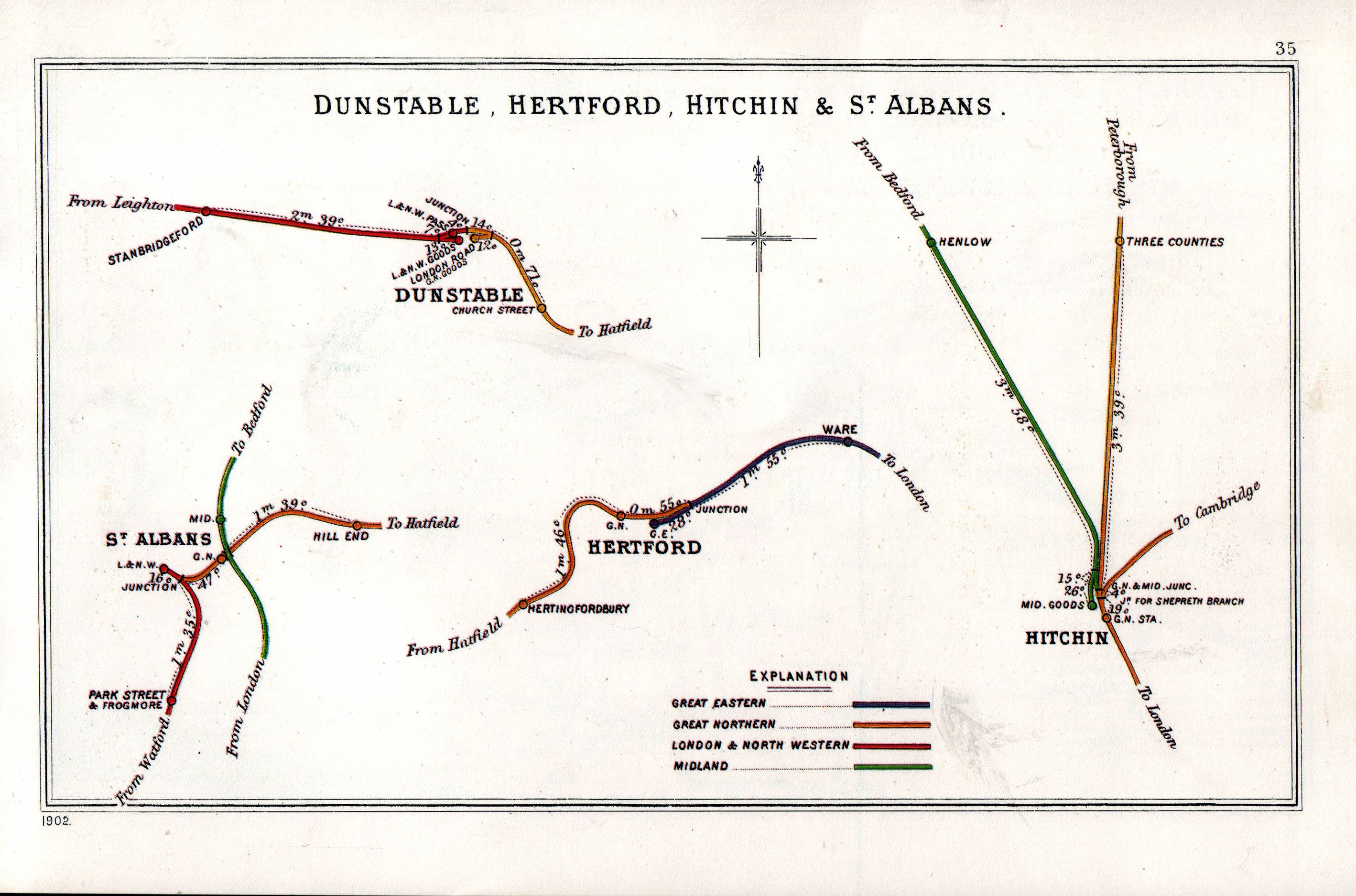
Hertford East Railway Station
Hertford East railway station is the northern terminus of the Hertford East branch line off the West Anglia Main Line in the east of England, and is located in the town of Hertford in Hertfordshire. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street and is one of two stations in the town, the other being on the Hertford Loop Line. Its three-letter station code is HFE. The station and all trains calling are operated by Greater Anglia. There are two platforms, although platform number one is generally only used during peak times, during times of disruption and primarily for trains to and from Stratford station. History The first station opened on 31st October 1843 sited to the east of the present station. The current station, designed by W. N. Ashbee, was opened by the Great Eastern Railway on 27 February 1888, replacing the first station. The station was listed in 1974 as a Grade II* listed building; in 1996 the buffer stop lights on platform 1 were separately listed in their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abellio Greater Anglia
Greater Anglia (legal name Abellio East Anglia Limited) is a train operating company in Great Britain owned as a joint venture by Abellio, the international arm of the state-owned Dutch national rail operator Nederlandse Spoorwegen, and the Japanese trading company Mitsui & Co. It operates the East Anglia franchise, providing the commuter and intercity services from its Central London terminus at London Liverpool Street to Essex, Suffolk, Norfolk and parts of Hertfordshire and Cambridgeshire as well as many regional services throughout the East of England. Abellio began operating the franchise, then known as the Greater Anglia franchise, in February 2012. Initially, it traded under the same name until it rebranded as Abellio Greater Anglia in December 2013. Shortly after taking over operations, the company initiated a series of projects to improve service levels, including the procurement of new trains and the launch of the 'Norwich in 90' programme to reduce travel times betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oyster Card
The Oyster card is a payment method for public transport in London (and certain areas around it) in England, United Kingdom. A standard Oyster card is a blue credit-card-sized stored-value contactless smart card. It is promoted by Transport for London (TfL) and can be used on travel modes across London including London Buses, London Underground, the Docklands Light Railway (DLR), London Overground, Tramlink, some river boat services, and most National Rail services within the London fare zones. Since its introduction in June 2003, more than 86 million cards have been used. Oyster cards can hold period tickets; travel permits and; most commonly, credit for travel ("Pay as you go"), which must be added to the card before travel. Passengers touch it on an electronic reader when entering and leaving the transport system in order to validate it and deduct funds from the stored credit. Cards may be "topped-up" by continuous payment authority, by online purchase, at credit card ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Express East Anglia
National Express East Anglia (NXEA) was a train operating company in England owned by National Express that operated the Greater Anglia franchise from April 2004 until February 2012. Originally trading as ''One'', it was rebranded National Express East Anglia in February 2008. It provided local, suburban and express services from London Liverpool Street to destinations in Essex, Hertfordshire, Cambridgeshire, Suffolk and Norfolk in the East of England. History When the British Rail services operating out of London Liverpool Street were privatised in January 1997, they were divided up between three train operating companies, Anglia Railways, First Great Eastern and West Anglia Great Northern. In December 2001, the Strategic Rail Authority announced it planned to combine all of the services operating out of London Liverpool Street into one Greater Anglia franchise. In April 2003, the Strategic Rail Authority announced Arriva, GB Railways and National Express had been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Express
National Express Group is a British multinational public transport company headquartered in Birmingham, England. It operates bus, coach, train and tram services in the United Kingdom, Ireland (National Express operates Eurolines in conjunction with Bus Éireann), United States, Canada, Spain, Portugal, Malta, Germany, Bahrain, and Morocco and long-distance coach services across Europe. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index. History In 1972, the state-owned National Bus Company decided to bring together the scheduled coach services operated by its bus operating companies in the United Kingdom under one brand. Sir Frederick Wood, a prominent businessman and industrialist, was asked to oversee the creation of this new business model and led the group as its chairman from 1972 to 1978. Initially branded as ''National'', the ''National Express'' brand was first used in 1974.Tram and V/Line Passenger rail franchises in the Australi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prism Rail
Prism Rail was formed in July 1995 to bid for rail franchises in the United Kingdom during the privatisation of British Rail. It expressed interest in eighteen franchises, was shortlisted for twelve and was ultimately awarded four, LTS Rail, Valley Lines, Wales & West, and West Anglia Great Northern. Prism Rail was founded by a number of individuals from the bus industry. The company raised the money to acquire its first passenger rail franchise from a small number of institutional investors, following which the shares were listed on the Alternative Investment Market in May 1996. In July 2000 Prism Rail was purchased by National Express. '' The Guardian
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Anglia Great Northern
West Anglia Great Northern, commonly shortened to ''WAGN'', was a train operating company in England. It operated the West Anglia Great Northern franchise between January 1997 and March 2004, as well as the Great Northern franchise between April 2004 and March 2006. It was initially owned by Prism Rail, and was subsequently acquired by the British transport conglomerate National Express. The West Anglia Great Northern franchise was created as part of the privatisation of British Rail, the recently-founded company Prism Rail successfully bid for it, being awarded a seven year concession for its operation during December 1996. It took over operations from British Rail on 5 January 1997. The company set about overhauling its inherited rolling stock, such as the Class 313 and Class 317 electric multiple units. By 1999, WAGN was amongst the best performing franchises according to statistics compiled by the Office of Passenger Rail Franchising. However, proposed open access service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privatisation Of British Rail
The privatisation of British Rail was the process by which ownership and operation of the railways of Great Britain passed from government control into private hands. Begun in 1994, it had been completed by 1997. The deregulation of the industry was initiated by EU Directive 91/440 in 1991, which aimed to create a more efficient rail network by creating greater competition. British Railways (BR) had been in state ownership since 1948, under the control of the British Railways Board (BRB). Under the Conservative government of Margaret Thatcher elected in 1979, various state-owned businesses were sold off, including various functions related to the railways – Sealink ferries and British Transport Hotels by 1984, Travellers Fare catering by 1988 and British Rail Engineering Limited (train building) by 1989. It was under Thatcher's successor John Major that the railways themselves were privatised, using the Railways Act 1993. The operations of the BRB were broken up and sold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railtrack
Railtrack was a group of companies that owned the track, signalling, tunnels, bridges, level crossings and all but a handful of the stations of the British railway system from 1994 until 2002. It was created as part of the privatisation of British Rail, listed on the London Stock Exchange, and was a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. In 2002, after experiencing major financial difficulty, most of Railtrack's operations were transferred to the state-controlled non-profit company Network Rail. The remainder of Railtrack was renamed RT Group plc and eventually dissolved on 22 June 2010. History Background and founding During the early 1990s, the Conservative Party decided to pursue the privatisation of Britain's nationalised railway operator British Rail. A white paper released in July 1992 had called for a publicly-owned company to be primarily responsible for the railway infrastructure, including the tracks, signalling, and stations, while train operations would be franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network SouthEast
Network SouthEast (NSE) was one of the three passenger sectors of British Rail created in 1982. NSE mainly operated commuter rail trains within Greater London and inter-urban services in densely populated South East England, although the network went as far west as Exeter. Before 1986, the sector was originally known as ''London & South Eastern''. During the privatisation of British Rail, it was gradually divided into a number of franchises. History Before the sectorisation of British Rail (BR) in 1982 the system was split into largely autonomous regional operations: those operating around London were the London Midland Region, Southern Region, Western Region and Eastern Region. Sectorisation of BR changed this setup by instead organising by the traffic type: commuter services in the south-east of England, long-distance intercity services, local services in the UK regions, parcels and freight. The aim was to introduce greater budgetary efficiency and managerial accountab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |