|
Breynia Carnosa
''Breynia'' is a plant genus in the family Phyllanthaceae, first described in 1776. It is native to Southeast Asia, China, the Indian Subcontinent, Papuasia, Australia, and the island of Réunion. The name ''Breynia'' is a conserved name, it is recognized despite the existence of an earlier use of the same name to refer to a different plant. ''Breynia'' L. 1753 is in the Capparaceae, but it is a rejected name. We here discuss ''Breynia'' J.R.Forst. & G.Forst. 1776. In a 2006 revision of the Phyllanthaceae, it was recommended that ''Breynia'' be subsumed in ''Phyllanthus''; however, new combinations in ''Phyllanthus'' for former ''Breynia'' species remain to be published. ''Breynia'' are of special note in the fields of pollination biology and coevolution because they have a specialized mutualism with moths in the genus ''Epicephala'' (leafflower moths), in which the moths actively pollinate the flowers—thereby ensuring that the tree may produce viable seeds—but also lay eg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breynia Disticha
''Breynia disticha'' is a plant in the family Phyllanthaceae, first described in 1776. It is native to New Caledonia and Vanuatu in the western Pacific, but naturalized on a wide assortment of other islands around the world (West Indies, São Tomé, Seychelles, Chagos Islands, Bonin Islands, Norfolk Island, Fiji, Line Islands, Society Islands, Hawaii, etc.), as well as in the U.S. state of Florida Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to .... ''Breynia disticha'' presumably is pollinated by leafflower moths (''Epicephala'' spp.) in its native range, like other species of plants in the genus ''Breynia''. Leafflower moths have been reared from fruit of this species in New Caledonia.Kawakita, A.; Kato, M. 2009. "Repeated independent evolution of obligate pollination mutualism i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capparaceae
The Capparaceae (or Capparidaceae), commonly known as the caper family, are a family of plants in the order Brassicales. As currently circumscribed, the family contains 33 genera and about 700 species. The largest genera are '' Capparis'' (about 150 species), '' Maerua'' (about 100 species), '' Boscia'' (37 species) and ''Cadaba'' (30 species). Taxonomy The Capparaceae have long been considered closely related to and have often been included in the Brassicaceae, the mustard family (APG, 1998), in part because both groups produce glucosinolate (mustard oil) compounds. Subsequent molecular studies support Capparaceae'' sensu stricto'' as paraphyletic with respect to the Brassicaceae. However ''Cleome'' and several related genera are more closely related to members of the Brassicaceae than to the other Capparaceae. These genera are now either placed in the Brassicaceae (as subfamily Clemoideae) or segregated into the Cleomaceae. Several more genera of the traditional Capparaceae ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breynia Carnosa
''Breynia'' is a plant genus in the family Phyllanthaceae, first described in 1776. It is native to Southeast Asia, China, the Indian Subcontinent, Papuasia, Australia, and the island of Réunion. The name ''Breynia'' is a conserved name, it is recognized despite the existence of an earlier use of the same name to refer to a different plant. ''Breynia'' L. 1753 is in the Capparaceae, but it is a rejected name. We here discuss ''Breynia'' J.R.Forst. & G.Forst. 1776. In a 2006 revision of the Phyllanthaceae, it was recommended that ''Breynia'' be subsumed in ''Phyllanthus''; however, new combinations in ''Phyllanthus'' for former ''Breynia'' species remain to be published. ''Breynia'' are of special note in the fields of pollination biology and coevolution because they have a specialized mutualism with moths in the genus ''Epicephala'' (leafflower moths), in which the moths actively pollinate the flowers—thereby ensuring that the tree may produce viable seeds—but also lay eg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breynia Calcarea
''Breynia'' is a plant genus in the family Phyllanthaceae, first described in 1776. It is native to Southeast Asia, China, the Indian Subcontinent, Papuasia, Australia, and the island of Réunion. The name ''Breynia'' is a conserved name, it is recognized despite the existence of an earlier use of the same name to refer to a different plant. ''Breynia'' L. 1753 is in the Capparaceae, but it is a rejected name. We here discuss ''Breynia'' J.R.Forst. & G.Forst. 1776. In a 2006 revision of the Phyllanthaceae, it was recommended that ''Breynia'' be subsumed in ''Phyllanthus''; however, new combinations in ''Phyllanthus'' for former ''Breynia'' species remain to be published. ''Breynia'' are of special note in the fields of pollination biology and coevolution because they have a specialized mutualism with moths in the genus ''Epicephala'' (leafflower moths), in which the moths actively pollinate the flowers—thereby ensuring that the tree may produce viable seeds—but also lay eg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breynia Baudouinii
''Breynia'' is a plant genus in the family Phyllanthaceae, first described in 1776. It is native to Southeast Asia, China, the Indian Subcontinent, Papuasia, Australia, and the island of Réunion. The name ''Breynia'' is a conserved name, it is recognized despite the existence of an earlier use of the same name to refer to a different plant. ''Breynia'' L. 1753 is in the Capparaceae, but it is a rejected name. We here discuss ''Breynia'' J.R.Forst. & G.Forst. 1776. In a 2006 revision of the Phyllanthaceae, it was recommended that ''Breynia'' be subsumed in ''Phyllanthus''; however, new combinations in ''Phyllanthus'' for former ''Breynia'' species remain to be published. ''Breynia'' are of special note in the fields of pollination biology and coevolution because they have a specialized mutualism with moths in the genus ''Epicephala'' (leafflower moths), in which the moths actively pollinate the flowers—thereby ensuring that the tree may produce viable seeds—but also lay eg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodoxidae
The Prodoxidae are a family of moths, generally small in size and nondescript in appearance. They include species of moderate pest status, such as the Lampronia capitella, currant shoot borer, and others of considerable ecological and evolutionary interest, such as various species of "yucca moths". Description and affinities Prodoxidae are a family of primitive monotrysian Lepidoptera. Some of these small-to-medium-sized moths are day flying, like ''Lampronia capitella'', known to European gardeners as the currant shoot borer. Others occur in Africa and Asia. The other common genera are generally confined to dry areas of the United States. ''Tetragma gei'' feeds on mountain avens (''Geum triflorum'') in the US. ''Greya politella'' lay eggs in the flowers of Saxifragaceae there. ''Prodoxoides asymmetra'' occurs in Chile and Argentina, but all other prodoxid moth genera have a northern distribution. The enigmatic genus ''Tridentaforma'' is sometimes placed here and assumed to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucca
''Yucca'' is a genus of perennial shrubs and trees in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Agavoideae. Its 40–50 species are notable for their rosettes of evergreen, tough, sword-shaped leaves and large terminal panicles of white or whitish flowers. They are native to the hot and dry (arid) parts of the Americas and the Caribbean. Early reports of the species were confused with the cassava (''Manihot esculenta''). Consequently, Linnaeus mistakenly derived the generic name from the Taíno word for the latter, ''yuca''. The Aztecs living in Mexico since before the Spanish arrival, in Nahuatl, call the local yucca species (''Yucca gigantea'') , which gave the Spanish . is also used for ''Yucca filifera''. Distribution The natural distribution range of the genus ''Yucca'' (49 species and 24 subspecies) covers a vast area of the Americas. The genus is represented throughout Mexico and extends into Guatemala (''Yucca guatemalensis''). It also extends to the north through Baja Cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
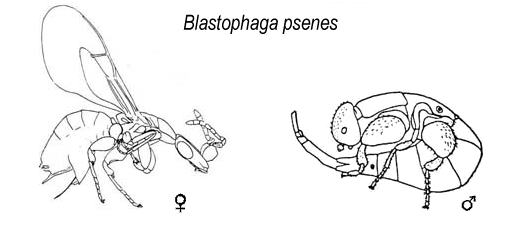
Fig Wasp
Fig wasps are wasps of the superfamily Chalcidoidea which spend their larval stage inside figs. Most are pollinators but others simply feed off the plant. The non-pollinators belong to several groups within the superfamily Chalcidoidea, while the pollinators are in the family Agaonidae. While pollinating fig wasps are gall-makers, the remaining types either make their own galls or usurp the galls of other fig wasps; reports of their being parasitoids are considered dubious. History Aristotle recorded in his ''History of Animals'' that the fruits of the wild fig (the caprifig) contain ''psenes'' (fig wasps); these begin life as grubs (larvae), and the adult ''psen'' splits its "skin" (pupa) and flies out of the fig to find and enter a cultivated fig, saving it from dropping. He believed that the ''psen'' was generated spontaneously; he did not recognise that the fig was reproducing sexually and that the ''psen'' was assisting in that process. Taxonomy The fig wasps are a pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ficus
''Ficus'' ( or ) is a genus of about 850 species of woody trees, shrubs, vines, epiphytes and hemiepiphytes in the family Moraceae. Collectively known as fig trees or figs, they are native throughout the tropics with a few species extending into the semi-warm temperate zone. The common fig (''F. carica'') is a temperate species native to southwest Asia and the Mediterranean region (from Afghanistan to Portugal), which has been widely cultivated from ancient times for its fruit, also referred to as figs. The fruit of most other species are also edible though they are usually of only local economic importance or eaten as bushfood. However, they are extremely important food resources for wildlife. Figs are also of considerable cultural importance throughout the tropics, both as objects of worship and for their many practical uses. Description ''Ficus'' is a pantropical genus of trees, shrubs, and vines occupying a wide variety of ecological niches; most are evergreen, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glochidion
''Glochidion'' is a genus of flowering plants, of the family Phyllanthaceae, known as cheese trees or buttonwood in Australia, and leafflower trees in the scientific literature. It comprises about 300 species, distributed from Madagascar to the Pacific Islands. ''Glochidion'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including '' Aenetus eximia'' and '' Endoclita damor''. The Nicobarese people have attested to the medicinal properties found in ''G. calocarpum'', saying that its bark and seed are most effective in curing abdominal disorders associated with amoebiasis. ''Glochidion'' are of note in the fields of pollination biology and coevolution because they have a specialized mutualism with moths in the genus ''Epicephala'' (leafflower moths), in which the moths actively pollinate the flowers—thereby ensuring that the tree may produce viable seeds—but also lay eggs in the flowers' ovaries, where their larvae consume a subset of the developing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllanthus
''Phyllanthus'' is the largest genus in the plant family Phyllanthaceae. Estimates of the number of species in this genus vary widely, from 750David J. Mabberley. 2008. ''Mabberley's Plant-Book.'' third edition (2008). Cambridge University Press. to 1200. ''Phyllanthus'' has a remarkable diversity of growth forms including annual and perennial herbs, shrubs, climbers, floating aquatics, and pachycaulous succulents. Some have flattened leaflike stems called cladodes. It has a wide variety of floral morphologies and chromosome numbers and has one of the widest range of pollen types of any seed plant genus. Despite their variety, almost all ''Phyllanthus'' species express a specific type of growth called "phyllanthoid branching" in which the vertical stems bear deciduous, floriferous (flower-bearing), plagiotropic (horizontal or oblique) stems. The leaves on the main (vertical) axes are reduced to scales called "cataphylls", while leaves on the other axes develop normally. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicephala
''Epicephala'' (leafflower moths) is a genus of moths in the family Gracillariidae. ''Epicephala'' is of note in the fields of pollination biology and coevolution because many species in this genus are pollinators of plants in the genera ''Glochidion'', ''Phyllanthus'', and ''Breynia'' (Phyllanthaceae). These pollinating ''Epicephala'' actively pollinate the flowers of their host plants—thereby ensuring that the plants may produce viable seeds—but also lay eggs in the flowers' ovaries, where their larvae consume a subset of the developing seeds as nourishment.Kawakita, A.; Kato, M. (2009) "Repeated independent evolution of obligate pollination mutualism in the Phyllantheae-''Epicephala'' association." ''Proceedings of the Royal Society B.'' 276: 417–426. This relationship is similar to other specialized pollinating seed-predation mutualisms such as those between figs and fig wasps and yuccas and yucca moths. Other species of ''Epicephala'' consume the seeds of species o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |