|
Breda International Airport
Breda International Airport ( nl, Breda International Airport ) is a small general aviation airfield located next to the A58 motorway on the outskirts of Bosschenhoofd, a village in the municipality of Halderberge in the province of North Brabant in the Netherlands. It is located southwest of Hoeven, west from Breda and east-northeast of Roosendaal. The airport has one single asphalt runway, 06/24(used to be 07/25), with a length of and a significantly displaced threshold (meaning an area at the beginning of that runway is not to be used for landing) on either side. Originally called Seppe Airport (after the nickname of Bosschenhoofd), the airport started in 1949 as a glider field and has been used by powered aircraft since 1969. In 2002, the grass runway surface was replaced with asphalt. The airfield is not used by aircraft using jet engines. Around 50,000 airplane movements (take-offs or landings) are made at Seppe annually. In February 2014 it was announced that the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoeven
Hoeven is a village in the municipality of Halderberge in the Netherlands. The name Hoeven originated from the purchase of a certain amount of ground in 1282 by the abbey of Cistercians of St. Bernard. This amount was equal to 100 "hoeven", a local measure of area in those days. A hoeve is approximately 12 bunder. A "bunder" equals the area of the average agricultural farm in the Netherlands. Municipality of Hoeven Hoeven was a separate municipality until 1997 including the three villages of Bosschenhoofd, Hoeven and Kruisstraat. In 1997 the municipality of Hoeven became a part of Halderberge. Different names Though the village officially is named Hoeven, most civilians use and pronounce it as "Oeve" or "d'Oeve" as 'Hoeven' is pronounced in the local dialect, Brabants. Remarkable in the southern parts of the Netherlands, where they officially celebrate carnival, is that during this period all places change names during this seven-day celebration. In case of Hoeven it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roosendaal
Roosendaal () is both a city and a municipality in the southern Netherlands, in the province of North Brabant. Towns/villages of the municipality * Roosendaal (population: 66,760) * Wouw (4,920) * Heerle (1,900) * Nispen (1,440) * Wouwse Plantage (1,230) * Moerstraten (660) The city of Roosendaal Under King Louis Bonaparte of the Kingdom of Holland, Roosendaal received city rights in 1809. Nispen merged with Roosendaal to form the municipality Roosendaal en Nispen. On 1 January 1997 the municipalities Roosendaal en Nispen and Wouw merged into the municipality now simply known as Roosendaal. History Roosendaal goes back to the 12th and 13th century. The name Rosendaele was first mentioned in a document of 1268. Roosendaal was always a part of North Brabant. In the Middle Ages, Roosendaal grew as a result of the turf business, but the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) put an end to the growth as Roosendaal and Wouw were suffering from itinerant combat troops that plu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
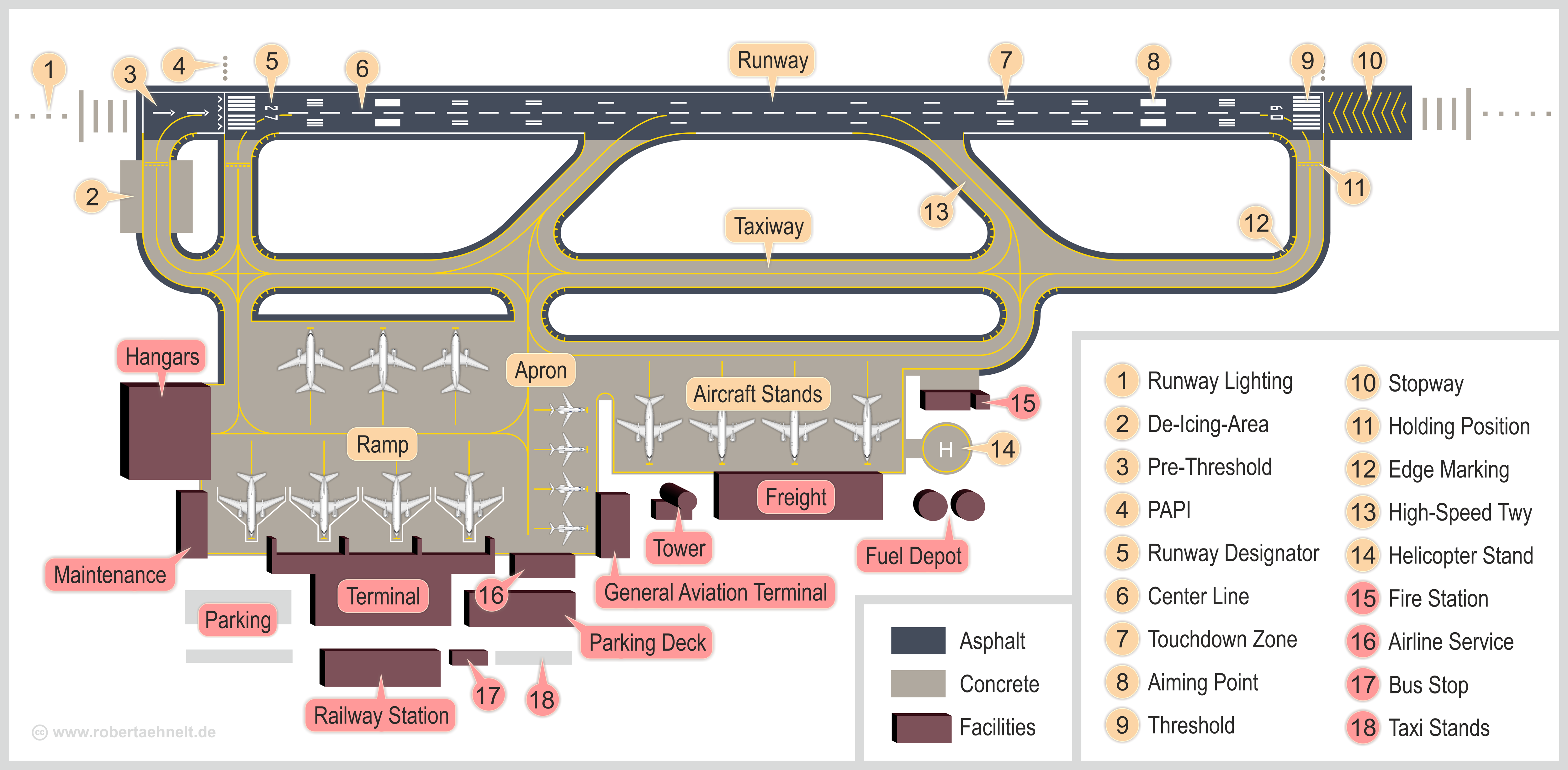
Airports In North Brabant
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airliners
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an airplane intended for carrying multiple passengers or cargo in commercial service. The largest of them are wide-body jets which are also called twin-aisle because they generally have two separate aisles running from the front to the back of the passenger cabin. These are usually used for long-haul flights between airline hubs and major cities. A smaller, more common class of airliners is the narrow-body or single-aisle. These are generally used for short to medium-distance flights with fewer passengers than their wide-body counterparts. Regional airliners typically seat fewer than 100 passengers and may be powered by turbofans or turboprops. These airliners are the non- mainline counterparts to the larger aircraft operated by the major car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation Performance Solutions
Aviation Performance Solutions is an aviation training company based in Mesa, Arizona. APS trains and instructs pilots of all experience levels in Upset Prevention and Recovery Training (UPRT). History In 2005, APS was founded, with a specific focus on advancing Upset Prevention and Recovery Training (UPRT) for all pilots. APS team members participated in shaping global UPRT recommendations by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) in 2014. APS's strategic partners include CAE, Inc. (and its military division CAE USA), Swiss Re, USAIG. Programs and courses According to Flying magazine, "APS provides training on Loss of Control In-flight (LOC-I), as well as recovery concepts and techniques". Upset Prevention and Recovery Training (UPRT) APS is known for their approach to UPRT that includes the combination of computer-based, on-aircraft, and full-flight simulator training platforms, which reduce the risk of Loss of Control In-flight (LOC-I) through flight trainin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakovlev Yak-52
The Yakovlev Yak-52 (russian: Яковлев Як-52) is a Soviet primary trainer aircraft which first flew in 1976. It was produced in Romania from 1977 to 1998 by Aerostar, as ''Iak-52'', which gained manufacturing rights under agreement within the former COMECON socialist trade organisation. The Yak-52 was designed as an aerobatic trainer for students in the Soviet DOSAAF training organisation, which trained civilian sport pilots and military pilots. Currently the Yak-52 is used in the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI) World Aerobatic Yak 52 Competition, a popular powered aircraft one-design World Aerobatic Championship. Design and development A descendant of the single-seat competition aerobatic Yakovlev Yak-50, the all-metal Yak-52 is powered by a 268 kW (360 hp) Vedeneyev M14P nine-cylinder radial engine. Since the aircraft was designed to serve as a military trainer, the development of the aircraft incorporates a number of features to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing Stearman
The Stearman (Boeing) Model 75 is a biplane formerly used as a military trainer aircraft, of which at least 10,626 were built in the United States during the 1930s and 1940s. Stearman Aircraft became a subsidiary of Boeing in 1934. Widely known as the Stearman, Boeing Stearman, or Kaydet, it served as a primary trainer for the United States Army Air Forces, the United States Navy (as the NS and N2S), and with the Royal Canadian Air Force as the Kaydet throughout World War II. After the conflict was over, thousands of surplus aircraft were sold on the civilian market. In the immediate postwar years, they became popular as crop dusters and sports planes, and for aerobatic and wing walking use in air shows. Design and development The Kaydet was a conventional biplane of rugged construction, with a large, fixed tailwheel undercarriage, and accommodation for the student and instructor in open cockpits in tandem. The radial engine was usually not cowled, although some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Havilland Tiger Moth
The de Havilland DH.82 Tiger Moth is a 1930s British biplane designed by Geoffrey de Havilland and built by the de Havilland, de Havilland Aircraft Company. It was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and other operators as a primary trainer (aircraft), trainer aircraft. In addition to the type's principal use for ''ab initio'' training, the World War II, Second World War had RAF Tiger Moths operating in other capacities, including Maritime patrol aircraft, maritime surveillance and defensive anti-invasion preparations; some aircraft were even outfitted to function as armed light bombers. The Tiger Moth remained in service with the RAF until it was replaced by the de Havilland Canada DHC-1 Chipmunk, de Havilland Chipmunk during the early 1950s. Many of the military surplus aircraft subsequently entered into civilian operation. Many nations have used the Tiger Moth in both military and civilian applications, and it remains in widespread use as a recreational aircraft. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glider Aircraft
A glider is a fixed-wing aircraft that is supported in flight by the dynamic reaction of the air against its lifting surfaces, and whose free flight does not depend on an engine. Most gliders do not have an engine, although motor-gliders have small engines for extending their flight when necessary by sustaining the altitude (normally a sailplane relies on rising air to maintain altitude) with some being powerful enough to take off by self-launch. There are a wide variety of types differing in the construction of their wings, aerodynamic efficiency, location of the pilot, controls and intended purpose. Most exploit meteorological phenomena to maintain or gain height. Gliders are principally used for the air sports of gliding, hang gliding and paragliding. However some spacecraft have been designed to descend as gliders and in the past military gliders have been used in warfare. Some simple and familiar types of glider are toys such as paper planes and balsa wood gliders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displaced Threshold
A displaced threshold or DTHR is a runway threshold located at a point other than the physical beginning or end of the runway. The portion of the runway behind a displaced threshold may be used for takeoff in either direction and landings from the opposite direction. After landing at the other end, the landing aircraft may use the area behind the displaced threshold for roll out.Aircraft Information Manual 2013, Chapter 2-3-3 h (2) Section 3. Airport Marking Aids and Signs /ref> Most often, the offset threshold is in place to give arriving aircraft clearance over an obstruction, while still allowi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breda
Breda () is a city and municipality in the southern part of the Netherlands, located in the province of North Brabant. The name derived from ''brede Aa'' ('wide Aa' or 'broad Aa') and refers to the confluence of the rivers Mark and Aa. Breda has 185,072 inhabitants on 13 September 2022 and is part of the Brabantse Stedenrij; it is the ninth largest city/municipality in the country, and the third largest in North Brabant after Eindhoven and Tilburg. It is equidistant between Rotterdam and Antwerp. As a fortified city, it was of strategic military and political significance. Although a direct Fiefdom of the Holy Roman Emperor, the city obtained a municipal charter; the acquisition of Breda, through marriage, by the House of Nassau ensured that Breda would be at the centre of political and social life in the Low Countries. Breda had a population of in ; the metropolitan area had a population of . History In the 11th century, Breda was a direct fief of the Holy Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosschenhoofd
Bosschenhoofd is a village in the municipality of Halderberge in the province of North Brabant in the Netherlands. The village is also known as Seppe, a name used by the nearby Seppe Airport. Seppe was derived from Jacobus Sep who ran an inn. Before the municipal reorganization of 1997, Bosschenhoofd belonged to the municipality of Hoeven. History The village was first mentioned in 1740 as Bossenhooft, and means "destination (of the peat ships) of Oudenbosch". Bosschenhoofd started during the peat excavation of the area, and became the replacement harbour for Oudenbosch after 1621. The village developed as a linear settlement in the 19th century. Bosschenhoofd was home to 269 people in 1840. The Seppe railway station was built in 1854 on the Roosendaal to Breda railway line. It was closed in 1940. The building is nowadays used as a flower shop. The Catholic Sacred Heart of Jesus Church was built in 1928. It was severely damaged during World War II, and rebuilt in 1946. Seppe Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




