|
Branch Prediction
In computer architecture, a branch predictor is a digital circuit that tries to guess which way a branch (e.g., an if–then–else structure) will go before this is known definitively. The purpose of the branch predictor is to improve the flow in the instruction pipeline. Branch predictors play a critical role in achieving high performance in many modern pipelined microprocessor architectures. Two-way branching is usually implemented with a conditional jump instruction. A conditional jump can either be "taken" and jump to a different place in program memory, or it can be "not taken" and continue execution immediately after the conditional jump. It is not known for certain whether a conditional jump will be taken or not taken until the condition has been calculated and the conditional jump has passed the execution stage in the instruction pipeline (see fig. 1). Without branch prediction, the processor would have to wait until the conditional jump instruction has passed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pentium 4
Pentium 4 is a series of single-core central processing unit, CPUs for Desktop computer, desktops, laptops and entry-level Server (computing), servers manufactured by Intel. The processors were shipped from November 20, 2000 until August 8, 2008. All Pentium 4 CPUs are based on the NetBurst microarchitecture, the successor to the P6 (microarchitecture), P6. The Pentium 4 #Willamette, Willamette (180 nm) introduced SSE2, while the #Prescott, Prescott (90 nm) introduced SSE3 and later 64-bit technology. Later versions introduced Hyper-threading, Hyper-Threading Technology (HTT). The first Pentium 4-branded processor to implement x86-64, 64-bit was the Prescott (90 nm) (February 2004), but this feature was not enabled. Intel subsequently began selling 64-bit Pentium 4s using the ''"E0" revision'' of the Prescotts, being sold on the OEM market as the Pentium 4, model F. The E0 revision also adds eXecute Disable (XD) (Intel's name for the NX bit) to Intel 64. Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Original Intel Pentium (P5 Microarchitecture)
The Pentium (also referred to as the i586 or P5 Pentium) is a microprocessor introduced by Intel on March 22, 1993. It is the first CPU using the Pentium brand. Considered the fifth generation in the x86 (8086) compatible line of processors, succeeding the i486, its implementation and microarchitecture was internally called ''P5''. Like the Intel i486, the Pentium is instruction set compatible with the 32-bit i386. It uses a very similar microarchitecture to the i486, but was extended enough to implement a dual integer pipeline design, as well as a more advanced floating-point unit (FPU) that was noted to be ten times faster than its predecessor. The Pentium was succeeded by the Pentium Pro in November 1995. In October 1996, the Pentium MMX was introduced, complementing the same basic microarchitecture of the original Pentium with the MMX instruction set, larger caches, and some other enhancements. Intel discontinued the P5 Pentium processors (sold as a cheaper product sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Branch Prediction 2bit Saturating Counter-dia
A branch, also called a ramus in botany, is a stem that grows off from another stem, or when structures like veins in leaves are divided into smaller veins. History and etymology In Old English, there are numerous words for branch, including , , , and . There are also numerous descriptive words, such as (that is, something that has bled, or 'bloomed', out), (literally 'little bough'), (literally 'on growth'), and (literally 'offspringing'). Numerous other words for twigs and boughs abound, including , which still survives as the ''-toe'' in ''mistletoe''. Latin words for branch are or . The latter term is an affix found in other modern words such as ''cladodont'' (prehistoric sharks with branched teeth), ''cladode'' (flattened leaf-like branches), or ''cladogram'' (a branched diagram showing relations among organisms). Woody branches Large branches are known as boughs and small branches are known as twigs. The term ''twig'' usually refers to a terminus, while ''bough ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
State Machine
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of ''states'' at any given time. The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some inputs; the change from one state to another is called a ''transition''. An FSM is defined by a list of its states, its initial state, and the inputs that trigger each transition. Finite-state machines are of two types— deterministic finite-state machines and non-deterministic finite-state machines. For any non-deterministic finite-state machine, an equivalent deterministic one can be constructed. The behavior of state machines can be observed in many devices in modern society that perform a predetermined sequence of actions depending on a sequence of events with which they are presented. Simple examples are: vending machines, which dispens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saturation Arithmetic
Saturation arithmetic is a version of arithmetic in which all operations, such as addition and multiplication, are limited to a fixed range between a minimum and maximum value. If the result of an operation is greater than the maximum, it is set (" clamped") to the maximum; if it is below the minimum, it is clamped to the minimum. The name comes from how the value becomes "saturated" once it reaches the extreme values; further additions to a maximum or subtractions from a minimum will not change the result. For example, if the valid range of values is from −100 to 100, the following ''saturating arithmetic operations'' produce the following values: *60 + 30 → 90. *60 + 43 → 100. (''not'' the expected 103.) *(60 + 43) − (75 + 25) → 0. (''not'' the expected 3.) (100 − 100 → 0.) *10 × 11 → 100. (''not'' the expected 110.) *99 × 99 → 100. (''not'' the expected 9801.) *30 × (5 − 1) → 100. (''not'' the expected 120.) (30 × 4 → 100.) *(30 × 5) − (30 × 1) � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, flip-flops and latches are electronic circuit, circuits that have two stable states that can store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will output its state (often along with its logical complement too). It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements to store a single ''bit'' (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a "one" and the other represents a "zero". Such data storage can be used for storage of ''state (computer science), state'', and such a circuit is described as sequential logic in electronics. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Delay Slot
In computer architecture, a delay slot is an instruction slot being executed without the effects of a preceding instruction. The most common form is a single arbitrary instruction located immediately after a branch instruction (computer science), instruction on a RISC or Digital signal processor, DSP architecture; this instruction will execute even if the preceding branch is taken. This makes the instruction execute Out-of-order execution, out-of-order compared to its location in the original assembler language code. Modern processor designs generally do not use delay slots, and instead perform ever more complex forms of branch prediction. In these systems, the CPU immediately moves on to what it believes will be the correct side of the branch and thereby eliminates the need for the code to specify some unrelated instruction, which may not always be obvious at compile-time. If the assumption is wrong, and the other side of the branch has to be called, this can introduce a lengthy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alpha 21464
The Alpha 21464 is an unfinished microprocessor that implements the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Digital Equipment Corporation and later by Compaq after it acquired Digital. The microprocessor was also known as EV8 (codenamed Araña). Slated for a 2004 release, it was canceled on 25 June 2001 when Compaq announced that Alpha would be phased out in favor of Itanium by 2004. When it was canceled, the Alpha 21464 was at a late stage of development but had not been taped out. The 21464's origins began in the mid-1990s when computer scientist Joel Emer was inspired by Dean Tullsen's research into simultaneous multithreading (SMT) at the University of Washington. Emer had researched the technology in the late 1990s and began to promote it once he was convinced of its value. Compaq made the announcement that the next Alpha microprocessor would use SMT in October 1999 at Microprocessor Forum 1999. At that time, it was expected that systems using the Alpha 21464 wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
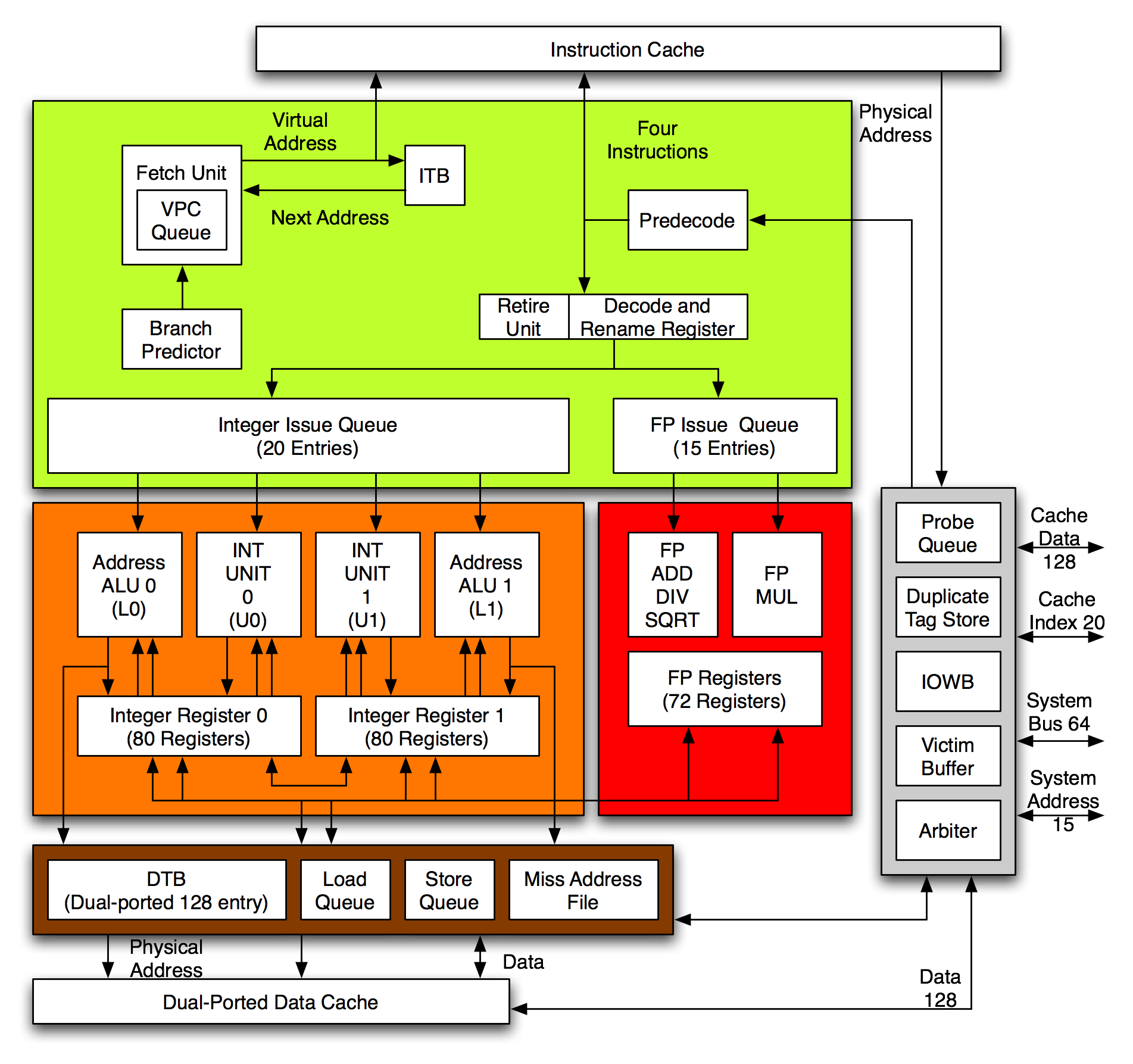
Alpha 21264
The Alpha 21264, also known by its code name, EV6, is a RISC microprocessor developed by Digital Equipment Corporation launched on 19 October 1998. The 21264 implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA). Description The Alpha 21264 is a four-issue superscalar microprocessor with out-of-order execution and speculative execution. It has a peak execution rate of six instructions per cycle and could sustain four instructions per cycle. It has a seven-stage instruction pipeline. Out of order execution At any given stage, the microprocessor could have up to 80 instructions in various stages of execution, surpassing any other contemporary microprocessor. Decoded instructions are held in instruction queues and are issued when their operands are available. The integer queue contained 20 entries and the floating-point queue 15. Each queue could issue as many instructions as there were pipelines. Ebox The Ebox executes integer, load and store instructions. It has tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
R8000
The R8000 is a microprocessor chipset developed by MIPS Technologies, MIPS Technologies, Inc. (MTI), Toshiba, and Weitek.Hsu 1994 It was the first implementation of the MIPS IV instruction set architecture. The R8000 is also known as the ''TFP'', for ''Tremendous Floating-Point'', its name during development. History Development of the R8000 started in the early 1990s at Silicon Graphics, Inc. (SGI). The R8000 was specifically designed to provide the performance of circa 1990s supercomputers with a microprocessor instead of a central processing unit (CPU) built from many discrete components such as gate arrays. At the time, the performance of traditional supercomputers was not advancing as rapidly as reduced instruction set computer (RISC) microprocessors. It was predicted that RISC microprocessors would eventually match the performance of more expensive and larger supercomputers at a fraction of the cost and size, making computers with this level of performance more accessible and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Superscalar Processor
A superscalar processor (or multiple-issue processor) is a CPU that implements a form of parallelism called instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. In contrast to a scalar processor, which can execute at most one single instruction per clock cycle, a superscalar processor can execute or start executing more than one instruction during a clock cycle by simultaneously dispatching multiple instructions to different execution units on the processor. It therefore allows more throughput (the number of instructions that can be executed in a unit of time which can even be less than 1) than would otherwise be possible at a given clock rate. Each execution unit is not a separate processor (or a core if the processor is a multi-core processor), but an execution resource within a single CPU such as an arithmetic logic unit. While a superscalar CPU is typically also pipelined, superscalar and pipelining execution are considered different performance enhancement techniq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |