|
Bradysaurus BW
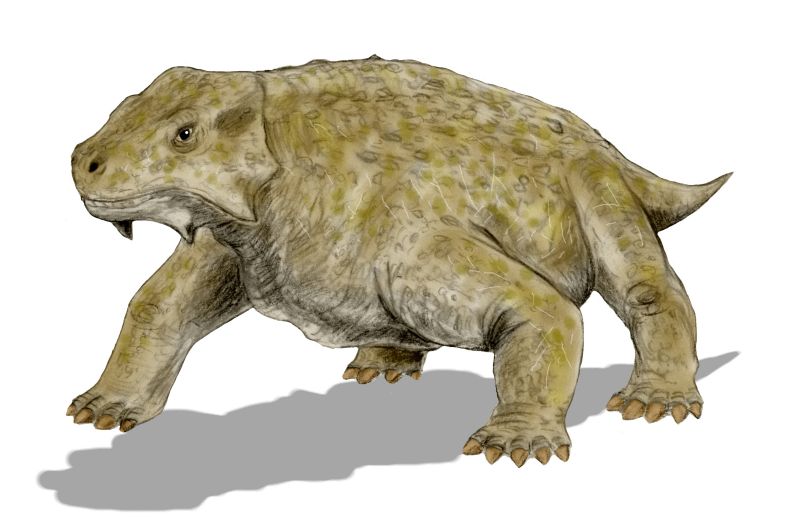
''Bradysaurus'' was a large, early and common pareiasaur, the fossils of which are known from the ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone (Capitanian age) of the South African Karoo. Along with the similarly large dinocephalia, the bradysaurs constituted the herbivorous megafauna of the late Middle Permian Period. In life they were probably slow, clumsy and inoffensive animals, that had evolved a covering of armoured scutes to protect them against their predators, the gorgonopsians. Description ''Bradysaurus'' was in length and half a tonne to a tonne in weight. The skull was large (about 42 to 48 centimeters long), broad and rounded at the front. It was coarsely sculptured and knobby, with the sutures between the bones not clearly visible. The marginal teeth were high-crowned, with only a few cusps, which is a primitive characteristic. The feet were short and broad, the phalangeal count being 2,3,3,3,2 on the fore-foot and 2,3,3,4,3 on the hind. The whole body is protect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hardveld") is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its extent is also not precisely defined. The Karoo is partly defined by its topography, geology and climate, and above all, its low rainfall, arid air, cloudless skies, and extremes of heat and cold.Potgieter, D.J. & du Plessis, T.C. (1972) ''Standard Encyclopaedia of Southern Africa''. Vol. 6. pp. 306–307. Nasou, Cape Town.''Reader’s Digest Illustrated Guide to Southern Africa''. (5th Ed. 1993). pp. 78–89. Reader’s Digest Association of South Africa Pty. Ltd., Cape Town. The Karoo also hosted a well-preserved ecosystem hundreds of million years ago which is now represented by many fossils. The ǃ’Aukarob formed an almost impenetrable barrier to the interior from Cape Town, and the early adventurers, explorers, hunters, and travelers o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitanian
In the geologic timescale, the Capitanian is an age or stage of the Permian. It is also the uppermost or latest of three subdivisions of the Guadalupian Epoch or Series. The Capitanian lasted between and million years ago. It was preceded by the Wordian and followed by the Wuchiapingian.; 2004: ''A Geologic Time Scale 2004'', Cambridge University Press A significant mass extinction event occurred at the end of this stage, which was associated with anoxia and acidification in the oceans and possibly caused by the volcanic eruptions that produced the Emeishan Traps. This extinction event may be related to the much larger Permian–Triassic extinction event that followed about 10 million years later. Stratigraphy The Capitanian Stage was introduced into scientific literature by George Burr Richardson in 1904. The name comes from the Capitan Reef in the Guadalupe Mountains (Texas, United States). The Capitanian was first used as a stratigraphic subdivision of the Guadalupian in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suture (anatomical)
In anatomy, a suture is a fairly rigid joint between two or more hard elements of an organism, with or without significant overlap of the elements. Sutures are found in the skeletons or exoskeletons of a wide range of animals, in both invertebrates and vertebrates. Sutures are found in animals with hard parts from the Cambrian period to the present day. Sutures were and are formed by several different methods, and they exist between hard parts that are made from several different materials. Vertebrate skeletons The skeletons of vertebrate animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals) are made of bone, in which the main rigid ingredient is calcium phosphate. Cranial sutures The skulls of most vertebrates consist of sets of bony plates held together by cranial sutures. These sutures are held together mainly by Sharpey's fibers which grow from each bone into the adjoining one. Sutures in the ankles of land vertebrates In the type of crurotarsal ankle which is found i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaurs
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with scutes which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, reaching sizes equivalent to those of contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct at the end of the Permian during the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, and may have weighed up to . They were stocky, with short tails, small heads, robust limbs, and broad feet. The cow-sized species ''Bunostegos'', which lived 260 million years ago, is the earliest known example of a tetrapod with a fully erect posture as its legs were positioned directly under its body. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms that were set into the skin. Their heavy skulls were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mildred Adams Fenton
Mildred Adams Fenton (November 14, 1899 – December 7, 1995) trained in paleontology and geology at the University of Iowa. She coauthored dozens of general science books with her husband, Carroll Lane Fenton, including ''Records of Evolution'' (1924), ''Land We Live On'' (1944), and ''Worlds in the Sky'' (1963). Early life and education Mildred Adams was born near West Branch, Iowa, the daughter of Ollie M. Adams and Mary Ann Yetter Adams. She graduated from the University of Chicago The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chic ..., where she met her husband Carroll Lane Fenton while they were both undergraduates. Selected publications In addition to their scholarly contributions, the couple wrote fifty books on general science topics, and her photographs were often used a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carroll Lane Fenton
Carroll Lane Fenton (February 12, 1900, Butler County, Iowa – November 16, 1969, New Brunswick, New Jersey) was a geologist, paleontologist, neoichnologist, and historian of science. Fenton was the author and illustrator of numerous books on geology and paleontology for a general audience. He published extensively in the field of paleontology in both the professional literature and in popular journals. He was an associate editor of the ''American Midland Naturalist'' from 1923 to 1960, expanding the coverage of the journal into the arena of paleontology. As an undergraduate in geology at the University of Chicago Fenton met and married fellow undergraduate, Mildred Adams. (Many of his later books were written with his wife, as Mildred Adams Fenton). He received his Bachelor of Science in 1921, then his Doctor of Philosophy in 1926. Fenton was a critic of creationism and documented the evidence for evolution in a series of Little Blue Book Little Blue Books are a series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dougal Dixon
Dougal Dixon (born 1 March 1947) is a Scottish geologist, palaeontologist, educator and author. Dixon has written well over a hundred books on geology and palaeontology, many of them for children, which have been credited with attracting many to the study of the prehistoric animals. Because of his work as a prolific science writer, he has also served as a consultant on dinosaur programmes. Dixon graduated from the University of St. Andrews with a Master of Science in 1970 and has since then worked in a variety of occupations, including as a geological consultant, tutor and teacher, a practical geologist on geological expeditions and as a civilian instructor for the Air Training Corps, a British volunteer-military youth organisation. At present, he lives in Wareham, Dorset, where he works as a full-time author and book editor and also manages a local movie theatre. Dixon is most famous for his 1980/90s trilogy of speculative evolution books: ''After Man'' (1981), '' The New Din ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwin H
The name Edwin means "rich friend". It comes from the Old English elements "ead" (rich, blessed) and "ƿine" (friend). The original Anglo-Saxon form is Eadƿine, which is also found for Anglo-Saxon figures. People * Edwin of Northumbria (died 632 or 633), King of Northumbria and Christian saint * Edwin (son of Edward the Elder) (died 933) * Eadwine of Sussex (died 982), King of Sussex * Eadwine of Abingdon (died 990), Abbot of Abingdon * Edwin, Earl of Mercia (died 1071), brother-in-law of Harold Godwinson (Harold II) *Edwin (director) (born 1978), Indonesian filmmaker * Edwin (musician) (born 1968), Canadian musician * Edwin Abeygunasekera, Sri Lankan Sinhala politician, member of the 1st and 2nd State Council of Ceylon * Edwin Ariyadasa (1922-2021), Sri Lankan Sinhala journalist * Edwin Austin Abbey (1852–1911) British artist * Edwin Eugene Aldrin (born 1930), although he changed it to Buzz Aldrin, American astronaut * Edwin Howard Armstrong (1890–1954), American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieuwe Dirk Boonstra
Lieuwe Dirk Boonstra (1905 – 1975) was a South African palaeontologist whose work focused on the therapsida, mammal-like reptiles of the Middle ( Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone, ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone) and Late Permian, whose fossil remains are common in the South African Karoo. He was the author of a large number of papers on Therapsids and Pareiasaurs, and described and revised a number of species. Work In 1927 Boonstra was appointed Assistant Palaeontologist of the South African Museum and promoted to Palaeontologist in 1931. He remained at the museum until his retirement in 1972. He was the sole curator of the museum's Karoo vertebrate fossil collection for 45 years. Awards He was awarded the Queen Victoria Scholarship by the University of Stellenbosch and received the Havenga prize for Biology from Suid-Afrikaanse Akademie vir Wetenskap en Kuns The Suid-Afrikaanse Akademie vir Wetenskap en Kuns (SAAWK) (literally ''South African Academy for Science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embrithosaurus
''Embrithosaurus'' was a pareiasaur from the Permian of South Africa. Description ''Embrithosaurus'' was in length and in weight. The skull is relatively deep and narrow. The body is lightly armoured with thin, smooth dermal scutes. Species * ''E. schwarzi'' (Watson, 1914). The type species. This is the most advanced species of this genus, as indicated by the teeth, which have nine cusps (in three groups of three). In cladistic analyses it is used as the monotypal species for the genus. * ''E. alexanderi'' (Haughton and Boonstra, 1929). This species was made the type for ''"Dolichopareia"''. As the name indicates, the skull is long and narrow. This would seem to indicate a different lifestyle or diet to other parieasaurs. More recently, it has been used as the monotypal species for the genus ''Nochelesaurus'' (it is not clear what the status of ''Embrithosaurus strubeni'' is, this may be a further transitional species). In cladistic analyses, this species is phylogenetically in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to the focal taxon (which may be a species, family or in general any clade). It can therefore be considered an apomorphy in relation to a single taxon. The word ''autapomorphy'', first introduced in 1950 by German entomologist Willi Hennig, is derived from the Greek words αὐτός, ''autos'' "self"; ἀπό, ''apo'' "away from"; and μορφή, ''morphḗ'' = "shape". Discussion Because autapomorphies are only present in a single taxon, they do not convey information about relationship. Therefore, autapomorphies are not useful to infer phylogenetic relationships. However, autapomorphy, like synapomorphy and plesiomorphy is a relative concept depending on the taxon in question. An autapomorphy at a given level may well be a synapomorphy at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_(2).jpg)