|
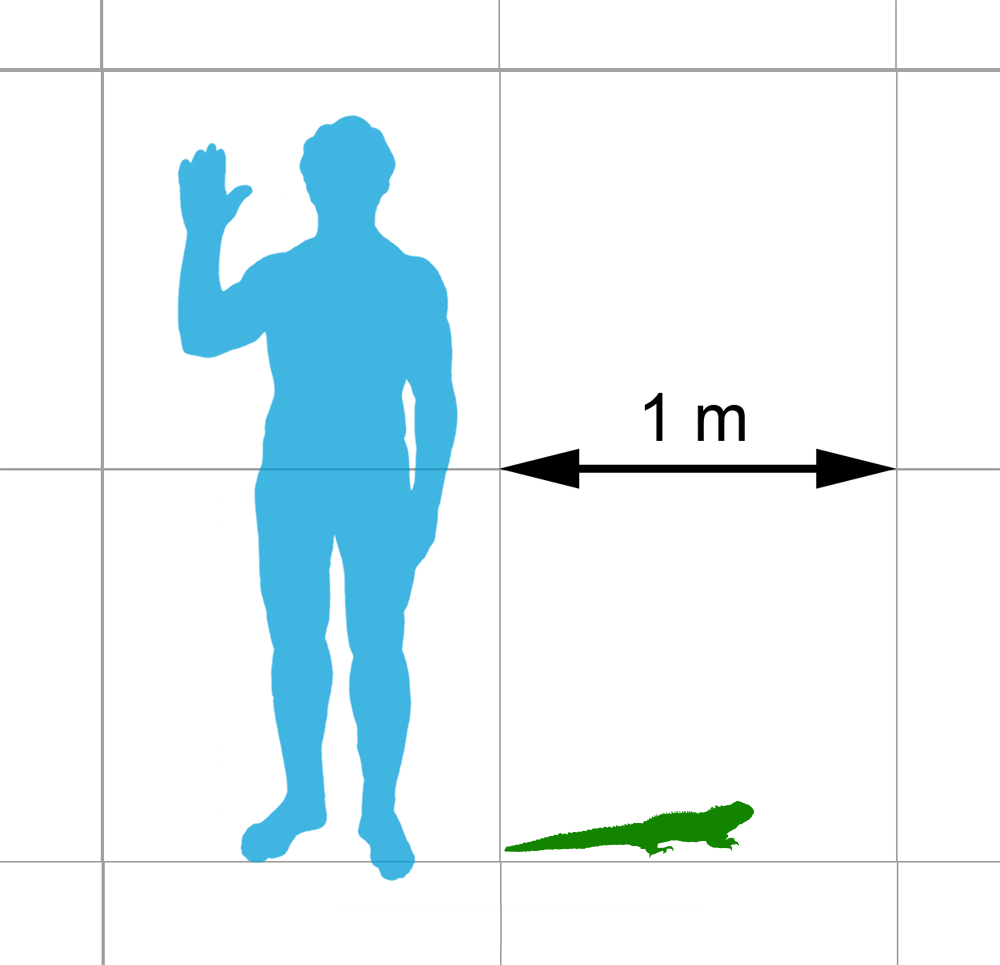
Brachyrhinodon
''Brachyrhinodon'' (meaning "short nose tooth") is an extinct genus of sphenodontian from the Late Triassic Lossiemouth Sandstone of Scotland. It is related to the tuatara, the only member of its order that is not extinct. ''Brachyrhinodon'' is known from the sandstone quarries near Elgin, and is one of the Elgin Reptiles. Sources * ''Vertebrate Palaeontology'' by Michael J. Benton * ''In the Shadow of the Dinosaurs: Early Mesozoic Tetrapods'' by Nicholas C. Fraser and Hans-Dieter Sues Hans-Dieter Sues (born January 13, 1956) is a German-born American paleontologist who is Senior Scientist and Curator of Vertebrate Paleontology at the National Museum of Natural History of the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, DC. He receiv ... *''The Beginning of the Age of Dinosaurs: Faunal Change across the Triassic-Jurassic Boundary'' by Kevin Padian Triassic lepidosaurs Triassic reptiles of Europe Sphenodontia Prehistoric reptile genera {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clevosauridae
Clevosaurs are an extinct group of rhynchocephalian reptiles from the Triassic and Jurassic periods. History and definition Although members of this group have been known since 1910, only recently has the group received a formal name. In the late 1990s, Victor-Hugo Reynoso established that three particular genera of Sphenodontia (''Clevosaurus, Brachyrhinodon'', and ''Polysphenodon'') were closely related to each other. He gave the informal name "clevosaurs" to these three genera, after the most numerous and well-known genus, ''Clevosaurus.'' He considered clevosaurs to be members of the family Sphenodontidae, the family of rhynchocephalians containing the only living member of the order, the tuatara (''Sphenodon).'' In 2006, Bonaparte and Sues finally gave "clevosaurs" a formal name and taxonomic rank as the family Clevosauridae. They defined Clevosauridae as the last common ancestor of ''Clevosaurus, Brachyrhinodon,'' and ''Polysphenodon,'' and all of its descendants. In 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenodontida
Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a diverse group including a wide array of morphologically distinct forms. The oldest record of the group is dated to the Middle Triassic around 238 to 240 million years ago, and they had achieved a worldwide distribution by the Early Jurassic. Most rhynchocephalians belong to the group Sphenodontia ('wedge-teeth'). Their closest living relatives are lizards and snakes in the order Squamata, with the two orders being grouped together in the superorder Lepidosauria. Many of the niches occupied by lizards today were held by sphenodontians during the Triassic and Jurassic, although lizard diversity began to overtake sphenodontian diversity in the Cretaceous, and they had disappeared almost entirely by the beginning of the Cenozoic. While the modern tuatara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elgin Reptiles
Elgin Reptiles is the name given to the Permian and Triassic fossils found in the sandstone deposits in and around the town of Elgin, in Moray, Scotland. They are of historical and scientific importance, and many of the specimens are housed in the Elgin Museum, and some in the Hunterian in Glasgow, and the National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh. The Elgin Reptiles include the dinosauriform ''Saltopus elginensis'', the dicynodont '' Gordonia'', and the pareiasaur ''Elginia''. There are also many footprints and tail-drags associated with the same Permian and Triassic sandstone deposits. History The sandstone in the Elgin area was originally quarried for building materials. The quarries were where the first reptile fossils were found, and they have continued to yield fossils to this day. The first Elgin Reptile was discovered in 1844, but because it was only a few scales scientists of the time believed it was an Old Red Sandstone fish fossil, which were relatively well-known from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuatara
Tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') are reptiles endemic to New Zealand. Despite their close resemblance to lizards, they are part of a distinct lineage, the order Rhynchocephalia. The name ''tuatara'' is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order. Rhynchocephalians originated during the Triassic (~250 million years ago), reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic and, with the exception of tuatara, were extinct by 60 million years ago. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). For this reason, tuatara are of interest in the study of the evolution of lizards and snakes, and for the reconstruction of the appearance and habits of the earliest diapsids, a group of amniote tetrapods that also includes dinosaurs (including birds) and crocodilians. Tuatara are greenish brown and grey, and measure up to from head to tail-tip and wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic Reptiles Of Europe
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic Lepidosaurs
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archosaurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans-Dieter Sues
Hans-Dieter Sues (born January 13, 1956) is a German-born American paleontologist who is Senior Scientist and Curator of Vertebrate Paleontology at the National Museum of Natural History of the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, DC. He received his education at Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz (University of Mainz), University of Alberta, and Harvard University (Ph.D., 1984). Before assuming his present position, Sues worked at the Royal Ontario Museum and the University of Toronto and at the Carnegie Museum of Natural History in Pittsburgh. He is interested in the diversity, paleoecology, and evolutionary history of Paleozoic and Mesozoic tetrapods, especially archosaurian reptiles and cynodont therapsids, and the history of biology and paleontology. Sues has discovered numerous new dinosaurs and other extinct terrestrial vertebrates in Paleozoic and Mesozoic continental strata in North America and Europe. He has authored or co-authored over 150 articles and book chapte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas C
Nicholas is a male given name and a surname. The Eastern Orthodox Church, the Roman Catholic Church, and the Anglican Churches celebrate Saint Nicholas every year on December 6, which is the name day for "Nicholas". In Greece, the name and its derivatives are especially popular in maritime regions, as St. Nicholas is considered the protector saint of seafarers. Origins The name is derived from the Greek name Νικόλαος (''Nikolaos''), understood to mean 'victory of the people', being a compound of νίκη ''nikē'' 'victory' and λαός ''laos'' 'people'.. An ancient paretymology of the latter is that originates from λᾶς ''las'' ( contracted form of λᾶας ''laas'') meaning 'stone' or 'rock', as in Greek mythology, Deucalion and Pyrrha recreated the people after they had vanished in a catastrophic deluge, by throwing stones behind their shoulders while they kept marching on. The name became popular through Saint Nicholas, Bishop of Myra in Lycia, the inspirati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael J
Michael may refer to: People * Michael (given name), a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name "Michael" * Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and Islamic religions * Michael (bishop elect), English 13th-century Bishop of Hereford elect * Michael (Khoroshy) (1885–1977), cleric of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada * Michael Donnellan (1915–1985), Irish-born London fashion designer, often referred to simply as "Michael" * Michael (footballer, born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born February 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born March 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian footballer Rulers =Byzantine emperors= *Michael I Rangabe (d. 844), married the daughter of Emperor Nikephoros I * M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate Palaeontology (Benton)
''Vertebrate Palaeontology'' is a basic textbook on vertebrate paleontology by Michael J. Benton, published by Blackwell's. It has so far appeared in four editions, published in 1990, 1997, 2005, and 2015. It is designed for paleontology graduate courses in biology and geology as well as for the interested layman. The book is widely used, and has received excellent reviews: *"This book is a ′must′ for a biology or geology student and researcher concerned by palaeontology. It perfectly succeeds in showing how palaeobiological information is obtained". Review of 3rd edition, ''Zentrallblatt fur Geologie und Palaontologie'', 2007. *"One anticipates that Benton's ''Vertebrate Palaeontology'' will become the 'industry standard', and as such it should occupy space on the shelves of all involved in undergraduate teaching". Ivan Sansom, School of Earth Sciences, University of Birmingham. Review of the 2nd edition for the Micropalaeontological Society. *"... his expertise in a ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elgin, Moray
Elgin (; sco, Ailgin; gd, Eilginn, ) is a town (former cathedral city) and formerly a Royal Burgh in Moray, Scotland. It is the administrative and commercial centre for Moray. The town originated to the south of the River Lossie on the higher ground above the floodplain where the town of Birnie is. There, the church of Birnie Kirk was built in 1140 and serves the community to this day. Elgin is first documented in the Cartulary of Moray in 1190 AD. It was created a royal burgh in the 12th century by King David I of Scotland, and by that time had a castle on top of the present-day Lady Hill to the west of the town. The origin of the name Elgin is likely to be Celtic. It may derive from 'Aille' literally signifying beauty, but in topography a beautiful place or valley. Another possibility is 'ealg', meaning both 'Ireland' and 'worthy'. The termination 'gin' or 'in' are Celtic endings signifying little or diminutive forms, hence Elgin could mean beautiful place, worthy place or litt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_601758.jpg)

.png)
