|
Brachymystax Tumensis
''Brachymystax tumensis'', the blunt-snouted lenok,Kartavtseva, I.V.; Ginatulina, L.K.; Nemkova, G.A.; and Shedko, S.V. (2013). ''Chromosomal study of the lenoks, Brachymystax (Salmoniformes, Salmonidae) from the South of the Russian Far East.'' Journal of Species Research 2(1):91-98. is a salmonid fish distributed in rivers and lakes in Eastern Asia. It was formerly included in the more widespread species ''Brachymystax lenok'' (now known as the sharp-snouted lenok), but more recent research based on differences in morphology and genetics have justified a distinction of the two species.Bo, M. A.; and Jiang, Zuo-fa (2007). ''Genetic diversity and relationship between two species of Brachymystax in Wusuli River revealed by microsatellites.'' Journal of Fishery Sciences of China 14: 39-45.Froufe, E.; Alekseyev, S.; Alexandrino, P.; and Weiss, S. (2008). The evolutionary history of sharp- and blunt-snouted lenok (Brachymystax lenok (Pallas, 1773)) and its implications for the paleo-h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Tamezo Mori
, (1884–1962) was a Japanese naturalist in Chōsen (1910–1945). He taught at a preparatory school for Keijō Imperial University in Seoul from 1909 until he was expelled by the American forces in 1945. Primarily an ichthyologist, he published numerous works on the zoology of the Korean Peninsula and Manchuria Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym "Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East ( Outer .... Some of these, such as his ''Checklist of the Fishes of Korea'' and the 1934 ''Coloured Butterflies from Korea'', are still in print. References *Austin, Oliver. 1948. The Birds of Korea. ''Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College'' 101 no. *Vladykov, V. & Greeley, J. 1963. ''Order Acipenseroidei'' in Soft-rayed Bony fishes : class Osteichthyes, order Acipenseroidei, order Lepisostei, order Isospon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
.jpeg/1200px-Prosopium_cylindraceum_(white_background).jpeg) |
Salmonidae
Salmonidae is a family of ray-finned fish that constitutes the only currently extant family in the order Salmoniformes . It includes salmon (both Atlantic and Pacific species), trout (both ocean-going and landlocked), chars, freshwater whitefishes, graylings, taimens and lenoks, which are collectively known as the salmonids ("salmon-like fish"). The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar''), whose Latin name became that of its genus '' Salmo'', is also the source of the family and order names. Salmonids have a relatively primitive appearance among the teleost fish, with the pelvic fins being placed far back, and an adipose fin towards the rear of the back. They have slender bodies, with rounded scales and forked tails, and their mouths contain a single row of sharp teeth. Although the smallest species is just long as an adult, most are much larger, with the largest reaching . All salmonids spawn in fresh water of upper reaches of rivers and creeks, but in many cases, the fish spend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Brachymystax Lenok
''Brachymystax lenok'', the sharp-snouted lenok,Kartavtseva, I.V.; Ginatulina, L.K.; Nemkova, G.A.; and Shedko, S.V. (2013). ''Chromosomal study of the lenoks, Brachymystax (Salmoniformes, Salmonidae) from the South of the Russian Far East.'' Journal of Species Research 2(1):91-98. is a salmonid fish distributed in rivers and lakes in northeastern Asia. It formerly included the blunt-snouted lenok, but recent authorities typically treat the latter as a separate species, '' B. tumensis'', based on differences in morphology and genetics.Bo, M. A.; and Jiang, Zuo-fa (2007). ''Genetic diversity and relationship between two species of Brachymystax in Wusuli River revealed by microsatellites.'' Journal of Fishery Sciences of China 14: 39-45.Froufe, E.; Alekseyev, S.; Alexandrino, P.; and Weiss, S. (2008). The evolutionary history of sharp- and blunt-snouted lenok (''Brachymystax lenok'' (Pallas, 1773)) and its implications for the paleo-hydrological history of Siberia.' BMC Evolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance ( shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external morphology (or eidonomy), as well as the form and structure of the internal parts like bones and organs, i.e. internal morphology (or anatomy). This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of gross structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
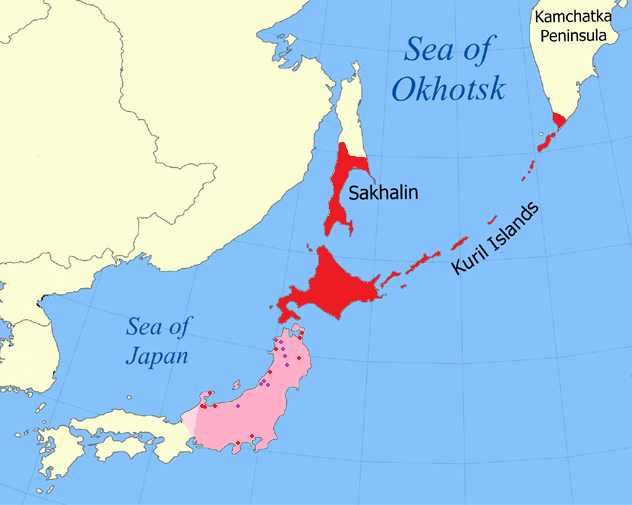 |
Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: Yh-mif) is the largest island of Russia. It is north of the Japanese archipelago, and is administered as part of the Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin is situated in the Pacific Ocean, sandwiched between the Sea of Okhotsk to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west. It is located just off Khabarovsk Krai, and is north of Hokkaido in Japan. The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of which are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The Island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ). Sakhalin was once part of China during the Qing dynasty, although Chinese control was relaxed at times. Sakhalin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, making it the world's most sparsely populated sovereign nation. Mongolia is the world's largest landlocked country that does not border a closed sea, and much of its area is covered by grassy steppe, with mountains to the north and west and the Gobi Desert to the south. Ulaanbaatar, the capital and largest city, is home to roughly half of the country's population. The territory of modern-day Mongolia has been ruled by various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu, the Xianbei, the Rouran, the First Turkic Khaganate, and others. In 1206, Genghis Khan founded the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous land empire in history. His grandson Kublai Khan conquered China proper and established the Yuan dynasty. After the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China ( Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long, and has a drainage basin of . ''mizu'' ("water") in Japanese. The name "Amur" may have evolved from a root word for water, coupled with a size modifier for "Big Water". Its ancient Chinese names were ''Yushui'', ''Wanshui'' and ''Heishui'', formed from variants to ''shui'', meaning "water".The fishes of the Amur River:updated check-list and zoogeography'' The modern Chinese name for the river, ''Heilong Jiang'' means "Black Dragon River", while the Manchurian name ''Sahaliyan Ula'', the Mongolian names " Amar mörön " (Cyrillic: Амар мөрөн) originates from the name " Amar " meaning to rest and ''Khar mörön'' (Cyrillic: Хар мөрөн) mean Black River. Course The river rises in the hills in the western part of Northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Tumen River
The Tumen River, also known as the Tuman River or Duman River (), is a long river that serves as part of the boundary between China, North Korea and Russia, rising on the slopes of Mount Paektu and flowing into the Sea of Japan. The river has a drainage basin of 33,800 km2 (13,050 sq mi). The river flows in northeast Asia, on the border between China and North Korea in its upper reaches, and between North Korea and Russia in its last before entering the Sea of Japan. The river forms much of the southern border of Jilin Province in Northeast China and the northern borders of North Korea's North Hamgyong and Ryanggang provinces. Baekdu Mountain on the Chinese-North Korean border is the source of the river, Much of the information comes from the captions to the large illustrated map published with the newspaper article and available online with it. as well as of the Amnok River, also called the Yalu River (which forms the western portion of the border of North Korea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eastern border is defined by the Sea of Japan. South Korea claims to be the sole legitimate government of the entire peninsula and List of islands of South Korea, adjacent islands. It has a Demographics of South Korea, population of 51.75 million, of which roughly half live in the Seoul Capital Area, the List of metropolitan areas by population, fourth most populous metropolitan area in the world. Other major cities include Incheon, Busan, and Daegu. The Korean Peninsula was inhabited as early as the Lower Paleolithic period. Its Gojoseon, first kingdom was noted in Chinese records in the early 7th century BCE. Following the unification of the Three Kingdoms of Korea into Unified Silla, Silla and Balhae in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
MtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondrion, mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. This sequencing revealed that the human mtDNA includes 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins. Since animal mtDNA evolves faster than nuclear genetic markers, it represents a mainstay of phylogenetics and evolutionary biology. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and biogeography. Origin Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |